给定无向图G ,任务是找到偶数长度的最短路径,给定1作为源节点,给定N作为目标节点。路径长度是指路径中存在的边数(而不是路径成本)。
例子:
Input: N = 5, G is given below:
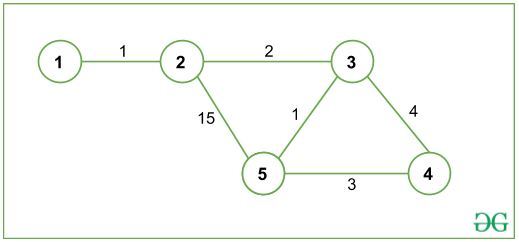
Output: 10
Explanation:
All paths from 1(source node) to 5 (destination node) are:
1->2->5
Cost: 16 Length: 2(even)
1->2->3->5
Cost: 4 Length: 3(odd)
1->2->3->4->5
Cost: 10 Length: 4(even)
The shortest path is 1->2->3->5 with total cost 4, but it has an odd-length path and since we are interested in even-length paths only, the shortest path with even-length is 1->2->3->4->5, with total cost 10.
Input 2: N = 4, G is given below:
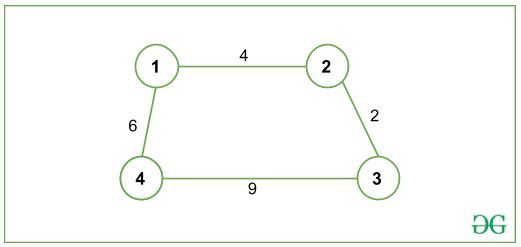
Output: -1
Explanation:
There is no path of even-length from 1(source node) to 4(destination node).
方法:
创建一个新图( G’ )。对于初始图G中的每个节点V ,创建两个新节点V_even和V_odd 。
Here, V_odd will be represented as ((V * 10) + 1) and V_even as ((V * 10) + 2).
For example, if node V = 4 then V_odd = 41 and V_even = 42.
现在,对于G中的每个边( U,V ),在G’中添加两个新边, (U_even,V_odd)和(U_odd,V_even) 。最后,使用Dijkstra最短路径算法找到从(source_even)节点到(destination_even)节点的最短路径。
对于输入1(上方)中给出的图, G’可以表示为:
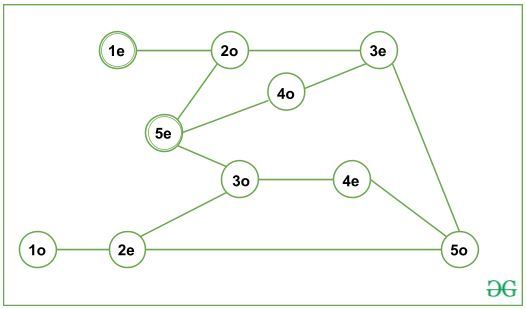
从图G’可以看出,只有从(1_even)到(5_even)的长度路径。因此,奇数长度的路径以G’分开,并且可以获得所需的最短路径。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAXX = 10000, INF = 1e9;
// Adjacency List: to represent graph
vector > >
adj(MAXX * 10 + 3);
// Distance Array: to store shortest
// distance to every node
vector dist(MAXX * 10 + 3, INF);
// returns value which will
// represent even_x
int even(int x)
{
return x * 10 + 2;
}
// returns value which will
// represent odd_x
int odd(int x)
{
return x * 10 + 1;
}
// converting edge (a->b) to 2
// different edges i.e. (a->b)
// converts to (1). even_a -> odd_b
// (2). odd_a -> even_b
// since, graph is undirected, so we
// push them in reverse order too
// hence, 4 push_back operations are
// there.
void addEdge(int a, int b, int cost)
{
adj[even(a)].push_back(
{ odd(b), cost });
adj[odd(a)].push_back(
{ even(b), cost });
adj[odd(b)].push_back(
{ even(a), cost });
adj[even(b)].push_back(
{ odd(a), cost });
}
// Function calculates shortest
// distance to all nodes from
// "source" using Dijkstra
// Shortest Path Algorithm
// and returns shortest distance
// to "destination"
int dijkstra(int source,
int destination)
{
/* Priority Queue/min-heap
to store and process
(distance, node) */
priority_queue,
vector >,
greater > >
pq;
// pushing source node to
// priority queue and dist from
// source to source is set to 0
pq.push({ 0, even(source) });
dist[even(source)] = 0;
while (!pq.empty()) {
// U is the node at top
// of the priority queue
// note that pq.top().first
// refers to the Distance
// and pq.top().second
// will refer to the Node
int u = pq.top().second;
pq.pop();
// exploring all neighbours
// of node u
for (pair p :
adj[u]) {
/* v is neighbour node of u
and c is the cost/weight
of edge (u, v) */
int v = p.first;
int c = p.second;
// relaxation: checking if there
// is a shorter path to v via u
if (dist[u] + c
< dist[v]) {
// updating distance of v
dist[v] = dist[u] + c;
pq.push({ dist[v], v });
}
}
}
// returning shortest
// distance to "destination"
return dist[even(destination)];
}
// Driver function
int main()
{
// n = number of Nodes,
// m = number of Edges
int n = 5, m = 6;
addEdge(1, 2, 1);
addEdge(2, 3, 2);
addEdge(2, 5, 15);
addEdge(3, 5, 1);
addEdge(3, 4, 4);
addEdge(5, 4, 3);
int source = 1;
int destination = n;
int ans = dijkstra(source, destination);
// if ans is INF: There is no
// even length path from source
// to destination else path
// exists and we print the
// shortest distance
if (ans == INF)
cout << "-1"
<< "\n";
else
cout << ans << "\n";
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
class GFG{
static class Pair implements Comparable
{
int first, second;
public Pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(GFG.Pair o)
{
if (this.first == o.first)
{
return this.second - o.second;
}
return this.first - o.first;
}
}
static final int MAXX = 10000, INF = (int)1e9;
// Adjacency List: to represent graph
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static ArrayList[] adj = new ArrayList[MAXX * 10 + 3];
// Distance Array: to store shortest
// distance to every node
static int[] dist = new int[MAXX * 10 + 3];
// Returns value which will
// represent even_x
static int even(int x)
{
return x * 10 + 2;
}
// Returns value which will
// represent odd_x
static int odd(int x)
{
return x * 10 + 1;
}
// Converting edge (a->b) to 2
// different edges i.e. (a->b)
// converts to (1). even_a -> odd_b
// (2). odd_a -> even_b
// since, graph is undirected, so we
// push them in reverse order too
// hence, 4 push_back operations are
// there.
static void addEdge(int a, int b, int cost)
{
adj[even(a)].add(new Pair(odd(b), cost));
adj[odd(a)].add(new Pair(even(b), cost));
adj[odd(b)].add(new Pair(even(a), cost));
adj[even(b)].add(new Pair(odd(a), cost));
}
// Function calculates shortest
// distance to all nodes from
// "source" using Dijkstra
// Shortest Path Algorithm
// and returns shortest distance
// to "destination"
static int dijkstra(int source, int destination)
{
// Priority Queue/min-heap to store
// and process (distance, node)
PriorityQueue pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
// Pushing source node to
// priority queue and dist from
// source to source is set to 0
pq.add(new Pair(0, even(source)));
dist[even(source)] = 0;
while (!pq.isEmpty())
{
// U is the node at top
// of the priority queue
// note that pq.top().first
// refers to the Distance
// and pq.top().second
// will refer to the Node
int u = pq.poll().second;
// Exploring all neighbours
// of node u
for(Pair p : adj[u])
{
// v is neighbour node of u and
// c is the cost/weight of edge (u, v)
int v = p.first;
int c = p.second;
// Relaxation: checking if there
// is a shorter path to v via u
if (dist[u] + c < dist[v])
{
// Updating distance of v
dist[v] = dist[u] + c;
pq.add(new Pair(dist[v], v));
}
}
}
// Returning shortest
// distance to "destination"
return dist[even(destination)];
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
for(int i = 0; i < MAXX * 10 + 3; i++)
{
adj[i] = new ArrayList();
}
Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
// n = number of Nodes,
// m = number of Edges
int n = 5, m = 6;
addEdge(1, 2, 1);
addEdge(2, 3, 2);
addEdge(2, 5, 15);
addEdge(3, 5, 1);
addEdge(3, 4, 4);
addEdge(5, 4, 3);
int source = 1;
int destination = n;
int ans = dijkstra(source, destination);
// If ans is INF: There is no
// even length path from source
// to destination else path
// exists and we print the
// shortest distance
if (ans == INF)
System.out.println("-1");
else
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed by sanjeev2552 10时间复杂度: (E * log(V))
如果您希望与行业专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅《 Geeks现场课程》和《 Geeks现场课程美国》。