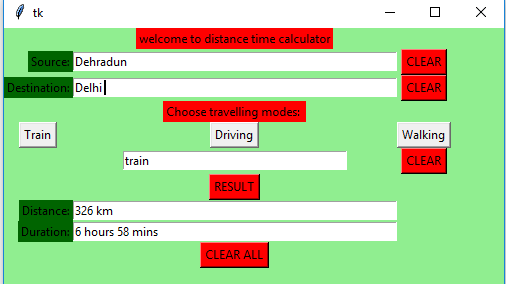
Python|使用 Tkinter 的距离时间 GUI 计算器
先决条件: Tkinter 简介 |使用谷歌距离矩阵 API
Python为开发 GUI(图形用户界面)提供了多种选择。在所有的 GUI 方法中,tkinter 是最常用的方法。它是Python随附的 Tk GUI 工具包的标准Python接口。带有 tkinter 的Python输出创建 GUI 应用程序的最快和最简单的方法。使用 tkinter 创建 GUI 是一项简单的任务。
创建一个 tkinter :
- 导入模块 – tkinter
- 创建主窗口(容器)
- 将任意数量的小部件添加到主窗口
- 在小部件上应用事件触发器。
让我们使用Python Tkinter 模块创建一个基于 GUI 的距离时间计算器,它可以判断两个城市/位置之间的距离以及从一个位置到另一个位置所花费的时间。
所需模块:
tkinter
requests
json
下面是实现:
# Python3 program to create Distance
# Time GUI calculator using Tkinter
# import everything from tkinter modules
from tkinter import *
# import modules
import requests, json
# Function for finding distance
# and duration between two places
def result(source, destination, travel_modes):
# Enter your API key here
api_key = 'Your_api_key'
# base variable to store base url
base = 'https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/distancematrix/json?'
# Check travel modes
if travel_modes == "train":
# complete_url variable to store complete url address
complete_url = base + 'origins =' + source + \
'&destinations =' + destination + \
'&mode = transit&transit_mode = train' + \
'&key ='+api_key
# get method of requests module
# return response object
r = requests.get(complete_url)
else:
# complete_url variable to
# store complete url address
complete_url = base + 'origins =' + source+ \
'&destinations ='+ destination + \
'&mode ='+travel_modes+'&key ='+ api_key
# get method of requests module
# return response object
r = requests.get(complete_url)
# json method of response object convert
# json format data into python format data
x = r.json()
# x contains list of nested dictionaries
# we know dictionary contains key value pair
# Extracting useful information
# from x dictionary
row = x['rows'][0]
cell = row['elements'][0]
# Check value corresponding to
# status key in cell dictionary
if cell['status'] == 'OK' :
# insert method inserting the
# value in the text entry box.
# Extracting useful information
# from cell dictionary and inserting
# into the respective text fields.
distance_field.insert(10, cell['distance']['text'])
duration_field.insert(10, cell['duration']['text'])
else :
# insert method inserting the
# value in the text entry box.
# Extract value corresponding to
# status key from cell dictionary and
# inserting into the respective text fields.
mode_field.insert(10, cell['status'])
distance_field.insert(10, cell['status'])
# Function for getting values from
# respective text entry boxes and
# calling result function .
def find() :
# get method returns current text
# as a string from text entry box
source = source_field.get()
destination = destination_field.get()
travel_modes = mode_field.get()
# Calling result() Function
result(source, destination, travel_modes)
# Function for inserting the train string
# in the mode_field text entry box
def train() :
mode_field.insert(10, "train")
# Function for inserting the driving string
# in the mode_field text entry box
def driving() :
mode_field.insert(10, "driving")
# Function for inserting the walking string
# in the mode_field text entry box
def walking() :
mode_field.insert(10, "walking")
# Function for clearing the contents
# of source_field, distance_field,
# duration_field text entry boxes.
def del_source() :
source_field.delete(0, END)
distance_field.delete(0, END)
duration_field.delete(0, END)
# Function for clearing the contents of
# destination_field, distance_field,
# duration_field text entry boxes.
def del_destination() :
destination_field.delete(0, END)
distance_field.delete(0, END)
duration_field.delete(0, END)
# function for clearing the contents of mode_field,
# distance_field, duration_field text entry boxes.
def del_modes() :
mode_field.delete(0, END)
distance_field.delete(0, END)
duration_field.delete(0, END)
# Function for clearing the
# contents of all text entry boxes
def delete_all() :
source_field.delete(0, END)
destination_field.delete(0, END)
mode_field.delete(0, END)
distance_field.delete(0, END)
duration_field.delete(0, END)
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__" :
# Create a GUI window
root = Tk()
# Set the background colour of GUI window
root.configure(background = 'light green')
# Set the configuration of GUI window
root.geometry("500x300")
# Create a welcome to distance time calculator label
headlabel = Label(root, text = 'welcome to distance time calculator',
fg = 'black', bg = "red")
# Create a Source: label
label1 = Label(root, text = "Source:",
fg = 'black', bg = 'dark green')
# Create a Destination: label
label2 = Label(root, text = "Destination:",
fg = 'black', bg = 'dark green')
# Create a Choose travelling modes: label
label3 = Label(root, text = "Choose travelling modes: ",
fg = 'black', bg = 'red')
# Create a Distance: label
label4 = Label(root, text = "Distance:",
fg = 'black', bg = 'dark green')
# Create a Duration: label
label5 = Label(root, text = "Duration:",
fg = 'black', bg = 'dark green')
# grid method is used for placing
# the widgets at respective positions
# in table like structure .
headlabel.grid(row = 0, column = 1)
label1.grid(row = 1, column = 0, sticky ="E")
label2.grid(row = 2, column = 0, sticky ="E")
label3.grid(row = 3, column = 1)
label4.grid(row = 7, column = 0, sticky ="E")
label5.grid(row = 8, column = 0, sticky ="E")
# Create a text entry box
# for filling or typing the information.
source_field = Entry(root)
destination_field = Entry(root)
mode_field = Entry(root)
distance_field = Entry(root)
duration_field = Entry(root)
# grid method is used for placing
# the widgets at respective positions
# in table like structure .
# ipadx keyword argument set width of entry space .
source_field.grid(row = 1, column = 1, ipadx ="100")
destination_field.grid(row = 2, column = 1, ipadx ="100")
mode_field.grid(row = 5, column = 1, ipadx ="50")
distance_field.grid(row = 7, column = 1, ipadx ="100")
duration_field.grid(row = 8, column = 1, ipadx ="100")
# Create a CLEAR Button and attached
# to del_source function
button1 = Button(root, text = "CLEAR", bg = "red",
fg = "black", command = del_source)
# Create a CLEAR Button and attached to del_destination
button2 = Button(root, text = "CLEAR", bg = "red",
fg = "black", command = del_destination)
# Create a RESULT Button and attached to find function
button3 = Button(root, text = "RESULT",
bg = "red", fg = "black",
command = find)
# Create a CLEAR ALL Button and attached to delete_all function
button4 = Button(root, text = "CLEAR ALL",
bg = "red", fg = "black",
command = delete_all)
# Create a Train Button and attached to train function
button5 = Button(root, text = "Train", command = train)
# Create a Driving Button and attached to driving function
button6 = Button(root, text = "Driving", command = driving)
# Create a Walking Button and attached to walking function
button7 = Button(root, text = "Walking", command = walking)
# Create a CLEAR Button and attached to del_modes function
button8 = Button(root, text = "CLEAR",
fg = "black", bg = "red",
command = del_modes)
# grid method is used for placing
# the widgets at respective positions
# in table like structure .
button1.grid(row = 1, column = 2)
button2.grid(row = 2, column = 2)
button3.grid(row = 6, column = 1)
button4.grid(row = 9, column = 1)
button5.grid(row = 4, column = 0)
button6.grid(row = 4, column = 1)
button7.grid(row = 4, column = 2)
button8.grid(row = 5, column = 2)
# Start the GUI
root.mainloop()
输出: