计算无向图中的边数
给定一个邻接表表示无向图。编写一个函数来计算无向图中的边数。
预期时间复杂度:O(V)
例子:
输入:下图的邻接表表示。输出:9 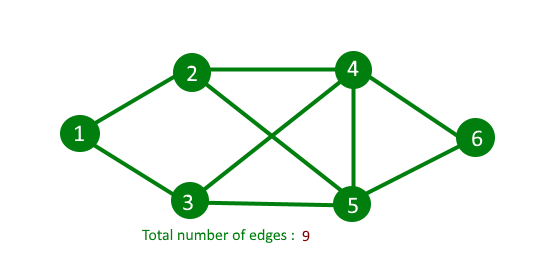
想法基于握手引理。握手引理是关于无向图的。在每个有限无向图中,奇数度的顶点数总是偶数。握手引理是度数和公式的结果(有时也称为握手引理)
![]()
所以我们遍历所有的顶点,计算它们的邻接表大小的总和,最后返回 sum/2。下面实现上述想法
C++
// C++ program to count number of edge in
// undirected graph
#include
using namespace std;
// Adjacency list representation of graph
class Graph
{
int V ;
list < int > *adj;
public :
Graph( int V )
{
this->V = V ;
adj = new list[V];
}
void addEdge ( int u, int v ) ;
int countEdges () ;
};
// add edge to graph
void Graph :: addEdge ( int u, int v )
{
adj[u].push_back(v);
adj[v].push_back(u);
}
// Returns count of edge in undirected graph
int Graph :: countEdges()
{
int sum = 0;
//traverse all vertex
for (int i = 0 ; i < V ; i++)
// add all edge that are linked to the
// current vertex
sum += adj[i].size();
// The count of edge is always even because in
// undirected graph every edge is connected
// twice between two vertices
return sum/2;
}
// driver program to check above function
int main()
{
int V = 9 ;
Graph g(V);
// making above shown graph
g.addEdge(0, 1 );
g.addEdge(0, 7 );
g.addEdge(1, 2 );
g.addEdge(1, 7 );
g.addEdge(2, 3 );
g.addEdge(2, 8 );
g.addEdge(2, 5 );
g.addEdge(3, 4 );
g.addEdge(3, 5 );
g.addEdge(4, 5 );
g.addEdge(5, 6 );
g.addEdge(6, 7 );
g.addEdge(6, 8 );
g.addEdge(7, 8 );
cout << g.countEdges() << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to count number of edge in
// undirected graph
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Adjacency list representation of graph
class Graph
{
int V;
Vector[] adj;
//@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Graph(int V)
{
this.V = V;
this.adj = new Vector[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
adj[i] = new Vector();
}
// add edge to graph
void addEdge(int u, int v)
{
adj[u].add(v);
adj[v].add(u);
}
// Returns count of edge in undirected graph
int countEdges()
{
int sum = 0;
// traverse all vertex
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
// add all edge that are linked to the
// current vertex
sum += adj[i].size();
// The count of edge is always even because in
// undirected graph every edge is connected
// twice between two vertices
return sum / 2;
}
}
class GFG
{
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
int V = 9;
Graph g = new Graph(V);
// making above shown graph
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 7);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 7);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(2, 8);
g.addEdge(2, 5);
g.addEdge(3, 4);
g.addEdge(3, 5);
g.addEdge(4, 5);
g.addEdge(5, 6);
g.addEdge(6, 7);
g.addEdge(6, 8);
g.addEdge(7, 8);
System.out.println(g.countEdges());
}
}
// This code is contributed by
// sanjeev2552 Python3
# Python3 program to count number of
# edge in undirected graph
# Adjacency list representation of graph
class Graph:
def __init__(self, V):
self.V = V
self.adj = [[] for i in range(V)]
# add edge to graph
def addEdge (self, u, v ):
self.adj[u].append(v)
self.adj[v].append(u)
# Returns count of edge in undirected graph
def countEdges(self):
Sum = 0
# traverse all vertex
for i in range(self.V):
# add all edge that are linked
# to the current vertex
Sum += len(self.adj[i])
# The count of edge is always even
# because in undirected graph every edge
# is connected twice between two vertices
return Sum // 2
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
V = 9
g = Graph(V)
# making above shown graph
g.addEdge(0, 1 )
g.addEdge(0, 7 )
g.addEdge(1, 2 )
g.addEdge(1, 7 )
g.addEdge(2, 3 )
g.addEdge(2, 8 )
g.addEdge(2, 5 )
g.addEdge(3, 4 )
g.addEdge(3, 5 )
g.addEdge(4, 5 )
g.addEdge(5, 6 )
g.addEdge(6, 7 )
g.addEdge(6, 8 )
g.addEdge(7, 8 )
print(g.countEdges())
# This code is contributed by PranchalKC#
// C# program to count number of edge in
// undirected graph
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// Adjacency list representation of graph
class Graph
{
public int V;
public List[] adj;
public Graph(int V)
{
this.V = V;
this.adj = new List[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
adj[i] = new List();
}
// add edge to graph
public void addEdge(int u, int v)
{
adj[u].Add(v);
adj[v].Add(u);
}
// Returns count of edge in undirected graph
public int countEdges()
{
int sum = 0;
// traverse all vertex
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
// add all edge that are linked to the
// current vertex
sum += adj[i].Count;
// The count of edge is always even because in
// undirected graph every edge is connected
// twice between two vertices
return sum / 2;
}
}
class GFG
{
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int V = 9;
Graph g = new Graph(V);
// making above shown graph
g.addEdge(0, 1);
g.addEdge(0, 7);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(1, 7);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(2, 8);
g.addEdge(2, 5);
g.addEdge(3, 4);
g.addEdge(3, 5);
g.addEdge(4, 5);
g.addEdge(5, 6);
g.addEdge(6, 7);
g.addEdge(6, 8);
g.addEdge(7, 8);
Console.WriteLine(g.countEdges());
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992 输出:
14
时间复杂度: O(V)