给定一个由N个顶点和M 个边组成的无向加权图G ,以及两个由图的M 个边组成的数组 Edges[][2]和Weight[],以及 权重 每条边分别的任务是找到图的最大连通分量的任意两个顶点的最大乘积,由连接具有相同权重的所有边形成。
例子:
Input: N = 4, Edges[][] = {{1, 2}, {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {2, 3}, {2, 4}}, Weight[] = {1, 2, 1, 3, 3}
Output: 12
Explanation:
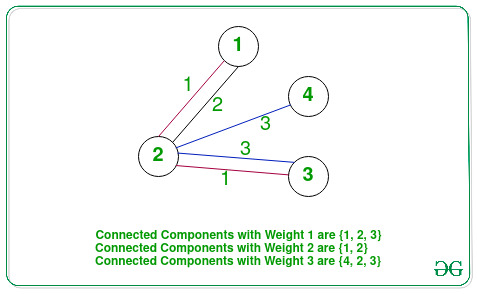
- Components of edges of weight 1, 1 ↔ 2 ↔ 3. The maximum product of any two vertices of this component is 6.
- Components of edges of weight 2, 1 ↔ 2. The maximum product of any two vertices of this component is 2.
- Components of edges of weight 3, 4 ↔ 2 ↔ 3. The maximum product of any two vertices of this component is 12.
Therefore, the maximum product among all the connected components of size 3 (which is maximum) is 12.
Input: N = 5, Edges[][] = {{1, 5}, {2, 5}, {3, 5}, {4, 5}, {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 4}}, Weight[] = {1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2}
Output: 20
方法:给定的问题可以通过对给定的图进行 DFS 遍历并最大化所有相同权重的连通分量的第一个和第二个最大节点的乘积来解决。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 将与所有唯一权重对应的所有边存储在地图M 中。
- 初始化一个变量,比如res为0来存储相同权重的连通分量的任意两个节点的最大乘积。
- 遍历地图并为每个键作为权重通过连接所有映射到特定权重的边创建一个图,并执行以下操作:
- 找到最大值(比如M1 )和第二个最大值(比如M2 )节点的值和 通过对创建的图执行 DFS 遍历,图的所有连接组件的大小。
- RE的值更新为最大的资源,M1,M2和如果当前连接的部件的尺寸是至少最大尺寸连接成分先前发现。
- 完成上述步骤后,打印res的值作为最大乘积。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Stores the first and second largest
// element in a connected componenet
int Max, sMax;
// Stores the count of nodes
// in the connected componenets
int cnt = 0;
// Function to perform DFS Traversal
// on a given graph and find the first
// and the second largest elements
void dfs(int u, int N, vector& vis,
vector >& adj)
{
// Update the maximum value
if (u > Max) {
sMax = Max;
Max = u;
}
// Update the second max value
else if (u > sMax) {
sMax = u;
}
// Increment size of component
cnt++;
// Mark current node visited
vis[u] = true;
// Traverse the adjacent nodes
for (auto to : adj[u]) {
// If to is not already visited
if (!vis[to]) {
dfs(to, N, vis, adj);
}
}
return;
}
// Function to find the maximum
// product of a connected component
int MaximumProduct(
int N, vector > Edge,
vector wt)
{
// Stores the count of edges
int M = wt.size();
// Stores all the edges mapped
// with a particular weight
unordered_map > >
mp;
// Update the map mp
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
mp[wt[i]].push_back(Edge[i]);
// Stores the result
int res = 0;
// Traverse the map mp
for (auto i : mp) {
// Stores the adjacency list
vector > adj(N + 1);
// Stores the edges of
// a particular weight
vector > v = i.second;
// Traverse the vector v
for (int j = 0; j < v.size(); j++) {
int U = v[j].first;
int V = v[j].second;
// Add an edge
adj[U].push_back(V);
adj[V].push_back(U);
}
// Stores if a vertex
// is visited or not
vector vis(N + 1, 0);
// Stores the maximum
// size of a component
int cntMax = 0;
// Iterate over the range [1, N]
for (int u = 1; u <= N; u++) {
// Assign Max, sMax, count = 0
Max = sMax = cnt = 0;
// If vertex u is not visited
if (!vis[u]) {
dfs(u, N, vis, adj);
// If cnt is greater
// than cntMax
if (cnt > cntMax) {
// Update the res
res = Max * sMax;
cntMax = cnt;
}
// If already largest
// connected component
else if (cnt == cntMax) {
// Update res
res = max(res, Max * sMax);
}
}
}
}
// Return res
return res;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int N = 5;
vector > Edges
= { { 1, 2 }, { 2, 5 }, { 3, 5 }, { 4, 5 }, { 1, 2 }, { 2, 3 }, { 3, 4 } };
vector Weight = { 1, 1, 1, 1,
2, 2, 2 };
cout << MaximumProduct(N, Edges, Weight);
return 0;
} 输出:
20
时间复杂度: O(N 2 * log N + M)
辅助空间: O(N 2 )
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live