给定一个有向图以及一个源节点和目标节点,我们需要找出需要反转多少条边,以便至少有 1 条从源节点到目标节点的路径。
例子:
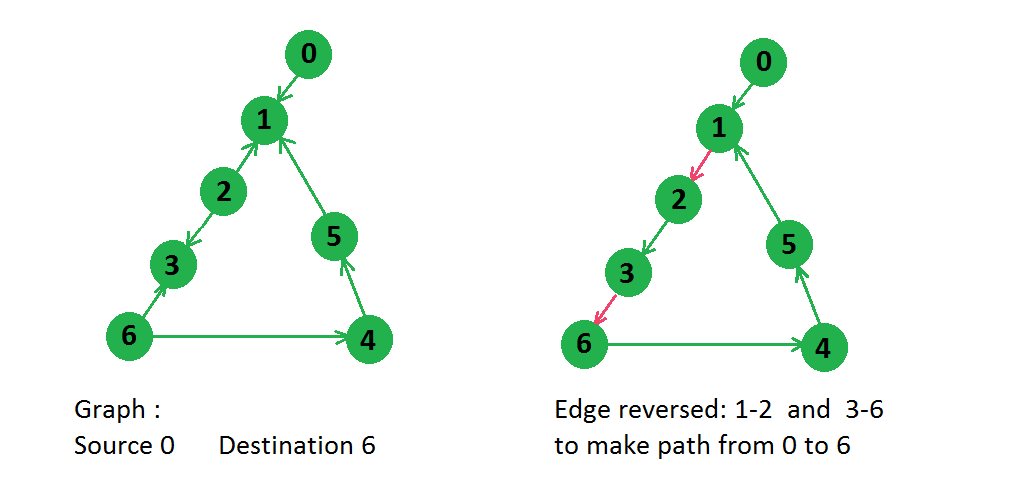
In above graph there were two paths from node 0 to node 6,
0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 6
0 -> 1 -> 5 -> 4 -> 6
But for first path only two edges need to be reversed, so answer will be 2 only.假设给定图形的不同版本,可以解决这个问题。在这个版本中,我们制作了一条与每条边相对应的反向边,并为其分配权重 1,并为原始边分配权重 0。上图修改后如下图所示,
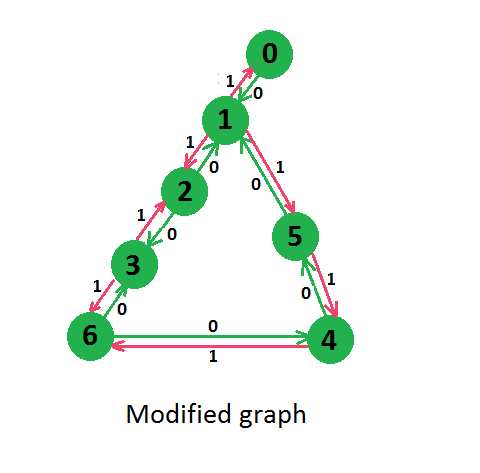
现在我们可以看到我们已经修改了图形,如果我们向原始边移动,则不会产生成本,但如果我们向反向边移动 1 成本会增加。因此,如果我们将 Dijkstra 的最短路径应用到这个修改后的图上,从给定的源,那么这将使我们达到从源到目的地的最小成本,即从源到目的地的最小边反转。
以下是基于上述概念的代码。
C++
// C++ Program to find minimum edge reversal to get
// atleast one path from source to destination
#include
using namespace std;
# define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
// This class represents a directed graph using
// adjacency list representation
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices
// In a weighted graph, we need to store vertex
// and weight pair for every edge
list< pair > *adj;
public:
Graph(int V); // Constructor
// function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int u, int v, int w);
// returns shortest path from s
vector shortestPath(int s);
};
// Allocates memory for adjacency list
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list< pair >[V];
}
// method adds a directed edge from u to v with weight w
void Graph::addEdge(int u, int v, int w)
{
adj[u].push_back(make_pair(v, w));
}
// Prints shortest paths from src to all other vertices
vector Graph::shortestPath(int src)
{
// Create a set to store vertices that are being
// prerocessed
set< pair > setds;
// Create a vector for distances and initialize all
// distances as infinite (INF)
vector dist(V, INF);
// Insert source itself in Set and initialize its
// distance as 0.
setds.insert(make_pair(0, src));
dist[src] = 0;
/* Looping till all shortest distance are finalized
then setds will become empty */
while (!setds.empty())
{
// The first vertex in Set is the minimum distance
// vertex, extract it from set.
pair tmp = *(setds.begin());
setds.erase(setds.begin());
// vertex label is stored in second of pair (it
// has to be done this way to keep the vertices
// sorted distance (distance must be first item
// in pair)
int u = tmp.second;
// 'i' is used to get all adjacent vertices of a vertex
list< pair >::iterator i;
for (i = adj[u].begin(); i != adj[u].end(); ++i)
{
// Get vertex label and weight of current adjacent
// of u.
int v = (*i).first;
int weight = (*i).second;
// If there is shorter path to v through u.
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + weight)
{
/* If distance of v is not INF then it must be in
our set, so removing it and inserting again
with updated less distance.
Note : We extract only those vertices from Set
for which distance is finalized. So for them,
we would never reach here. */
if (dist[v] != INF)
setds.erase(setds.find(make_pair(dist[v], v)));
// Updating distance of v
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;
setds.insert(make_pair(dist[v], v));
}
}
}
return dist;
}
/* method adds reverse edge of each original edge
in the graph. It gives reverse edge a weight = 1
and all original edges a weight of 0. Now, the
length of the shortest path will give us the answer.
If shortest path is p: it means we used p reverse
edges in the shortest path. */
Graph modelGraphWithEdgeWeight(int edge[][2], int E, int V)
{
Graph g(V);
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++)
{
// original edge : weight 0
g.addEdge(edge[i][0], edge[i][1], 0);
// reverse edge : weight 1
g.addEdge(edge[i][1], edge[i][0], 1);
}
return g;
}
// Method returns minimum number of edges to be
// reversed to reach from src to dest
int getMinEdgeReversal(int edge[][2], int E, int V,
int src, int dest)
{
// get modified graph with edge weight
Graph g = modelGraphWithEdgeWeight(edge, E, V);
// get shortes path vector
vector dist = g.shortestPath(src);
// If distance of destination is still INF,
// not possible
if (dist[dest] == INF)
return -1;
else
return dist[dest];
}
// Driver code to test above method
int main()
{
int V = 7;
int edge[][2] = {{0, 1}, {2, 1}, {2, 3}, {5, 1},
{4, 5}, {6, 4}, {6, 3}};
int E = sizeof(edge) / sizeof(edge[0]);
int minEdgeToReverse =
getMinEdgeReversal(edge, E, V, 0, 6);
if (minEdgeToReverse != -1)
cout << minEdgeToReverse << endl;
else
cout << "Not possible" << endl;
return 0;
}Java
// Java program to find minimum edge reversal to get
// atleast one path from source to destination
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
class Pair
{
int first, second;
public Pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// This class represents a directed graph using
// adjacency list representation
class Graph{
final int INF = (int)0x3f3f3f3f;
// No. of vertices
int V;
// In a weighted graph, we need to store vertex
// and weight pair for every edge
List[] adj;
// Allocates memory for adjacency list
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Graph(int V)
{
this.V = V;
adj = new ArrayList[V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
adj[i] = new ArrayList();
}
}
// Function adds a directed edge from
// u to v with weight w
void addEdge(int u, int v, int w)
{
adj[u].add(new Pair(v, w));
}
// Prints shortest paths from
// src to all other vertices
int[] shortestPath(int src)
{
// Create a set to store vertices
// that are being prerocessed
Set setds = new HashSet();
// Create a vector for distances and
// initialize all distances as infinite(INF)
int[] dist = new int[V];
Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
// Insert source itself in Set and initialize
// its distance as 0.
setds.add(new Pair(0, src));
dist[src] = 0;
// Looping till all shortest distance are
// finalized then setds will become empty
while (!setds.isEmpty())
{
// The first vertex in Set is the minimum
// distance vertex, extract it from set.
Iterator itr = setds.iterator();
Pair tmp = itr.next();
itr.remove();
// Vertex label is stored in second of pair (it
// has to be done this way to keep the vertices
// sorted distance (distance must be first item
// in pair)
int u = tmp.second;
// 'i' is used to get all adjacent
// vertices of a vertex
for(Pair p : adj[u])
{
// Get vertex label and weight of
// current adjacent of u.
int v = p.first;
int weight = p.second;
// If there is shorter path to v through u.
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + weight)
{
// If distance of v is not INF then it
// must be in our set, so removing it
// and inserting again with updated
// less distance. Note : We extract
// only those vertices from Set for
// which distance is finalized. So
// for them, we would never reach here.
if (dist[v] != INF)
{
setds.remove(new Pair(dist[v], v));
}
// setds.erase(setds.find(new Pair(dist[v], v)));
// Updating distance of v
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;
setds.add(new Pair(dist[v], v));
}
}
}
return dist;
}
}
class GFG{
static final int INF = (int)0x3f3f3f3f;
// Function adds reverse edge of each original
// edge in the graph. It gives reverse edge
// a weight = 1 and all original edges a
// weight of 0. Now, the length of the
// shortest path will give us the answer.
// If shortest path is p: it means we
// used p reverse edges in the shortest path.
static Graph modelGraphWithEdgeWeight(int edge[][],
int E, int V)
{
Graph g = new Graph(V);
for(int i = 0; i < E; i++)
{
// Original edge : weight 0
g.addEdge(edge[i][0], edge[i][1], 0);
// Reverse edge : weight 1
g.addEdge(edge[i][1], edge[i][0], 1);
}
return g;
}
// Function returns minimum number of edges to be
// reversed to reach from src to dest
static int getMinEdgeReversal(int edge[][], int E,
int V, int src, int dest)
{
// Get modified graph with edge weight
Graph g = modelGraphWithEdgeWeight(edge, E, V);
// Get shortes path vector
int[] dist = g.shortestPath(src);
// If distance of destination is still INF,
// not possible
if (dist[dest] == INF)
return -1;
else
return dist[dest];
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int V = 7;
int edge[][] = { { 0, 1 }, { 2, 1 },
{ 2, 3 }, { 5, 1 },
{ 4, 5 }, { 6, 4 },
{ 6, 3 } };
int E = edge.length;
int minEdgeToReverse = getMinEdgeReversal(
edge, E, V, 0, 6);
if (minEdgeToReverse != -1)
System.out.println(minEdgeToReverse);
else
System.out.println("Not possible");
}
}
// This code is contributed by sanjeev2552 Python3
# Python3 Program to find minimum edge reversal to get
# atleast one path from source to destination
# method adds a directed edge from u to v with weight w
def addEdge(u, v, w):
global adj
adj[u].append((v, w))
# Prints shortest paths from src to all other vertices
def shortestPath(src):
# Create a set to store vertices that are being
# prerocessed
setds = {}
# Create a vector for distances and initialize all
# distances as infinite (INF)
dist = [10**18 for i in range(V)]
# Insert source itself in Set and initialize its
global adj
setds[(0, src)] = 1
dist[src] = 0
# /* Looping till all shortest distance are finalized
# then setds will become empty */
while (len(setds) > 0):
# The first vertex in Set is the minimum distance
# vertex, extract it from set.
tmp = list(setds.keys())[0]
del setds[tmp]
# vertex label is stored in second of pair (it
# has to be done this way to keep the vertices
# sorted distance (distance must be first item
# in pair)
u = tmp[1]
# 'i' is used to get all adjacent vertices of a vertex
# list< pair >::iterator i;
for i in adj[u]:
# Get vertex label and weight of current adjacent
# of u.
v = i[0];
weight = i[1]
# If there is shorter path to v through u.
if (dist[v] > dist[u] + weight):
# /* If distance of v is not INF then it must be in
# our set, so removing it and inserting again
# with updated less distance.
# Note : We extract only those vertices from Set
# for which distance is finalized. So for them,
# we would never reach here. */
if (dist[v] != 10**18):
del setds[(dist[v], v)]
# Updating distance of v
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight
setds[(dist[v], v)] = 1
return dist
# /* method adds reverse edge of each original edge
# in the graph. It gives reverse edge a weight = 1
# and all original edges a weight of 0. Now, the
# length of the shortest path will give us the answer.
# If shortest path is p: it means we used p reverse
# edges in the shortest path. */
def modelGraphWithEdgeWeight(edge, E, V):
global adj
for i in range(E):
# original edge : weight 0
addEdge(edge[i][0], edge[i][1], 0)
# reverse edge : weight 1
addEdge(edge[i][1], edge[i][0], 1)
# Method returns minimum number of edges to be
# reversed to reach from src to dest
def getMinEdgeReversal(edge, E, V,src, dest):
# get modified graph with edge weight
modelGraphWithEdgeWeight(edge, E, V)
# get shortes path vector
dist = shortestPath(src)
# If distance of destination is still INF,
# not possible
if (dist[dest] == 10**18):
return -1
else:
return dist[dest]
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
V = 7
edge = [[0, 1], [2, 1], [2, 3], [5, 1],[4, 5], [6, 4], [6, 3]]
E, adj = len(edge), [[] for i in range(V + 1)]
minEdgeToReverse = getMinEdgeReversal(edge, E, V, 0, 6)
if (minEdgeToReverse != -1):
print(minEdgeToReverse)
else:
print("Not possible")
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29 输出:
2如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。