给定一个由V个顶点和一个表示节点对之间边的二维数组E[][2]组成的无向图。给定另一个数组arr[]表示分配给每个节点的值,任务是在图中所有连接组件的 GCD 中找到最大的 GCD。
例子:
Input: V = 5, E[][2] = {{1, 3}, {2, 3}, {1, 2}}, arr[] = {23, 43, 123, 54, 2}
Output: 54
Explanation:
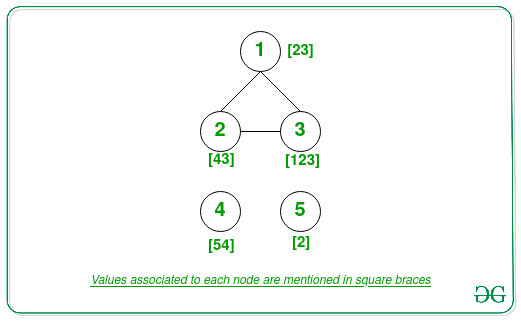
Connected component {1, 2, 3}: GCD(arr[1], arr[2], arr[3]) = GCD(23, 43, 123) = 1.
Connected component {4}: GCD = 54.
Connected component {5}: GCD = 2.
Therefore, the maximum GCD is 54.
Input: V = 5, E = {{1, 2}, {1, 3}, {4, 5}}, arr[] = { 10, 10, 10, 15, 15 }
Output: 15
方法:可以通过对给定图执行深度优先搜索遍历,然后在所有连通分量中找到最大 GCD 来解决给定问题。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 初始化一个变量,比如maxGCD为INT_MIN ,以存储所有连接组件之间的最大 GCD。
- 初始化另一个变量,比如currentGCD为0 ,以独立存储每个连接组件的 GCD。
- 将一个辅助数组visited[]初始化为false,以在DFS Traversal 中存储访问过的节点。
- 在范围[1, V] 上迭代每个顶点并执行以下步骤:
- 如果当前顶点未被访问,即visited[i] = false ,则将currentGCD初始化为0 。
- 从与currentGCD值和更新currentGCD值作为currentGCD的GCD当前顶点执行DFS遍历和常用3 [I – 1]中的每个递归调用。
- 如果currentGCD的值大于maxGCD ,则将maxGCD更新为currentGCD 。
- 完成以上步骤后,打印maxGCD的值作为结果。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find the GCD of two
// numbers a and b
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
// Base Case
if (b == 0)
return a;
// Recursively find the GCD
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
// Function to perform DFS Traversal
void depthFirst(int v, vector graph[],
vector& visited,
int& currGCD,
vector values)
{
// Mark the visited vertex as true
visited[v] = true;
// Update GCD of current
// connected component
currGCD = gcd(currGCD, values[v - 1]);
// Traverse all adjacent nodes
for (auto child : graph[v]) {
if (visited[child] == false) {
// Recursive call to perform
// DFS traversal
depthFirst(child, graph, visited,
currGCD, values);
}
}
}
// Function to find the maximum GCD
// of nodes among all the connected
// components of an undirected graph
void maximumGcd(int Edges[][2], int E,
int V, vector& arr)
{
vector graph[V + 1];
// Traverse the edges
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int u = Edges[i][0];
int v = Edges[i][1];
graph[u].push_back(v);
graph[v].push_back(u);
}
// Initialize boolean array
// to mark visited vertices
vector visited(V + 1, false);
// Stores the maximum GCD value
int maxGCD = INT_MIN;
// Traverse all the vertices
for (int i = 1; i <= V; i++) {
// If node is not visited
if (visited[i] == false) {
// Stores GCD of current
// connected component
int currGCD = 0;
// Perform DFS Traversal
depthFirst(i, graph, visited,
currGCD, arr);
// Update maxGCD
if (currGCD > maxGCD) {
maxGCD = currGCD;
}
}
}
// Print the result
cout << maxGCD;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int E = 3, V = 5;
vector arr = { 23, 43, 123, 54, 2 };
int Edges[][2] = { { 1, 3 }, { 2, 3 }, { 1, 2 } };
maximumGcd(Edges, E, V, arr);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int currGCD;
// Function to find the GCD of two
// numbers a and b
static int gcd(int a, int b)
{
// Base Case
if (b == 0)
return a;
// Recursively find the GCD
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
// Function to perform DFS Traversal
static void depthFirst(int v,
ArrayList graph[],
boolean visited[], int values[])
{
// Mark the visited vertex as true
visited[v] = true;
// Update GCD of current
// connected component
currGCD = gcd(currGCD, values[v - 1]);
// Traverse all adjacent nodes
for (int child : graph[v]) {
if (visited[child] == false) {
// Recursive call to perform
// DFS traversal
depthFirst(child, graph, visited, values);
}
}
}
// Function to find the maximum GCD
// of nodes among all the connected
// components of an undirected graph
static void maximumGcd(int Edges[][], int E, int V,
int arr[])
{
ArrayList graph[] = new ArrayList[V + 1];
// Initialize the graph
for (int i = 0; i < V + 1; i++)
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
// Traverse the edges
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int u = Edges[i][0];
int v = Edges[i][1];
graph[u].add(v);
graph[v].add(u);
}
// Initialize boolean array
// to mark visited vertices
boolean visited[] = new boolean[V + 1];
// Stores the maximum GCD value
int maxGCD = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
// Traverse all the vertices
for (int i = 1; i <= V; i++) {
// If node is not visited
if (visited[i] == false) {
// Stores GCD of current
// connected component
currGCD = 0;
// Perform DFS Traversal
depthFirst(i, graph, visited, arr);
// Update maxGCD
if (currGCD > maxGCD) {
maxGCD = currGCD;
}
}
}
// Print the result
System.out.println(maxGCD);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int E = 3, V = 5;
int arr[] = { 23, 43, 123, 54, 2 };
int Edges[][] = { { 1, 3 }, { 2, 3 }, { 1, 2 } };
maximumGcd(Edges, E, V, arr);
}
}
// Thi code is contributed by Kingash. Python3
# Python 3 program for the above approach
from math import gcd
import sys
# Function to find the GCD of two
# numbers a and b
currGCD = 0
# Function to perform DFS Traversal
def depthFirst(v, graph, visited, values):
global currGCD
# Mark the visited vertex as true
visited[v] = True
# Update GCD of current
# connected component
currGCD = gcd(currGCD, values[v - 1])
# Traverse all adjacent nodes
for child in graph[v]:
if (visited[child] == False):
# Recursive call to perform
# DFS traversal
depthFirst(child, graph, visited, values)
# Function to find the maximum GCD
# of nodes among all the connected
# components of an undirected graph
def maximumGcd(Edges, E, V, arr):
global currGCD
graph = [[] for i in range(V + 1)]
# Traverse the edges
for i in range(E):
u = Edges[i][0]
v = Edges[i][1]
graph[u].append(v)
graph[v].append(u)
# Initialize boolean array
# to mark visited vertices
visited = [False for i in range(V+1)]
# Stores the maximum GCD value
maxGCD = -sys.maxsize - 1
# Traverse all the vertices
for i in range(1, V + 1, 1):
# If node is not visited
if (visited[i] == False):
# Stores GCD of current
# connected component
currGCD = 0
# Perform DFS Traversal
depthFirst(i, graph, visited, arr)
# Update maxGCD
if (currGCD > maxGCD):
maxGCD = currGCD
# Print the result
print(maxGCD)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
E = 3
V = 5
arr = [23, 43, 123, 54, 2]
Edges = [[1, 3 ], [2, 3], [1, 2]]
maximumGcd(Edges, E, V, arr)
# This code is contributed by ipg2016107.输出:
54时间复杂度: O((V + E) * log(M)),其中M是给定数组arr[]的最小元素。
辅助空间: O(V)
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live