弹性势能
物品由于其位置而存储在其中的能量称为势能。当我们想到势能时,首先想到的图像通常是刚刚开始下落的高空物品。由于它的高度,它具有存储在其中的势能。当它下降时,这种能量转化为动能。但是,在某些其他情况下,物品可能具有势能。弹性物质就是一个这样的例子。通过一个例子,我们将在本文中复习弹性势能公式。让我们研究一下这个想法!
什么是势能?
作为其位置的函数,物体可以存储能量。当拆除机器的重球保持在高处时,它会储存能量。这种存储的位置能量称为势能。同样,由于其姿势,拉弓可以储存能量。
当弓处于正常位置时(即未拉动),弓中没有能量存储。然而,当它的位置从其典型的平衡状态改变时,由于其位置,弓可以储存能量。这种存储的位置能量称为势能。势能是物体所在位置储存的能量。
Potential energy is the energy possessed by a body as a result of its location with respect to a reference point.
势能分为两种:
- 重力势能:当物体被提升到地面以上的特定高度时,它所包含的能量称为重力势能。
- 弹性势能:弹性势能是能量的第二种形式。弹性势能可以在两个方向上被拉伸或挤压。为了使弹性势能起作用,物体必须具有弹性。
让我们详细讨论弹性势能:
弹性势能
这是由于形状变形而存储在物品中的能量。弹性势能可以在任何可以扭曲然后恢复其原始形状的物品中找到。橡皮筋、海绵、弹力绳和其他类似物品就是例子。
弹性势能是由于使用力使弹性元件变形而积累的能量。能量积累,直到力被解决,物体将恢复原状,完成过程中的任务。变形可以是物体的压缩、拉伸或扭曲。例如,许多物体是专门为存储弹性势能而设计的:
一个物体被设计用于储存弹性势能并具有高屈服强度,然而,边境税的所有灵活特性,他们将能够阻止它。当物体变形超过其弹性极限时,它不会恢复到原来的形状。在前几代中,齿轮、机械表也是由于资源造成的,这些资源也是流行的配件。此时,我们不太可能是机械的、智能手机,因为没有具有高弹性极限的材料,即以足够高的能量密度存储弹性势能。
Elastic potential energy is the potential energy stored by stretching or compressing an elastic object by an external force such as the stretching of a spring or an elastic rubber cord.
胡克定律
在考虑弹性势能时,最典型的要考虑的项目之一是弹簧。弹簧可以通过两种方式扭曲,这两种方式都会导致恢复平衡。它们可以被拉伸也可以被压缩。为了得到弹簧的弹性势能公式,我们必须首先考察胡克定律。
当弓处于正常位置时(即未拉动),弓中没有能量存储。然而,当它的位置从其典型的平衡状态改变时,由于其位置,弓可以储存能量。这种存储的位置能量称为势能。势能是物体所在位置储存的能量。
弹簧的位移用 x 表示,而弹簧常数用 k 表示。这个常数是弹簧刚度的量度,每个弹簧都是独一无二的。弹簧常数受弹簧材料和盘绕线材厚度等因素的影响。
The Hooke’s law, states that the strain of the material is proportional to the applied stress within the elastic limit of that material.
数学上,
F = –kx
其中 F 是力,x 是延伸长度,k 是弹簧常数,单位为 N/m。
带有负号的公式通常用于将胡克定律描述为恢复力,但也可以使用正数。弹簧的位移用 x 表示,而弹簧常数用 k 表示。这个常数是弹簧刚度的量度,每个弹簧都是独一无二的。
弹簧常数受弹簧材料和盘绕线材厚度等因素的影响。
当弹性物体拉伸时,原子和分子会退化,直到施加压力,当压力消除时,它们会恢复到原来的状态。所以根据胡克定律,拉伸弹簧的力与拉伸量成正比。
Formula for Elastic Potential Energy
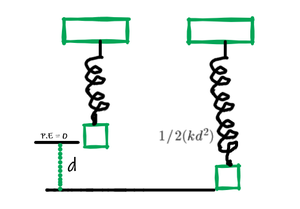
We can say that Elastic potential energy is equal to the work done to stretch the spring which depends on the spring constant k and the distance stretched.
Elastic potential energy
From the above diagram, we can say that the force required to stretch the spring is directly proportional to its displacement.
The force required to stretch the spring is directly proportional to its displacement. It is given as
P.E. = Magnitude of Force × Displacement
or
P.E. = 1/2 × kx2
Here, -ve sign indicates the opposite direction.
示例问题
问题 1:Geek 拉一个弹簧常数 k=100 N/m 的弹簧,将其从 0.10 m 的静止长度拉伸到 0.20 m,弹簧中存储的弹性势能是多少?
解决方案:
The Potential Energy stored in the spring is ![]() J
J
displacement d= 0.20 m – 0.10 m
d = 0.10 m
k = 100 N/m
lets substuite all the values in formula.
PE = ![]() J
J
= ![]() J
J
= 0.50 J
问题 2:垂直弹簧与质量为 10 kg 的负载相关联,该负载被压缩 10m。确定弹簧的力常数。
解决方案:
Mass m = 10kg
Displacement d = 10 m
F = ma
=
= 98 N
Force in the stretched spring is
F = kd
Then k = F / d
= 98 / 10
= 9.8 N/m
k = 9.8 N/m
问题3:势能如何计算?
解决方案:
It is the product of the Force applied on the object and th displacement of the object
P.E = F X d
F -> Force
d -> displacement
问题 4:一个男孩拉一个弹簧常数 k=200 N/m 拉伸 0.10m 的弹簧,弹簧中储存的弹性势能是多少?
解决方案:
The Potential Energy stored in the spring is ![]()
displacement d= 0.10 m
d = 0.10 m
k = 200 N/m
lets substuite all the values in formula.
PE =
= ![]()
= 1.00 J
问题 5:什么是胡克定律?
解决方案:
Hooke’s Law states that the strain of the material is proportional to the applied stress within the elastic limit of that material.
F = –k.x
where
F is the force
x is the extension length
k is spring constant in N/m