我们知道像(x + 2) 2和(x + 3) 3这样的项的展开。这些很简单,但是有时我们会遇到一些表达式,例如(x + 2) 5 。这些表达式很难扩展,例如,我们可以使用一些技巧来简化这些表达式,
(x + 2) 5 =(x + 2)(x + 2) 2 (x + 2) 2
研究人员研究了涉及数千个指数的二项式展开式。知道扩展它们的简单方法就变得至关重要。这仍然是很多工作,这就是二项式定理为我们提供帮助的地方。它允许我们扩展任何通用表达式,例如(x + a) n 。让我们详细看一下这个定理。
二项式表达
二项式表达式定义为具有两个由运算符(如+或-)连接的项的表达式。例如,x + a,x – 6等是二项式表达式的示例。将二项式表达式提高到大于3的幂非常困难且麻烦。让我们看一些二项式展开,并尝试在其中找到一些模式,
(x + a) 0 = 1
(x + a) 1 = x + a
(x + a) 2 = x 2 + 2ax + a 2
(x + a) 3 = x 3 + 3a 2 x + 3ax 2 + a 3
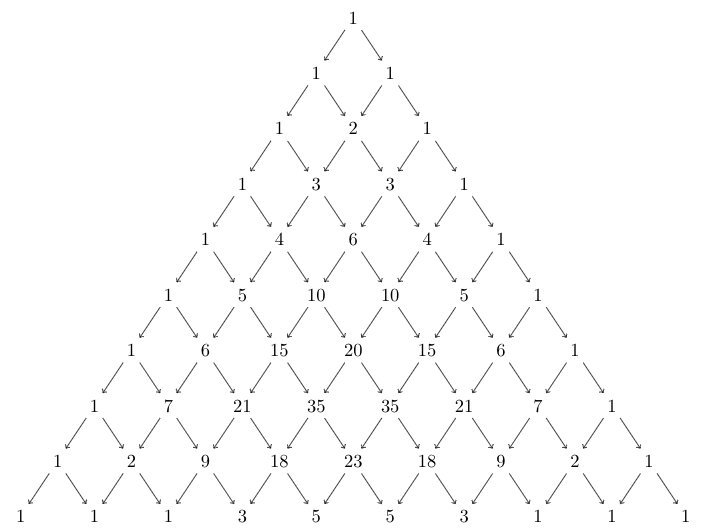
注意,我们需要知道这些项的系数,然后描述它们的展开可能会更容易一些。 Pascals的三角形可用于真正快速地产生这些结果。
什么是帕斯卡的三角形?
它以著名的哲学家和数学家“帕斯卡”(Pascal)的名字命名,后者开发了以1开头的数字模式,下面的数字是上述数字的总和。要开始制作Pascal的三角形,首先写下数字1。第二行再次写下两个1。其他行是使用前几行生成的,以形成一个数字三角形。每行以1开头和结尾。
1
1 1
1 x 1
1 x x 1
x给出的数字是通过将前一行的数字相加得出的,该数字位于给定位置的上方和左侧。下图演示了建立Pascal三角形的过程。

这样,可以生成帕斯卡的三角形。
问题1:生成Pascal三角形的第六行。
回答:
问题2:生成Pascal三角形的第十行。
回答:
Pascal三角形扩展二项式表达式
让我们再次看上面的等式,
(x + a) 0 = 1
(x + a) 1 = x + a
(x + a) 2 = x 2 + 2ax + a 2
(x + a) 3 = x 3 + 3a 2 x + 3ax 2 + a 3
我们可以从(x + a) n的这些方程式得出一些结论,
- 总比n的值多一个项。
- 对于每个项,指数的总和始终等于n。
- 对于变量“ x”,指数从n开始并持续减小直到零。同样,对于“ a”,指数从0开始直到n。
- 这些项的系数由帕斯卡的三角形给出。
让我们看一个例子,假设我们想通过这个扩展概念来扩展(x + a) 3 。应该有四个项,并且这些项应分别具有递减的指数“ x”和递增的指数“ a”。
(x + a) 3 = C 1 x 3 + C 2 x 2 a + C 3 xa 2 + C 4 a 3
值C 1, C 2 ,C 3 , 和C 4是系数,我们将用帕斯卡三角形计算出系数。让我们看一下n +1行的Pascal三角形,

最后一行的值给出了系数C 1 ,C 2 ,C 3和C 4的值。
在此,C 1 = 1,C 2 = 3,C 3 = 3和C 4 = 1。
因此,通过这种方式,我们可以扩展我们的二项式表达式。
For any binomial expression, (x + a)n the expansions is given by,
(a + b)n = c0anb0 + c1an-1b1 + c2an-2b2 + …. + cn-1a1bn-1 + cna0bn
The coefficients are given by the n+1 row of the Pascal’s triangle.
样本问题
问题1:展开并验证(a + b) 2 。
解决方案:
First write the generic expressions without the coefficients.
(a + b)2 = c0a2b0 + c1a1b1 + c2a0b2
Now let’s build a Pascal’s triangle for 3 rows to find out the coefficients.
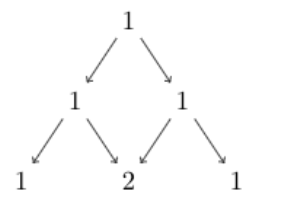
The values of the last row give us the value of coefficients.
c0 = 1, c1 = 2, c2 =1
(a + b)2 = a2b0 + 2a1b1 + a0b2
Thus verified.
问题2:展开(a + b) 4 。
解决方案:
First write the generic expressions without the coefficients.
(a + b)4 = c0a4b0 + c1a3b1 + c2a2b2 + c3a1b3 + c4a0b4
Now let’s build a Pascal’s triangle for 5 rows to find out the coefficients.
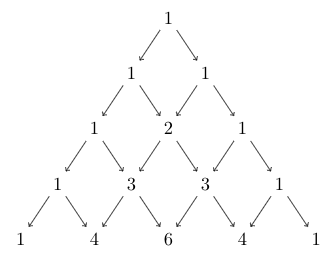
The values of the last row give us the value of coefficients.
c0 = 1, c1 = 4, c2 = 6, c3 = 4 and c4 =1.
Thus, (a + b)4 = a4b0 + 4a3b1 +6a2b2 + 4a1b3 + a0b4
问题3:展开(a + b) 5 。
解决方案:
First write the generic expressions without the coefficients.
(a + b)5 = c0a5b0 + c1a4b1 + c2a3b2 + c3a2b3 + c4a1b4 + c5a0b5
Now let’s build a Pascal’s triangle for 6 rows to find out the coefficients.

The values of the last row give us the value of coefficients.
c0 = 1, c1 = 5, c2 = 10, c3 = 10, c4 =5 and c5 = 1.
(a + b)5 = a5b0 + 5a4b1 + 10a3b2 + 10a2b3 + 5a1b4 + a0b5
问题4:展开(a + b) 6 。
解决方案:
First write the generic expressions without the coefficients.
(a + b)6 = c0a6b0 + c1a5b1 + c2a4b2 + c3a3b3 + c4a2b4 + c5a1b5 + c6a0b6
Now let’s build a Pascal’s triangle for 7 rows to find out the coefficients.

The values of the last row give us the value of coefficients.
c0 = 1, c1 = 6, c2 = 15, c3 = 20, c4 =15, c5 = 6 and c6 = 1.
(a + b)6 = 1a6b0 + 6a5b1 + 15a4b2 + 20a3b3 + 15a2b4 + 6a1b5 + 1a0b6