牛顿冷却定律
当热水或牛奶放在桌子上时,它会逐渐冷却。它最终达到周围环境的温度。热水或牛奶可以通过与环境进行热交换来冷却。在这里,热水的冷却取决于其温度与周围环境之间的差异。
从图中可以看出,降温的速度起初更快,然后随着体温的下降而减慢。热的物体以热辐射的形式将热量散失到周围环境中。热量散失的速度取决于身体与其周围环境之间的温差。
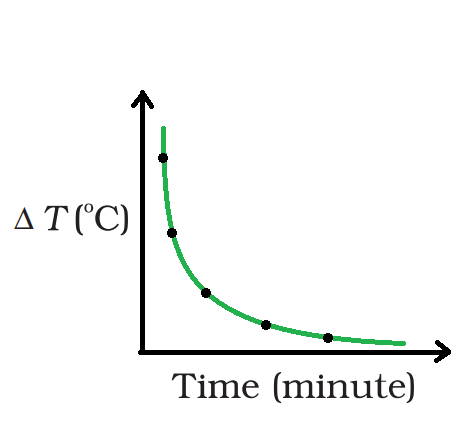
显示热水随时间冷却的曲线
牛顿冷却定律
牛顿是第一个系统地分析了物体在特定外壳中的热量损失与其温度之间的关系的人。
牛顿冷却定律定义了暴露的物体通过辐射改变温度的速率,它大致等于物体与其周围环境之间的温差,前提是温差很小。但是,请记住,这里的差异非常小。
Newton’s law of cooling states that the rate of heat loss from a body is directly proportional to the difference in temperature between the body and its surroundings.
使用牛顿冷却法则,我们可以确定在给定温度下的物质在任何给定环境中冷却的速度。此外,它解释了物体的冷却速率如何不仅受材料与其周围环境之间的温差影响,还受材料冷却常数的影响。
牛顿冷却公式定律
著名物理学家艾萨克·牛顿爵士设计了一个公式来计算材料在失去热量时的温度。此外,来自物体的热量传递到周围环境。如前所述,温度变化率与物品与其周围环境之间的温差有关。
根据牛顿冷却定律,物体的热损失率,即-dQ/dt与物体与周围环境的温差成正比, ΔT = (T 2 - T 1 ) 。
该定律仅适用于较小的温差。此外,通过辐射损失的热量取决于身体表面的成分和暴露表面的范围。
因此,表达式可以写成
– dQ/dt = k(T 2 – T 1 ) ……(1)
这里, k是一个正常数,取决于物体表面的面积和性质。
Derivation of Newton’s Law of Cooling
Let a body of mass m, with specific heat capacity s, is at temperature T2 and T1 is the temperature of the surroundings.
If the temperature falls by a small amount dT2 in time dt, then the amount of heat lost is,
dQ = ms dT2
The rate of loss of heat is given by,
dQ/dt = ms (dT2/dt) ……..(2)
Compare the equations (1) and (2) as,
– ms (dT2/dt) = k (T2 – T1)
Rearrange the above equation as:
dT2/(T2–T1) = – (k / ms) dt
dT2 /(T2 – T1) = – Kdt
where K = k/m s
Integrating the above expression as,
loge (T2 – T1) = – K t + c
or
T2 = T1 + C’ e–Kt
where C’ = ec
The above expression is used to calculate the time of cooling of a body through a particular range of temperature.
The cooling curve is a graph that shows the relationship between body temperature and time. The rate of temperature fall is determined by the slope of the tangent to the curve at any point.
The Cooling curve
In general, T(t) = TA+(TH-TA)e-kt
where T(t) is the Temperature at time t, TA is the Ambient temperature or temp of surroundings, TH is the temperature of the hot object, k is the positive constant and t is the time.
应用牛顿冷却定律的方法
假设冷却速率恒定,等于在需要牛顿定律粗略值的区间内与身体平均温度相关的冷却速率。 IE
dθ\dt = k( – q 0 )
……..(3)
如果q i是初始温度, q f是物体的最终温度,那么,
= (q i + q f )/2
……….(4)
上述方程(4)只是一个近似值或粗略值,方程(3)用于牛顿冷却定律的精确值。
未知参数 k 可以使用这种类型的冷却数据来计算,这些数据可以被监控和可视化。在某些情况下,可以用数值计算参数。
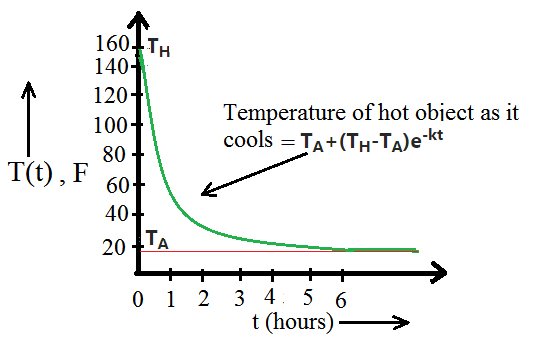
显示温度与时间图的示例。
牛顿冷却定律的验证
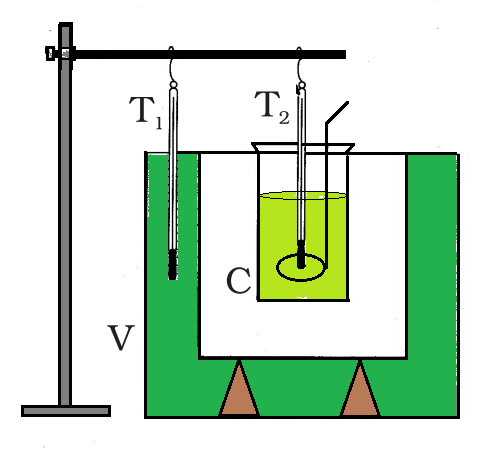
牛顿冷却定律的验证。
图中所示的实验装置可用于验证牛顿冷却定律。一个双壁容器 (V) 与两壁之间的水构成了设置。双壁容器内部是一个装有热水的铜热量计 (C)。
两个温度计分别用于记录热量计中水的温度T 2和通过软木塞的双壁之间的热水的T 1 。在相等的时间间隔后,记录热量计中热水的温度。
log e (T 2 –T 1 ) 和时间 (t) 之间的图形显示为具有负斜率的直线。
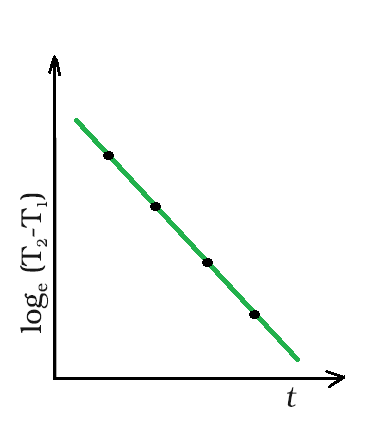
log e (T 2 –T 1 ) 和时间 (t) 之间的图表
牛顿冷却定律的局限性是:
- 人体与环境的温差一定要小。
- 只有辐射应该被用作身体热量的损失。
- 在身体冷却期间,周围的温度必须保持恒定,这是牛顿冷却定律的关键约束。
牛顿冷却定律的应用是:
- 估计一个温暖的物体需要多长时间才能冷却到一个特定的温度。
- 在经过特定时间后确定冰箱中饮料的温度。
- 它有助于通过查看死亡时可能的体温和当前体温来指示死亡时间。
示例问题
问题 1:当室温为 20°C 时,盛满热食的平底锅在 2 分钟内从 94°C 冷却到 86°C。从 71°C 冷却到 69°C 需要多长时间?
解决方案:
The average temperature of 94 °C and 86 °C is 90 °C, which is 70 °C above the room temperature. Under these conditions the pan cools 8 °C in 2 minutes.
According to Newton’s law of cooling,
– dQ/dt = k(T2–T1)
Substitute the value in the above expression,
8 °C /2 min = k(70 °C) ………(1)
The average of 69 °C and 71 °C is 70 °C, which is 50 °C above room temperature. the value of K is the same.
Substitute the value in the above expression,
2 °C /dt = k(50°C) ……(2)
Equate equation (1) and (2),
dt = 0.7 min
or time is equal to 42 s.
问题 2:什么是牛顿冷却定律?
解决方案:
Newton’s law of cooling states that the rate of heat loss from a body is directly proportional to the difference in temperature between the body and its surroundings.
According to Newton’s law of cooling, the rate of loss of heat, that is – dQ/dt of the body is directly proportional to the difference of temperature ΔT = (T2–T1) of the body and the surroundings. The law is only valid for small temperature differences. Furthermore, the amount of heat lost through radiation is determined by the composition of the body’s surface and the extent of the exposed surface.
Therefore, the expression can be written as
– dQ/dt = k(T2–T1)
问题 3:为什么用碗喝热牛奶比喝玻璃杯更容易。
解决方案:
Bowl has greater surface area than glass therefore the more heat loses to its surroundings in the form of heat radiation through the bowl. The cooling of hot water depends upon the difference between its temperature and the surroundings. The rate of cooling is faster at first and then slows as the temperature drops.
问题 4:画出表示热水到冷水转变的图形。
解决方案:
A curve showing cooling of hot water with time:
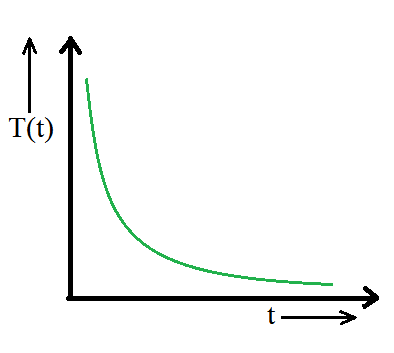
A curve showing cooling of hot water with time
The cooling of hot water depends upon the difference between its temperature and the surroundings. It is observed in the graph that the rate of cooling is faster at first and then slows as the body temperature drops. A hot body loses heat to its surroundings in the form of heat radiation. The rate of loss of heat depends on the difference in temperature between the body and its surroundings.
问题 5:温度为 40ºC 的物体被保持在恒温 20ºC 的环境中。据观察,其温度在 10 分钟内降至 35ºC。找出身体温度达到 30ºC 需要多长时间。
解决方案:
According to Newtons law of cooling
qf = qi e-kt
Now, for the interval in which temperature falls from 40 ºC to 35 ºC.
(35 – 20) = (40 – 20) e-(10k)
e-10k = 3/4
-10k = (ln 4/3)
k = 0.2876/10
k = 0.02876
Now, for the next interval;
(30 – 20) = (35 – 20)e-kt
10 = 15e-kt
e-kt = 2/3
-kt = ln(2/3)
t = 0.40546/k
Subtitte the value of k in the above equation,
t = 0.40546/0.02876
t = 14.098 min.
问题 6:油被加热到 70 ºC。 6 分钟后冷却至 50 ºC。在给定环境温度 Ts = 25 ºC 的情况下,计算油从 50 ºC 冷却到 40 ºC 所需的时间
解决方案:
Given,
The temperature of oil after 6 min i.e. T(t) is equal to 50 ºC.
The ambient temperature Ts is 25 ºC.
The temperature of oil, To is 70 ºC.
The time to cool to 50ºC is 6 min.
According to Newton’s law of cooling,
T(t) = Ts + (T0 – Ts) e-kt
(T(t) – Ts)/(To – Ts) = e-kt
-kt = ln[(T(t) – Ts)/(To – Ts)] ………(1)
Substitute the above data in Newton’s law of cooling expression,
-kt = ln[(50 – 25)/(70 – 25)]
-k = (ln 0.55556)/6
k = 0.09796
The average temperature is equal to 45 ºC
Substitute the values in equation (1),
-(0.09796) t = ln[(45 – 25)/(70 – 25)]
-0.09796t = ln(0.44444)
0.09796t = 0.81093
t = 0.09796/0.58778 = 8.278 min.
问题 7:将水加热到 80 ºC 10 分钟。如果 k = 0.056 每分钟并且周围温度为 25 ºC,那么温度是多少摄氏度?
解决方案:
Given,
The ambient temperature Ts is 25 ºC,
The temperature of water T0 is 80 ºC.
The time that water is heated is t 10 min.
The value of constant k is 0.056.
According to Newton’s law of cooling,
T(t) = Ts + (T0 – Ts) e-kt
Substitute the above data in the above expression,
T(t)= 25 + (80 – 25)e-(0.056×10)
T(t) = 25+55 e-(0.056×10)
T(t) = 25+31.42
T(t) = 56.42
After 10 min the temperature cools down from 80 ºC to 56.42 ºC.