给定一个二叉树,任务是执行树的特定级别顺序遍历,以便在每个级别打印第一个元素,然后是最后一个元素,然后是第二个元素和第二个元素,直到打印该级别的所有元素,依此类推。
例子:
Input: Below is the given tree:
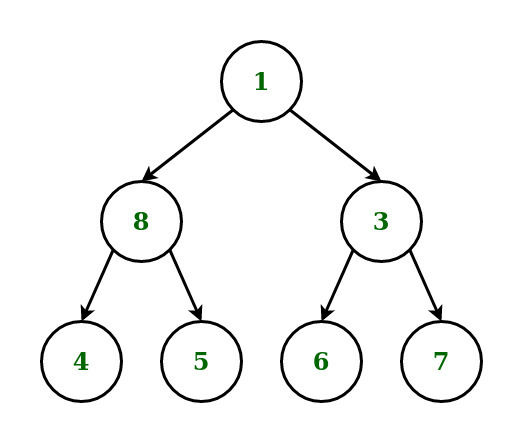
Output: 1 8 3 4 7 5 6
Explanation:
1st level: 1(root)
2nd level: 8(left), 3(right)
3rd level: 4(left), 7(right), 5(left), 6(right)
Input: Below is the given tree:
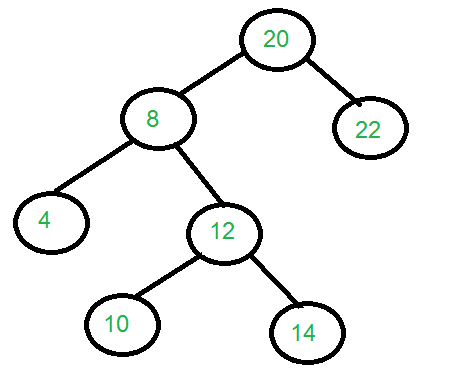
Output: 20 8 22 4 12 10 14
Explanation:
1st level: 20(root)
2nd level: 8(left), 22(right)
3rd level: 4(left), 12(right)
4th level: 10(left), 14(right)
方法:想法是对给定的二叉树进行层序遍历,并将这棵树转化为完美二叉树。在遍历时,如果任何节点的子节点不存在,则在队列中附加NULL节点作为子节点。以下是步骤:
- 执行给定树的层序遍历。
- 在遍历过程中,如果任何节点的子节点不存在,则在队列中附加NULL节点作为子节点
- 在遍历每个级别期间,请执行以下操作:
- 维护两个队列来存储每个级别的两个半部分的节点。
- 对于前半部分,以从左到右的方式存储节点。
- 后半层的节点以从右到左的方式存储。
- 迭代上面形成的两个队列,并以交替方式打印,用于特定的层序遍历。
下面是上述方法的实现:
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Node structure
static class node
{
int data;
node left = null;
node right = null;
}
// Creates and initialize a new node
static node newNode(int ch)
{
// Allocating memory to a new node
node n = new node();
n.data = ch;
n.left = null;
n.right = null;
return n;
}
// Function to find the height of tree
static int Height(node root)
{
if (root == null)
return 0;
return 1 + Math.max(Height(root.left),
Height(root.right));
}
// Given a perfect binary tree
// print its node in Specific order
static void printSpecificLevelOrder(Queue A,
Queue B,
int height)
{
while (height != 0)
{
// Get each one front
// element of both queue
node X = A.poll();
node Y = B.poll();
// Check if X exist or not
if (X == null)
{
// Assume is has and put
// their both child as none
A.add(null);
A.add(null);
}
else
{
// print the data and store
// their child first left
// then right
System.out.print(X.data + " ");
A.add(X.left);
A.add(X.right);
}
// Check Y exist or not
if (Y == null)
{
// Assume is has and put
// their both child as none
B.add(null);
B.add(null);
}
else
{
// Print the data and store their
// child first left then right
System.out.print(Y.data + " ");
B.add(Y.right);
B.add(Y.left);
}
// Decrease by 1 unit
height -= 1;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
// Given tree
node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.right.right = newNode(7);
root.left.left.left = newNode(8);
root.left.left.right = newNode(9);
root.left.right.left = newNode(10);
root.left.right.right = newNode(11);
root.right.right.left = newNode(14);
root.right.right.right = newNode(15);
root.left.left.left.left = newNode(16);
root.left.left.left.right = newNode(17);
root.left.left.right.left = newNode(18);
root.left.left.right.right = newNode(19);
root.left.right.left.left = newNode(20);
root.left.right.left.right = newNode(21);
root.left.right.right.left = newNode(22);
root.left.right.right.right = newNode(23);
root.right.right.left.left = newNode(28);
root.right.right.left.right = newNode(29);
root.right.right.right.left = newNode(30);
root.right.right.right.right = newNode(31);
// Initialise Queue
Queue A = new LinkedList<>();
Queue B = new LinkedList<>();
int height = 0;
// Check top root manually
if (root != null)
{
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
A.add(root.left);
B.add(root.right);
height = Height(root);
height = (int)Math.pow(2, (height - 1)) - 1;
}
// Function Call
printSpecificLevelOrder(A, B, height);
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
from queue import Queue
# A binary tree node
class Node:
# A constructor for making
# a new node
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to find the height of tree
def Height(root):
if root == None:
return 0
return 1 + max(Height(root.left), Height(root.right))
# Given a perfect binary tree
# print its node in Specific order
def printSpecificLevelOrder(A, B, height):
while height != 0:
# Get each one front
# element of both queue
X = A.get()
Y = B.get()
# Check if X exist or not
if X == None:
# Assume is has and put
# their both child as none
A.put(None)
A.put(None)
else:
# print the data and store
# their child first left
# then right
print(X.data, end =" ")
A.put(X.left)
A.put(X.right)
# Check Y exist or not
if Y == None:
# Assume is has and put
# their both child as none
B.put(None)
B.put(None)
else:
# print the data and store their
# child first left then right
print(Y.data, end =" ")
B.put(Y.right)
B.put(Y.left)
# Decrease by 1 unit
height-= 1
# Driver Code
# Given Tree
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.right = Node(7)
root.left.left.left = Node(8)
root.left.left.right = Node(9)
root.left.right.left = Node(10)
root.left.right.right = Node(11)
root.right.right.left = Node(14)
root.right.right.right = Node(15)
root.left.left.left.left = Node(16)
root.left.left.left.right = Node(17)
root.left.left.right.left = Node(18)
root.left.left.right.right = Node(19)
root.left.right.left.left = Node(20)
root.left.right.left.right = Node(21)
root.left.right.right.left = Node(22)
root.left.right.right.right = Node(23)
root.right.right.left.left = Node(28)
root.right.right.left.right = Node(29)
root.right.right.right.left = Node(30)
root.right.right.right.right = Node(31)
# Initialise Queue
A = Queue(100)
B = Queue(100)
# Check top root manually
if root != None:
print(root.data, end =" ")
A.put(root.left)
B.put(root.right)
height = Height(root)
height = 2**(height-1)-1
# Function Call
printSpecificLevelOrder(A, B, height)C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Node structure
class node
{
public int data;
public node left = null;
public node right = null;
}
// Creates and initialize a new node
static node newNode(int ch)
{
// Allocating memory to a new node
node n = new node();
n.data = ch;
n.left = null;
n.right = null;
return n;
}
// Function to find the height of tree
static int Height(node root)
{
if (root == null)
return 0;
return 1 + Math.Max(Height(root.left),
Height(root.right));
}
// Given a perfect binary tree
// print its node in Specific order
static void printSpecificLevelOrder(Queue A,
Queue B,
int height)
{
while (height != 0)
{
// Get each one front
// element of both queue
node X = A.Peek();
A.Dequeue();
node Y = B.Peek();
B.Dequeue();
// Check if X exist or not
if (X == null)
{
// Assume is has and put
// their both child as none
A.Enqueue(null);
A.Enqueue(null);
}
else
{
// print the data and store
// their child first left
// then right
Console.Write(X.data + " ");
A.Enqueue(X.left);
A.Enqueue(X.right);
}
// Check Y exist or not
if (Y == null)
{
// Assume is has and put
// their both child as none
B.Enqueue(null);
B.Enqueue(null);
}
else
{
// Print the data and store their
// child first left then right
Console.Write(Y.data + " ");
B.Enqueue(Y.right);
B.Enqueue(Y.left);
}
// Decrease by 1 unit
height -= 1;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// Given tree
node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.right.right = newNode(7);
root.left.left.left = newNode(8);
root.left.left.right = newNode(9);
root.left.right.left = newNode(10);
root.left.right.right = newNode(11);
root.right.right.left = newNode(14);
root.right.right.right = newNode(15);
root.left.left.left.left = newNode(16);
root.left.left.left.right = newNode(17);
root.left.left.right.left = newNode(18);
root.left.left.right.right = newNode(19);
root.left.right.left.left = newNode(20);
root.left.right.left.right = newNode(21);
root.left.right.right.left = newNode(22);
root.left.right.right.right = newNode(23);
root.right.right.left.left = newNode(28);
root.right.right.left.right = newNode(29);
root.right.right.right.left = newNode(30);
root.right.right.right.right = newNode(31);
// Initialise Queue
Queue A = new Queue();
Queue B = new Queue();
int height = 0;
// Check top root manually
if (root != null)
{
Console.Write(root.data + " ");
A.Enqueue(root.left);
B.Enqueue(root.right);
height = Height(root);
height = (int)Math.Pow(2, (height - 1)) - 1;
}
// Function Call
printSpecificLevelOrder(A, B, height);
}
}
// This code is contributed by ipg2016107 输出:
1 2 3 4 7 5 8 15 9 14 10 11 16 31 17 30 18 29 19 28 20 21 22 23
1 2 3 4 7 5 8 15 9 14 10 11 16 31 17 30 18 29 19 28 20 21 22 23
时间复杂度: O(N),N为节点数
辅助空间: O(N),N为节点数
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live