牛顿万有引力定律
虽然苹果不可能像历史一样落在艾萨克·牛顿爵士的头上,但它确实激发了他做出力学中最重要的发现之一:万有引力定律。牛顿在思考为什么苹果从不向下、向后或除垂直于地面以外的任何其他方向坠落之后,发现地球本身将负责苹果的向下运动。牛顿利用现有的关于地球和月球之间力的平方反比关系的观察结果,假设该力将等于相关两个力的质量,然后通过推论得出了一般物理定律。因此,我们先来讨论一下这个引力。
什么是万有引力?
万有引力是任何两个物体之间的吸引力。宇宙中的所有物体都以一定的力相互吸引,但在大多数情况下,由于分离距离非常大,这种力太弱而无法观察到。这种吸引力,也称为万有引力,最早是由一位名叫艾萨克·牛顿的伟大科学家发现的。这个概念在 1680 年被发展为牛顿的万有引力定律。
Important Properties of the gravitational force are:
- Gravitational force is the weakest force in nature but has infinite range.
- Gravitational force is always attractive.
- Gravitational force acts between any two pieces of matter in the Universe since mass is its source.
- Gravitational force is a central force that depends only on the position of test mass from the source mass.
- Gravitational force always acts along the line joining the centers of two bodies.
Some examples of the gravitational force are:
- If someone jumps upwards in the sky, someone can’t float in the air, it again comes back to earth due to gravitational force.
- If a ball is thrown upwards, it reaches a certain height and falls downwards because of gravitational force.
- The force of attraction between the sun and the planets in the Universe is Gravitational Force.
牛顿万有引力定律
根据万有引力定律,宇宙中的每个点质量都通过指向它们质心之间的直线的力来吸引宇宙中的所有其他点质量,这个力等于粒子的质量和与它们的差异成反比。从一个点到另一个点,这种吸引力通常指向内部。
这条定律适用于所有有重量的物体,无论它们有多大或多小。如果两个大质量物体之间的差异与它们的大小相比非常大,或者它们是球对称的,它们可能被称为点状质量。在这些情况下,每个物体的质量都可以通过其质心处的点质量来测量。
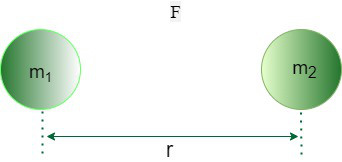
牛顿万有引力定律的两个质量的表示
因此,根据牛顿万有引力定律,宇宙中的每一个粒子都以大小为的力吸引其他粒子,
- 与它们的质量的乘积成正比,即
F ∝ (m 1 × m 2 ) ……(1)
- 与它们的中心之间的距离的平方成反比(也称为平方反比定律),即
F ∝ (1 / r 2 ) ……(2)
结合等式 (1) 和 (2) 可以得出,
F ∝ (m 1 × m 2 ) / r 2 ……(3)
因此,从方程(3)可以说,两个粒子或物体之间的万有引力或重力与它们的质量与它们之间的距离的平方的乘积成正比。
F = G × (m 1 × m 2 ) / r 2 ……(4)
这里 G 是比例常数,也称为万有引力常数,它始终是一个通用常数,
F是重力,
m 1是一个物体的质量,
m 2是另一个物体的质量,并且
r 是这些对象之间的距离。
什么是万有引力常数?
Gravitational Constant is a proportionality constant, and it is used in Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation. It is denoted by G.
It can also be defined as a force of attraction between any two unit masses separated by unit distance. From Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation i.e. from equation (4), the expression for G is:
F = G × (m1 × m2) / r2
G = F × r2 / (m1 × m2)
When r =1 m and m1 = m2 = 1 kg. then
G = F
Dimensional Formula for G is [M-1L3T-2].
Its values in SI units is 6.67 × 10-11 Nm2 kg-2 and in CGS system is 6.67×10-8 dyne cm2 g-2.
万有引力定律的重要性
万有引力定律成功地解释了许多概念,例如:
- 行星运动是如何发生的?
- 宇宙中的所有物体如何相互影响?
- 月球绕地球运动是如何发生的?
- 我们如何始终保持在地面上,以及重力如何影响身体的重量?
牛顿万有引力定律的向量形式
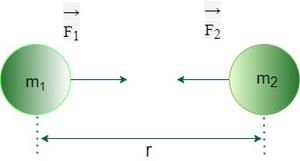
由作用在两个粒子之间的引力形成的作用-反应对称为牛顿万有引力定律的向量形式。考虑两个质量分别为 m1 和 m2 的点质量体 A 和 B,它们的距离为 r,如下图所示:
这里![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

从上图中可以看出,两个质量为 和 的粒子被放置在远处
![]()
因此,根据牛顿万有引力定律,m 1施加在 m 2上的力为
负号表示力的吸引力。
类似地,m 1 by m 2上的引力
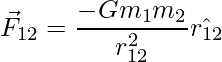
我们知道![]()
⇒ | 12 | 2 = | r 21 | 2
因此,可以得出:
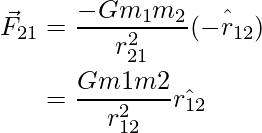
![]()
这意味着上述两个向量相等且彼此相反,这说明万有引力满足牛顿第三定律。
因此,牛顿万有引力定律的这种矢量形式意味着作用在两个粒子之间的引力形成了如上所示的作用-反应对。
万有引力叠加原理
引力叠加原理指出,任何物体上的总引力等于作用在该物体上的单个引力的总和。换句话说,一个点的净引力场是该点由于不同来源而产生的引力场的矢量和,给出为:
在哪里![]() 是物体上的总引力,
是物体上的总引力, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() 和
和![]() 是单独作用于该物体的独立力。
是单独作用于该物体的独立力。
从开普勒定律推演牛顿万有引力定律
假设一颗质量为 m 的行星以恒定角速度 ω 在半径为 r 的近圆形轨道上围绕质量为 M 的太阳旋转。令 T 为行星绕太阳公转的时间周期。
所以,
F = 先生ω 2
= mr × (2π/T) 2 ……(1)
根据开普勒第三定律,行星时间周期的平方与半长轴长度的平方成正比,给出如下:
T 2 ∝ r 3
要么
T 2 = kr 3
其中k是比例常数,T是行星的时间周期,r是半长轴的长度。
现在在等式(1)中应用它:
F = mr × (4π 2 / kr 3 )
= (4π 2 × m) / kr 2
但是 k = 4π 2 / GM,将上面的表达式替换为:
F = (G × M × m) / r 2
这是牛顿万有引力定律的方程。
因此,牛顿从开普勒定律推导出以下内容:
- 由于太阳而在地球上产生的力是向心力,它指向太阳。
- 行星的引力必须与其到太阳距离的平方成反比。
- 作用在地球上的力与地球和太阳质量的乘积成正比。
牛顿万有引力定律的样题
问题1:如果相同的物体被带到月球上并保持它们的分离距离保持不变,引力会有所不同吗?
解决方案:
If the same bodies are taken on to the moon keeping their separation distance constant then the gravitational force of attraction between the two bodies remains the same since the gravitational force of attraction between two bodies is unaffected by the presence of the third body and the medium between the two bodies.
Thus, the gravitational force of attraction remains the same between those bodies after taking to the moon.
问题 2:两个质量分别为 5 kg 和 6 kg 的物体被放置,它们的中心相距 64 m。假设没有其他力作用在两个质量上,计算它们的初始加速度。
解决方案:
Given that,
The mass of the first body, m1 is 5 kg.
The mass of the second body, m2 is 6 kg.
The distance between the two bodies, r is 64 m.
And the value of universal gravitational constant, G is 6.67 × 10-11 Nm2 kg-2
By the Newton’s law of Gravitation, the formula for gravitational force is given as
F = G × (m1 × m2) / r2
Substitute the given values in the above expression as:
F = 6.67 × 10-11 Nm2 kg-2 × (5 kg × 6 kg) / (64 m)2
= 48.85 × 10-14 N
Now, it is known that, the net force on an object is given by:
F = ma
or
a = F / m
Substitute the given and the obtained values in the above expression to calculate a for two bodies as:
a1 = 48.85 × 10-14 N / 5 kg
= 9.77 × 10-14 m/s2
And
a2 = 48.85 × 10-14 N / 6 kg
= 8.142 × 10-14 m/s2
Thus, the initial accelerations of two bodies are 9.77 × 10-14 m/s2 and 8.142 × 10-14 m/s2 respectively.
问题 3:一个质量为 1 kg 的物体和另一个质量为 10 kg 的物体相隔 100 m,它们被 19.6×10 -10 N 的力所吸引。计算万有引力常数的值给定的情况。
解决方案:
Given that,
The mass of the first body, m1 is 1 kg.
The mass of the second body, m2 is 10 kg.
The distance between the two bodies, r is 100 m.
The gravitational force of attraction between the two bodies F is 19.6 × 10-10 N.
Therefore, from the Newton’s law of Gravitation:
G = F × r2 / (m1 × m2)
= 19.6 × 10-10 N × (100 m)2 / (1 kg × 100 kg)
= 19.6 × 10-7 Nm2 kg-2
Thus, the value of universal gravitation constant for this case is 19.6 × 10-7 Nm2 kg-2.
问题4:如果两个物体以F单位的引力相互吸引。如果两个物体的质量都增加了两倍,物体之间的距离也增加了一倍。两个物体之间的新吸引力是什么?
解决方案:
Let the force of attraction between two bodies be F N.
And it is known from Newton’s law of Gravitation that the force of gravitational attraction is,
F = G × (m1 × m2) / r2
where m1 is the mass of first object, m2 is the mass of second object and r is the distance between the two bodies.
Let F1 be the new force of attraction between two objects.
When the mass of both objects are tripled and the distance between the objects is doubled then the force acting between two objects is,
F1 = G × (3 × m1 × 3 × m2) / (2r)2
= 9G × m1 × m2 / 4r2
= 9F / 4
Thus, the new force of attraction between two objects is 9F / 4 units.
问题 5:计算作用在位置 1 的质量 m 上的合力,所有等于 m 的质量都放在边长为 r 的等边三角形的顶点上。
解决方案:
Given that, the masses whose weight equal to m are placed on the three corners of equilateral triangle.
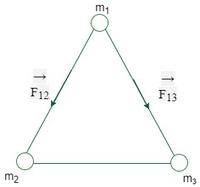
Let F1 be the force acting on mass m which is at position 1.
By the Principle of Superposition of Gravitational Forces,
![]()
F1=forces acting on mass m due to another mass m which is at position 2+forces acting on mass m due to another mass m which is at position 3.
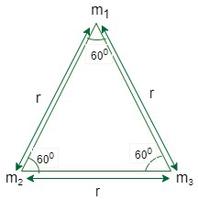
![]()
Here ![]() and
and ![]() makes an angle of 60° to each other since they act along the sides of equilateral triangle.
makes an angle of 60° to each other since they act along the sides of equilateral triangle.
![]()
![]()
Let ![]()
Fres=![]()
=![]()
Fres=√3f=√3×Gm2/r2
Thus the resultant force acting on mass m which is at position 1 and all the masses which are equal to m are placed in the vertices of the equilateral triangle having the length of its side is √3Gm2/r2.
问题 6:保持三个均匀的球体,每个球体的质量为 M,半径为 a,每个球体都与其他两个球体相接触。求其他两个球体对任何球体的引力大小。
解决方案:
Let A, B and C be the centers of three uniform spheres.
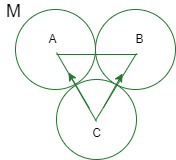
Let ![]() be the Force acting on C due to A and
be the Force acting on C due to A and be the force acting on C due to B
Let the total force acting on C due to A and B be ![]()
By the Principle of Superposition of Gravitational Forces,
⇒ ![]() ……(1)
……(1)
On joining A,B and C, we get a equilateral triangle i.e, it makes an angle of 60° to each other.
Given radius of each sphere is a
so, AB=BC=CA =2a
From Newton’s law of Gravitation, ![]()
Here ![]()
![]()
From (1),
![]()
=
= ![]()
|F| =![]()
Thus the magnitude of the gravitational force on any of the sphere due to the other two spheres is ![]()
问题 7:如果水星、金星和太阳成直角三角形排列。计算由于水银和太阳作用在金星上的力的矢量和。合力的方向和大小是多少?
解决方案:

Given that,
Distance between Sun and Venus (rv)=108×109 meters.
Distance between Sun and Mercury(rm)=57.6×109 meters
Distance between Mercury and Venus (rmv)=![]()
⇒ rmv=1.08×1011 meters.
Mass of Sun= 1.99×1030 kg
Mass of Mercury =3.3×1023 kg
Mass of Venus =4.87×1024 kg
Let Force acting on Venus due to Sun is FS
From Newton’s law of Gravitation, ![]()
= 6.67×10-11×1.99×1030×4.87×1024/(108×109)^2
FS=5.54×1022 N
Let Force acting on Venus due to Mercury is FM
⇒ ![]()
= 6.67×10-11×3.3×1023×4.87×1024/(1.08×1011)2
FM= 9.19×1015 N
Here Force due to Sun is more than a million times greater than Force due to Mercury and so the net Force is mainly due to Sun and its magnitude is equal to Force acting due to Sun. And the direction of resulting Force similar to direction due to Sun.