N叉树的层序遍历
给定一个 N 叉树。任务是打印树的级别顺序遍历,其中每个级别将在新行中。
例子:
Input:
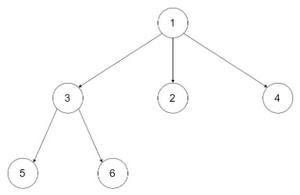
Image
Output:
1
3 2 4
5 6
Explanation: At level 1: only 1 is present.
At level 2: 3, 2, 4 is present
At level 3: 5, 6 is present
Input:

Image
Output:
1
2 3 4 5
6 7 8 9 10
11 12 13
14
Explanation: For the above example there are 5 level present in the n-ary tree.
At level 1: only 1 is present.
At level 2: 2, 3, 4, 5 is present.
At level 3: 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 is present
At level 4:11, 12, 13 is present
At level 5 :- 14 is present
方法:该问题的方法是使用 Level Order Traversal 并将所有级别存储在 2D 数组中,其中每个级别存储在不同的行中。
请按照以下步骤实施该方法:
- 创建一个向量ans和temp来存储 N 叉树的层序遍历。
- 将根节点推入队列。
- 运行 while 循环,直到队列不为空:
- 确定当前级别的大小,即队列的大小(比如N ):
- 为i = 1 到 N运行一个循环
- 在每个步骤中删除前端节点(比如cur )并将其数据推送到temp作为当前级别的一部分。
- 将cur的所有孩子推入队列。
- 将temp推入最终的ans向量中,该向量将不同的级别存储在不同的行中。
- 确定当前级别的大小,即队列的大小(比如N ):
- 返回ans向量。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ code for above implementation
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node {
char val;
vector children;
};
// Utility function to create a new tree
// node
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->val = key;
return temp;
}
// Function for level order traversal
// for n-array tree
vector > levelOrder(Node* root)
{
vector > ans;
if (!root)
cout << "N-Ary tree does not any nodes";
// Create two queues main_queue
// and child_queue
queue main_queue;
// Push the root value in the main_queue
main_queue.push(root);
// Create a temp vector to store the
// all the node values present at a
// particular level
vector temp;
// Run a while loop until the
// main_queue is empty
while (!main_queue.empty()) {
// Get the front of the main_queue
int n = main_queue.size();
// Iterate through the current level
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Node* cur = main_queue.front();
main_queue.pop();
temp.push_back(cur->val);
for (auto u : cur->children)
main_queue.push(u);
}
ans.push_back(temp);
temp.clear();
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(1);
root->children.push_back(newNode(3));
root->children.push_back(newNode(2));
root->children.push_back(newNode(4));
root->children[0]->children.push_back(newNode(5));
root->children[0]->children.push_back(newNode(6));
// LevelOrderTraversal obj;
vector > ans = levelOrder(root);
for (auto v : ans) {
for (int x : v)
cout << x << " ";
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
} 输出
1
3 2 4
5 6
时间复杂度: O(V) 其中 V 是节点数
辅助空间: O(V)