给定一个具有V个顶点和E 个边的无向图。每个节点都被分配了一个给定的值。任务是在图中的所有连接组件中找到具有最大值总和的连接链。
例子:
Input: V = 7, E = 4
Values = {10, 25, 5, 15, 5, 20, 0}
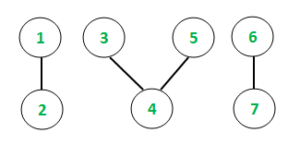
Output : Max Sum value = 35
Explanation:
Component {1, 2} – Value {10, 25}: sumValue = 10 + 25 = 35
Component {3, 4, 5} – Value {5, 15, 5}: sumValue = 5 + 15 + 5 = 25
Component {6, 7} – Value {20, 0}: sumValue = 20 + 0 = 20
Max Sum value chain is {1, 2} with values {10, 25}, hence 35 is answer.
Input: V = 10, E = 6
Values = {5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50}
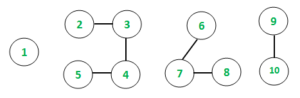
Output : Max Sum value = 105
方法:想法是使用深度优先搜索遍历方法来跟踪所有连接的组件。临时变量用于汇总连接链的各个值的所有值。在每次遍历连接的组件时,将迄今为止最重的值与当前值进行比较并相应地更新。在遍历所有连接的组件后,所有组件中的最大值将是答案。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to find Maximum sum of values
// of nodes among all connected
// components of an undirected graph
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to implement DFS
void depthFirst(int v, vector graph[],
vector& visited,
int& sum,
vector values)
{
// Marking the visited vertex as true
visited[v] = true;
// Updating the value of connection
sum += values[v - 1];
// Traverse for all adjacent nodes
for (auto i : graph[v]) {
if (visited[i] == false) {
// Recursive call to the DFS algorithm
depthFirst(i, graph, visited,
sum, values);
}
}
}
void maximumSumOfValues(vector graph[],
int vertices, vector values)
{
// Initializing boolean array to mark visited vertices
vector visited(values.size() + 1, false);
// maxChain stores the maximum chain size
int maxValueSum = INT_MIN;
// Following loop invokes DFS algorithm
for (int i = 1; i <= vertices; i++) {
if (visited[i] == false) {
// Variable to hold temporary values
int sum = 0;
// DFS algorithm
depthFirst(i, graph, visited,
sum, values);
// Conditional to update max value
if (sum > maxValueSum) {
maxValueSum = sum;
}
}
}
// Printing the heaviest chain value
cout << "Max Sum value = ";
cout << maxValueSum << "\n";
}
// Driver function to test above function
int main()
{
// Initializing graph in the form of adjacency list
vector graph[1001];
// Defining the number of edges and vertices
int E = 4, V = 7;
// Assigning the values for each
// vertex of the undirected graph
vector values;
values.push_back(10);
values.push_back(25);
values.push_back(5);
values.push_back(15);
values.push_back(5);
values.push_back(20);
values.push_back(0);
// Constructing the undirected graph
graph[1].push_back(2);
graph[2].push_back(1);
graph[3].push_back(4);
graph[4].push_back(3);
graph[3].push_back(5);
graph[5].push_back(3);
graph[6].push_back(7);
graph[7].push_back(6);
maximumSumOfValues(graph, V, values);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find Maximum sum of
// values of nodes among all connected
// components of an undirected graph
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int sum;
// Function to implement DFS
static void depthFirst(int v,
Vector graph[],
boolean []visited,
Vector values)
{
// Marking the visited vertex as true
visited[v] = true;
// Updating the value of connection
sum += values.get(v - 1);
// Traverse for all adjacent nodes
for(int i : graph[v])
{
if (visited[i] == false)
{
// Recursive call to the DFS algorithm
depthFirst(i, graph, visited, values);
}
}
}
static void maximumSumOfValues(Vector graph[],
int vertices,
Vector values)
{
// Initializing boolean array to
// mark visited vertices
boolean []visited = new boolean[values.size() + 1];
// maxChain stores the maximum chain size
int maxValueSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
// Following loop invokes DFS algorithm
for(int i = 1; i <= vertices; i++)
{
if (visited[i] == false)
{
// Variable to hold temporary values
sum = 0;
// DFS algorithm
depthFirst(i, graph, visited, values);
// Conditional to update max value
if (sum > maxValueSum)
{
maxValueSum = sum;
}
}
}
// Printing the heaviest chain value
System.out.print("Max Sum value = ");
System.out.print(maxValueSum + "\n");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initializing graph in the form
// of adjacency list
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Vector []graph = new Vector[1001];
for(int i = 0; i < graph.length; i++)
graph[i] = new Vector();
// Defining the number of edges and vertices
int E = 4, V = 7;
// Assigning the values for each
// vertex of the undirected graph
Vector values = new Vector();
values.add(10);
values.add(25);
values.add(5);
values.add(15);
values.add(5);
values.add(20);
values.add(0);
// Constructing the undirected graph
graph[1].add(2);
graph[2].add(1);
graph[3].add(4);
graph[4].add(3);
graph[3].add(5);
graph[5].add(3);
graph[6].add(7);
graph[7].add(6);
maximumSumOfValues(graph, V, values);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji Python3
# Python3 program to find Maximum sum
# of values of nodes among all connected
# components of an undirected graph
import sys
graph = [[] for i in range(1001)]
visited = [False] * (1001 + 1)
sum = 0
# Function to implement DFS
def depthFirst(v, values):
global sum
# Marking the visited vertex as true
visited[v] = True
# Updating the value of connection
sum += values[v - 1]
# Traverse for all adjacent nodes
for i in graph[v]:
if (visited[i] == False):
# Recursive call to the
# DFS algorithm
depthFirst(i, values)
def maximumSumOfValues(vertices,values):
global sum
# Initializing boolean array to
# mark visited vertices
# maxChain stores the maximum chain size
maxValueSum = -sys.maxsize - 1
# Following loop invokes DFS algorithm
for i in range(1, vertices + 1):
if (visited[i] == False):
# Variable to hold temporary values
# sum = 0
# DFS algorithm
depthFirst(i, values)
# Conditional to update max value
if (sum > maxValueSum):
maxValueSum = sum
sum = 0
# Printing the heaviest chain value
print("Max Sum value = ", end = "")
print(maxValueSum)
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Initializing graph in the
# form of adjacency list
# Defining the number of
# edges and vertices
E = 4
V = 7
# Assigning the values for each
# vertex of the undirected graph
values = []
values.append(10)
values.append(25)
values.append(5)
values.append(15)
values.append(5)
values.append(20)
values.append(0)
# Constructing the undirected graph
graph[1].append(2)
graph[2].append(1)
graph[3].append(4)
graph[4].append(3)
graph[3].append(5)
graph[5].append(3)
graph[6].append(7)
graph[7].append(6)
maximumSumOfValues(V, values)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29C#
// C# program to find Maximum sum of
// values of nodes among all connected
// components of an undirected graph
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static int sum;
// Function to implement DFS
static void depthFirst(int v,
List []graph,
bool []visited,
List values)
{
// Marking the visited vertex as true
visited[v] = true;
// Updating the value of connection
sum += values[v - 1];
// Traverse for all adjacent nodes
foreach(int i in graph[v])
{
if (visited[i] == false)
{
// Recursive call to the DFS algorithm
depthFirst(i, graph, visited, values);
}
}
}
static void maximumSumOfValues(List []graph,
int vertices,
List values)
{
// Initializing bool array to
// mark visited vertices
bool []visited = new bool[values.Count + 1];
// maxChain stores the maximum chain size
int maxValueSum = int.MinValue;
// Following loop invokes DFS algorithm
for(int i = 1; i <= vertices; i++)
{
if (visited[i] == false)
{
// Variable to hold temporary values
sum = 0;
// DFS algorithm
depthFirst(i, graph, visited, values);
// Conditional to update max value
if (sum > maxValueSum)
{
maxValueSum = sum;
}
}
}
// Printing the heaviest chain value
Console.Write("Max Sum value = ");
Console.Write(maxValueSum + "\n");
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Initializing graph in the form
// of adjacency list
List []graph = new List[1001];
for(int i = 0; i < graph.Length; i++)
graph[i] = new List();
// Defining the number of edges and vertices
int V = 7;
// Assigning the values for each
// vertex of the undirected graph
List values = new List();
values.Add(10);
values.Add(25);
values.Add(5);
values.Add(15);
values.Add(5);
values.Add(20);
values.Add(0);
// Constructing the undirected graph
graph[1].Add(2);
graph[2].Add(1);
graph[3].Add(4);
graph[4].Add(3);
graph[3].Add(5);
graph[5].Add(3);
graph[6].Add(7);
graph[7].Add(6);
maximumSumOfValues(graph, V, values);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar 输出:
Max Sum value = 35时间复杂度:O(E + V)
辅助空间: O(E + V)