素子集积问题
给定一个包含N个整数的数组arr[] 。数组A的子集的值定义为该子集中所有素数的乘积。如果子集中没有素数,则该子集的值为1 。任务是计算给定数组模数100000007的所有可能非空子集的值的乘积。
例子:
Input: arr[] = {3, 7}
Output: 441
val({3}) = 3
val({7}) = 7
val({3, 7}) = 3 * 7 = 21
3 * 7 * 21 = 441
Input: arr[] = {1, 1, 1}
Output: 1
方法:由于已知一个数字在给定大小为N的数组的所有子集中出现2 N – 1次。所以如果一个数X是素数,那么 X 的贡献将是X * X * X * ..... * 2 N – 1倍,即
由于2 N – 1也会是一个很大的数,所以不能直接计算。此处将使用费马定理来计算功率。
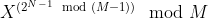
之后,可以很容易地计算每个元素的值。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
int power(int a, int b, int mod)
{
int aa = 1;
while(b)
{
if(b & 1)
{
aa = aa * a;
aa %= mod;
}
a = a * a;
a %= mod;
b /= 2;
}
return aa;
}
// Function to return the prime subset
// product of the given array
int product(int A[], int n)
{
// Create Sieve to check whether a
// number is prime or not
int N = 100010;
int mod = 1000000007;
vector prime(N, 1);
prime[0] = prime[1] = 0;
int i = 2;
while (i * i < N)
{
if (prime[i])
for (int j = 2 * i;
j <= N;j += i)
prime[j] = 0;
i += 1;
}
// Length of the array
// Calculating 2^(n-1) % mod
int t = power(2, n - 1, mod - 1);
int ans = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
int i = A[j];
// If element is prime then add
// its contribution in the result
if( prime[i])
{
ans *= power(i, t, mod);
ans %= mod;
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int A[] = {3, 7};
int n = sizeof(A) / sizeof(A[0]);
printf("%d", product(A, n));
}
// This code is contributed by Mohit Kumar Java
// Java implementation of the approach
class GFG
{
static int power(int a, int b, int mod)
{
int aa = 1;
while(b > 0)
{
if(b % 2 == 1)
{
aa = aa * a;
aa %= mod;
}
a = a * a;
a %= mod;
b /= 2;
}
return aa;
}
// Function to return the prime subset
// product of the given array
static int product(int A[], int n)
{
// Create Sieve to check whether a
// number is prime or not
int N = 100010;
int mod = 1000000007;
int []prime = new int[N];
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
prime[j] = 1;
}
prime[0] = prime[1] = 0;
int i = 2;
while (i * i < N)
{
if (prime[i] == 1)
for (int j = 2 * i;
j < N;j += i)
prime[j] = 0;
i += 1;
}
// Length of the array
// Calculating 2^(n-1) % mod
int t = power(2, n - 1, mod - 1);
int ans = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
i = A[j];
// If element is prime then add
// its contribution in the result
if( prime[i] == 1)
{
ans *= power(i, t, mod);
ans %= mod;
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int A[] = {3, 7};
int n = A.length;
System.out.printf("%d", product(A, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-JiPython3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
# Function to return the prime subset
# product of the given array
def product(A):
# Create Sieve to check whether a
# number is prime or not
N = 100010
mod = 1000000007
prime = [1] * N
prime[0] = prime[1] = 0
i = 2
while i * i < N:
if prime[i]:
for j in range(i * i, N, i):
prime[j] = 0
i += 1
# Length of the array
n = len(A)
# Calculating 2^(n-1) % mod
t = pow(2, n-1, mod-1)
ans = 1
for i in A:
# If element is prime then add
# its contribution in the result
if prime[i]:
ans *= pow(i, t, mod)
ans %= mod
return ans
# Driver code
A = [3, 7]
print(product(A))C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
static int power(int a, int b, int mod)
{
int aa = 1;
while(b > 0)
{
if(b % 2 == 1)
{
aa = aa * a;
aa %= mod;
}
a = a * a;
a %= mod;
b /= 2;
}
return aa;
}
// Function to return the prime subset
// product of the given array
static int product(int []A, int n)
{
// Create Sieve to check whether a
// number is prime or not
int N = 100010;
int mod = 1000000007;
int []prime = new int[N];
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
prime[j] = 1;
}
prime[0] = prime[1] = 0;
int i = 2;
while (i * i < N)
{
if (prime[i] == 1)
for (int j = 2 * i;
j < N; j += i)
prime[j] = 0;
i += 1;
}
// Length of the array
// Calculating 2^(n-1) % mod
int t = power(2, n - 1, mod - 1);
int ans = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
i = A[j];
// If element is prime then add
// its contribution in the result
if( prime[i] == 1)
{
ans *= power(i, t, mod);
ans %= mod;
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int []A = {3, 7};
int n = A.Length;
Console.Write("{0}", product(A, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-JiJavascript
输出:
441