给定n根不同长度的绳子,我们需要将这些绳子连接成一根绳子。连接两条绳索的成本等于它们的长度之和。我们需要以最小的成本连接绳索。
例如,如果我们有 4 根长度为 4、3、2 和 6 的绳索。我们可以通过以下方式连接绳索。
1) 首先,连接长度为 2 和 3 的绳索。 现在我们有 3 根长度为 4、6 和 5 的绳索。
2) 现在连接长度为 4 和 5 的绳索。现在我们有两条长度为 6 和 9 的绳索。
3) 最后将两根绳子连接起来,所有的绳子都连接好了。
连接所有绳索的总成本为 5 + 9 + 15 = 29。这是连接绳索的优化成本。连接绳索的其他方式总是具有相同或更多的成本。例如,如果我们先连接 4 和 6(我们得到三个字符串3、2 和 10),然后连接 10 和 3(我们得到两个字符串13 和 2)。最后我们将 13 和 2 连接起来。 这样的总成本是 10 + 13 + 15 = 38。
我们强烈建议您在继续解决方案之前单击此处进行练习。
解决方案:
如果我们仔细观察上述问题,我们可以注意到,首先被拣选的绳索长度在总成本中不止一次包括在内。因此,这个想法是先连接最小的两根绳子,然后再连接剩余的绳子。这种方法类似于霍夫曼编码。我们将最小的绳索放在树上,以便它们可以重复多次,而不是较长的绳索。
所以它形成了一个像树一样的结构:
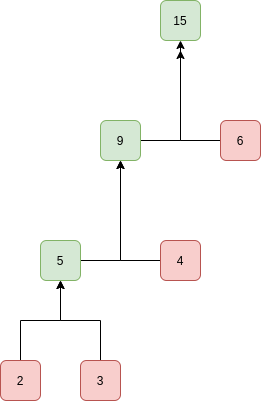
总和包含每个值的深度总和。对于数组 (2, 3, 4, 6),总和等于 2 * 3 + 3 * 3 + 4 * 2 + 6 * 1 = 29(根据图表)。
算法:
- 创建一个最小堆并将所有长度插入到最小堆中。
- 当最小堆中的元素数不是一时,请执行以下操作。
- 从最小堆中提取最小值和第二最小值
- 将上面两个提取的值相加,并将相加的值插入到最小堆中。
- 维护总成本的变量,并通过提取值的总和不断增加它。
- 返回此总成本的值。
下面是上述算法的实现。
C++
// C++ program for connecting
// n ropes with minimum cost
#include
using namespace std;
// A Min Heap: Collection of min heap nodes
struct MinHeap {
unsigned size; // Current size of min heap
unsigned capacity; // capacity of min heap
int* harr; // Attay of minheap nodes
};
// A utility function to create
// a min-heap of a given capacity
struct MinHeap* createMinHeap(unsigned capacity)
{
struct MinHeap* minHeap = new MinHeap;
minHeap->size = 0; // current size is 0
minHeap->capacity = capacity;
minHeap->harr = new int[capacity];
return minHeap;
}
// A utility function to swap two min heap nodes
void swapMinHeapNode(int* a, int* b)
{
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
// The standard minHeapify function.
void minHeapify(struct MinHeap* minHeap, int idx)
{
int smallest = idx;
int left = 2 * idx + 1;
int right = 2 * idx + 2;
if (left < minHeap->size
&& minHeap->harr[left] < minHeap->harr[smallest])
smallest = left;
if (right < minHeap->size
&& minHeap->harr[right] < minHeap->harr[smallest])
smallest = right;
if (smallest != idx) {
swapMinHeapNode(&minHeap->harr[smallest], &minHeap->harr[idx]);
minHeapify(minHeap, smallest);
}
}
// A utility function to check
// if size of heap is 1 or not
int isSizeOne(struct MinHeap* minHeap)
{
return (minHeap->size == 1);
}
// A standard function to extract
// minimum value node from heap
int extractMin(struct MinHeap* minHeap)
{
int temp = minHeap->harr[0];
minHeap->harr[0] = minHeap->harr[minHeap->size - 1];
--minHeap->size;
minHeapify(minHeap, 0);
return temp;
}
// A utility function to insert
// a new node to Min Heap
void insertMinHeap(struct MinHeap* minHeap, int val)
{
++minHeap->size;
int i = minHeap->size - 1;
while (i && (val < minHeap->harr[(i - 1) / 2])) {
minHeap->harr[i] = minHeap->harr[(i - 1) / 2];
i = (i - 1) / 2;
}
minHeap->harr[i] = val;
}
// A standard function to build min-heap
void buildMinHeap(struct MinHeap* minHeap)
{
int n = minHeap->size - 1;
int i;
for (i = (n - 1) / 2; i >= 0; --i)
minHeapify(minHeap, i);
}
// Creates a min-heap of capacity
// equal to size and inserts all values
// from len[] in it. Initially, size
// of min heap is equal to capacity
struct MinHeap* createAndBuildMinHeap(
int len[], int size)
{
struct MinHeap* minHeap = createMinHeap(size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
minHeap->harr[i] = len[i];
minHeap->size = size;
buildMinHeap(minHeap);
return minHeap;
}
// The main function that returns
// the minimum cost to connect n
// ropes of lengths stored in len[0..n-1]
int minCost(int len[], int n)
{
int cost = 0; // Initialize result
// Create a min heap of capacity
// equal to n and put all ropes in it
struct MinHeap* minHeap = createAndBuildMinHeap(len, n);
// Iterate while size of heap doesn't become 1
while (!isSizeOne(minHeap)) {
// Extract two minimum length
// ropes from min heap
int min = extractMin(minHeap);
int sec_min = extractMin(minHeap);
cost += (min + sec_min); // Update total cost
// Insert a new rope in min heap
// with length equal to sum
// of two extracted minimum lengths
insertMinHeap(minHeap, min + sec_min);
}
// Finally return total minimum
// cost for connecting all ropes
return cost;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
int len[] = { 4, 3, 2, 6 };
int size = sizeof(len) / sizeof(len[0]);
cout << "Total cost for connecting ropes is "
<< minCost(len, size);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to connect n
// ropes with minimum cost
// A class for Min Heap
class MinHeap {
int[] harr; // Array of elements in heap
int heap_size; // Current number of elements in min heap
int capacity; // maximum possible size of min heap
// Constructor: Builds a heap from
// a given array a[] of given size
public MinHeap(int a[], int size)
{
heap_size = size;
capacity = size;
harr = a;
int i = (heap_size - 1) / 2;
while (i >= 0) {
MinHeapify(i);
i--;
}
}
// A recursive method to heapify a subtree
// with the root at given index
// This method assumes that the subtrees
// are already heapified
void MinHeapify(int i)
{
int l = left(i);
int r = right(i);
int smallest = i;
if (l < heap_size && harr[l] < harr[i])
smallest = l;
if (r < heap_size && harr[r] < harr[smallest])
smallest = r;
if (smallest != i) {
swap(i, smallest);
MinHeapify(smallest);
}
}
int parent(int i) { return (i - 1) / 2; }
// to get index of left child of node at index i
int left(int i) { return (2 * i + 1); }
// to get index of right child of node at index i
int right(int i) { return (2 * i + 2); }
// Method to remove minimum element (or root) from min heap
int extractMin()
{
if (heap_size <= 0)
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if (heap_size == 1) {
heap_size--;
return harr[0];
}
// Store the minimum value, and remove it from heap
int root = harr[0];
harr[0] = harr[heap_size - 1];
heap_size--;
MinHeapify(0);
return root;
}
// Inserts a new key 'k'
void insertKey(int k)
{
if (heap_size == capacity) {
System.out.println("Overflow: Could not insertKey");
return;
}
// First insert the new key at the end
heap_size++;
int i = heap_size - 1;
harr[i] = k;
// Fix the min heap property if it is violated
while (i != 0 && harr[parent(i)] > harr[i]) {
swap(i, parent(i));
i = parent(i);
}
}
// A utility function to check
// if size of heap is 1 or not
boolean isSizeOne()
{
return (heap_size == 1);
}
// A utility function to swap two elements
void swap(int x, int y)
{
int temp = harr[x];
harr[x] = harr[y];
harr[y] = temp;
}
// The main function that returns the
// minimum cost to connect n ropes of
// lengths stored in len[0..n-1]
static int minCost(int len[], int n)
{
int cost = 0; // Initialize result
// Create a min heap of capacity equal
// to n and put all ropes in it
MinHeap minHeap = new MinHeap(len, n);
// Iterate while size of heap doesn't become 1
while (!minHeap.isSizeOne()) {
// Extract two minimum length ropes from min heap
int min = minHeap.extractMin();
int sec_min = minHeap.extractMin();
cost += (min + sec_min); // Update total cost
// Insert a new rope in min heap with length equal to sum
// of two extracted minimum lengths
minHeap.insertKey(min + sec_min);
}
// Finally return total minimum
// cost for connecting all ropes
return cost;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int len[] = { 4, 3, 2, 6 };
int size = len.length;
System.out.println("Total cost for connecting ropes is " + minCost(len, size));
}
};
// This code is contributed by shubham96301C#
// C# program to connect n ropes with minimum cost
using System;
// A class for Min Heap
class MinHeap {
int[] harr; // Array of elements in heap
int heap_size; // Current number of elements in min heap
int capacity; // maximum possible size of min heap
// Constructor: Builds a heap from
// a given array a[] of given size
public MinHeap(int[] a, int size)
{
heap_size = size;
capacity = size;
harr = a;
int i = (heap_size - 1) / 2;
while (i >= 0) {
MinHeapify(i);
i--;
}
}
// A recursive method to heapify a subtree
// with the root at given index
// This method assumes that the subtrees
// are already heapified
void MinHeapify(int i)
{
int l = left(i);
int r = right(i);
int smallest = i;
if (l < heap_size && harr[l] < harr[i])
smallest = l;
if (r < heap_size && harr[r] < harr[smallest])
smallest = r;
if (smallest != i) {
swap(i, smallest);
MinHeapify(smallest);
}
}
int parent(int i) { return (i - 1) / 2; }
// to get index of left child of node at index i
int left(int i) { return (2 * i + 1); }
// to get index of right child of node at index i
int right(int i) { return (2 * i + 2); }
// Method to remove minimum element (or root) from min heap
int extractMin()
{
if (heap_size <= 0)
return int.MaxValue;
if (heap_size == 1) {
heap_size--;
return harr[0];
}
// Store the minimum value, and remove it from heap
int root = harr[0];
harr[0] = harr[heap_size - 1];
heap_size--;
MinHeapify(0);
return root;
}
// Inserts a new key 'k'
void insertKey(int k)
{
if (heap_size == capacity) {
Console.WriteLine("Overflow: Could not insertKey");
return;
}
// First insert the new key at the end
heap_size++;
int i = heap_size - 1;
harr[i] = k;
// Fix the min heap property if it is violated
while (i != 0 && harr[parent(i)] > harr[i]) {
swap(i, parent(i));
i = parent(i);
}
}
// A utility function to check
// if size of heap is 1 or not
Boolean isSizeOne()
{
return (heap_size == 1);
}
// A utility function to swap two elements
void swap(int x, int y)
{
int temp = harr[x];
harr[x] = harr[y];
harr[y] = temp;
}
// The main function that returns the
// minimum cost to connect n ropes of
// lengths stored in len[0..n-1]
static int minCost(int[] len, int n)
{
int cost = 0; // Initialize result
// Create a min heap of capacity equal
// to n and put all ropes in it
MinHeap minHeap = new MinHeap(len, n);
// Iterate while size of heap doesn't become 1
while (!minHeap.isSizeOne()) {
// Extract two minimum length ropes from min heap
int min = minHeap.extractMin();
int sec_min = minHeap.extractMin();
cost += (min + sec_min); // Update total cost
// Insert a new rope in min heap with length equal to sum
// of two extracted minimum lengths
minHeap.insertKey(min + sec_min);
}
// Finally return total minimum
// cost for connecting all ropes
return cost;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int[] len = { 4, 3, 2, 6 };
int size = len.Length;
Console.WriteLine("Total cost for connecting ropes is " + minCost(len, size));
}
};
// This code is contributed by Arnab KunduC++
#include
using namespace std;
int minCost(int arr[], int n)
{
// Create a priority queue
// https:// www.geeksforgeeks.org/priority-queue-in-cpp-stl/
// By default 'less' is used which is for decreasing order
// and 'greater' is used for increasing order
priority_queue, greater > pq(arr, arr + n);
// Initialize result
int res = 0;
// While size of priority queue is more than 1
while (pq.size() > 1) {
// Extract shortest two ropes from pq
int first = pq.top();
pq.pop();
int second = pq.top();
pq.pop();
// Connect the ropes: update result and
// insert the new rope to pq
res += first + second;
pq.push(first + second);
}
return res;
}
// Driver program to test above function
int main()
{
int len[] = { 4, 3, 2, 6 };
int size = sizeof(len) / sizeof(len[0]);
cout << "Total cost for connecting ropes is " << minCost(len, size);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to connect n
// ropes with minimum cost
import java.util.*;
class ConnectRopes {
static int minCost(int arr[], int n)
{
// Create a priority queue
PriorityQueue pq = new PriorityQueue();
// Adding items to the pQueue
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
pq.add(arr[i]);
}
// Initialize result
int res = 0;
// While size of priority queue
// is more than 1
while (pq.size() > 1) {
// Extract shortest two ropes from pq
int first = pq.poll();
int second = pq.poll();
// Connect the ropes: update result
// and insert the new rope to pq
res += first + second;
pq.add(first + second);
}
return res;
}
// Driver program to test above function
public static void main(String args[])
{
int len[] = { 4, 3, 2, 6 };
int size = len.length;
System.out.println("Total cost for connecting"
+ " ropes is " + minCost(len, size));
}
}
// This code is contributed by yash_pec Python3
# Python3 program to connect n
# ropes with minimum cost
import heapq
def minCost(arr, n):
# Create a priority queue out of the
# given list
heapq.heapify(arr)
# Initializ result
res = 0
# While size of priority queue
# is more than 1
while(len(arr) > 1):
# Extract shortest two ropes from arr
first = heapq.heappop(arr)
second = heapq.heappop(arr)
#Connect the ropes: update result
# and insert the new rope to arr
res += first + second
heapq.heappush(arr, first + second)
return res
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
lengths = [ 4, 3, 2, 6 ]
size = len(lengths)
print("Total cost for connecting ropes is " +
str(minCost(lengths, size)))
# This code is contributed by shivampatel5C#
// C# program to connect n
// ropes with minimum cost
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class ConnectRopes
{
static int minCost(int []arr, int n)
{
// Create a priority queue
List pq = new List();
// Adding items to the pQueue
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
pq.Add(arr[i]);
}
// Initialize result
int res = 0;
// While size of priority queue
// is more than 1
while (pq.Count > 1)
{
pq.Sort();
// Extract shortest two ropes from pq
int first = pq[0];
int second = pq[1];
pq.RemoveRange(0, 2);
// Connect the ropes: update result
// and insert the new rope to pq
res += first + second;
pq.Add(first + second);
}
return res;
}
// Driver program to test above function
public static void Main(String []args)
{
int []len = { 4, 3, 2, 6 };
int size = len.Length;
Console.WriteLine("Total cost for connecting"
+ " ropes is " + minCost(len, size));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji Javascript
输出:
Total cost for connecting ropes is 29复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(nLogn),假设我们使用 O(nLogn) 排序算法。请注意,像插入和提取这样的堆操作需要 O(Logn) 时间。
- 辅助复杂度: O(n),在最小堆中存储值所需的空间
算法范式:贪心算法
在 C++ 中使用 STL 的简单实现
这使用 STL 中可用的 priority_queue。感谢 Pango89 提供以下代码。方法和算法保持不变。最小堆被优先队列取代。
C++
#include
using namespace std;
int minCost(int arr[], int n)
{
// Create a priority queue
// https:// www.geeksforgeeks.org/priority-queue-in-cpp-stl/
// By default 'less' is used which is for decreasing order
// and 'greater' is used for increasing order
priority_queue, greater > pq(arr, arr + n);
// Initialize result
int res = 0;
// While size of priority queue is more than 1
while (pq.size() > 1) {
// Extract shortest two ropes from pq
int first = pq.top();
pq.pop();
int second = pq.top();
pq.pop();
// Connect the ropes: update result and
// insert the new rope to pq
res += first + second;
pq.push(first + second);
}
return res;
}
// Driver program to test above function
int main()
{
int len[] = { 4, 3, 2, 6 };
int size = sizeof(len) / sizeof(len[0]);
cout << "Total cost for connecting ropes is " << minCost(len, size);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to connect n
// ropes with minimum cost
import java.util.*;
class ConnectRopes {
static int minCost(int arr[], int n)
{
// Create a priority queue
PriorityQueue pq = new PriorityQueue();
// Adding items to the pQueue
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
pq.add(arr[i]);
}
// Initialize result
int res = 0;
// While size of priority queue
// is more than 1
while (pq.size() > 1) {
// Extract shortest two ropes from pq
int first = pq.poll();
int second = pq.poll();
// Connect the ropes: update result
// and insert the new rope to pq
res += first + second;
pq.add(first + second);
}
return res;
}
// Driver program to test above function
public static void main(String args[])
{
int len[] = { 4, 3, 2, 6 };
int size = len.length;
System.out.println("Total cost for connecting"
+ " ropes is " + minCost(len, size));
}
}
// This code is contributed by yash_pec
蟒蛇3
# Python3 program to connect n
# ropes with minimum cost
import heapq
def minCost(arr, n):
# Create a priority queue out of the
# given list
heapq.heapify(arr)
# Initializ result
res = 0
# While size of priority queue
# is more than 1
while(len(arr) > 1):
# Extract shortest two ropes from arr
first = heapq.heappop(arr)
second = heapq.heappop(arr)
#Connect the ropes: update result
# and insert the new rope to arr
res += first + second
heapq.heappush(arr, first + second)
return res
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
lengths = [ 4, 3, 2, 6 ]
size = len(lengths)
print("Total cost for connecting ropes is " +
str(minCost(lengths, size)))
# This code is contributed by shivampatel5
C#
// C# program to connect n
// ropes with minimum cost
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class ConnectRopes
{
static int minCost(int []arr, int n)
{
// Create a priority queue
List pq = new List();
// Adding items to the pQueue
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
pq.Add(arr[i]);
}
// Initialize result
int res = 0;
// While size of priority queue
// is more than 1
while (pq.Count > 1)
{
pq.Sort();
// Extract shortest two ropes from pq
int first = pq[0];
int second = pq[1];
pq.RemoveRange(0, 2);
// Connect the ropes: update result
// and insert the new rope to pq
res += first + second;
pq.Add(first + second);
}
return res;
}
// Driver program to test above function
public static void Main(String []args)
{
int []len = { 4, 3, 2, 6 };
int size = len.Length;
Console.WriteLine("Total cost for connecting"
+ " ropes is " + minCost(len, size));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
输出:
Total cost for connecting ropes is 29复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(nLogn),假设我们使用 O(nLogn) 排序算法。
请注意,像插入和提取这样的堆操作需要 O(Logn) 时间。 - 辅助复杂度: O(n)。
在最小堆中存储值所需的空间
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。