📌 相关文章
- Python -SciPy(1)
- Python -SciPy
- 更新 scipy (1)
- SciPy-空间
- SciPy-空间(1)
- SciPy教程
- SciPy教程(1)
- SciPy-简介(1)
- SciPy-简介
- 讨论SciPy
- 讨论SciPy(1)
- 导入 scipy python (1)
- SciPy 线性代数 – SciPy Linalg(1)
- SciPy 线性代数 – SciPy Linalg
- SciPy-统计(1)
- SciPy-统计
- 更新 scipy - 任何代码示例
- 导入 scipy python 代码示例
- SciPy – 集成
- SciPy – 集成(1)
- SciPy-集成(1)
- SciPy-集成
- SciPy-优化
- SciPy-优化(1)
- 如何安装 scipy - Shell-Bash (1)
- SciPy – 常量
- SciPy-常量(1)
- SciPy – 常量(1)
- SciPy-常量
📜 SciPy-ODR
📅 最后修改于: 2020-11-05 04:37:10 🧑 作者: Mango
ODR代表“正交距离回归” ,它用于回归研究中。基本线性回归通常用于通过在图中绘制最佳拟合线来估计两个变量y和x之间的关系。
为此使用的数学方法称为最小二乘,其目的是最小化每个点的平方误差之和。这里的关键问题是如何计算每个点的误差(也称为残差)?
在标准线性回归中,目标是从X值预测Y值-因此,明智的做法是计算Y值中的误差(下图中的灰线所示)。但是,有时将X和Y的误差都考虑进去是更明智的(如下图的红色虚线所示)。
例如-当您知道X的测量值不确定时,或者不想将焦点放在一个变量的误差上。
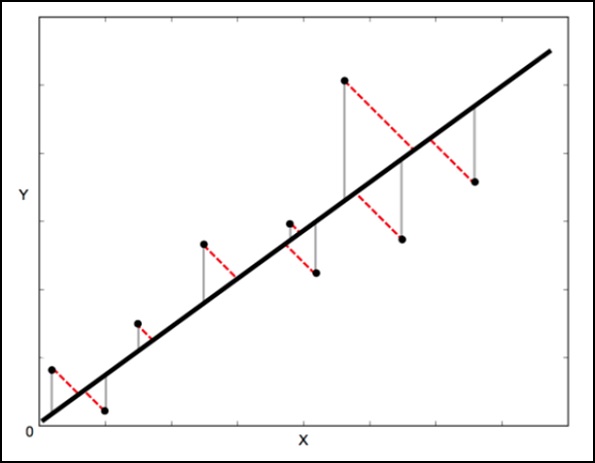
正交距离回归(ODR)是一种可以做到这一点的方法(在此上下文中,正交表示垂直–因此它计算的是垂直于直线的误差,而不仅仅是“垂直”)。
单变量回归的scipy.odr实现
下面的示例演示了单变量回归的scipy.odr实现。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.odr import *
import random
# Initiate some data, giving some randomness using random.random().
x = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
y = np.array([i**2 + random.random() for i in x])
# Define a function (quadratic in our case) to fit the data with.
def linear_func(p, x):
m, c = p
return m*x + c
# Create a model for fitting.
linear_model = Model(linear_func)
# Create a RealData object using our initiated data from above.
data = RealData(x, y)
# Set up ODR with the model and data.
odr = ODR(data, linear_model, beta0=[0., 1.])
# Run the regression.
out = odr.run()
# Use the in-built pprint method to give us results.
out.pprint()
上面的程序将生成以下输出。
Beta: [ 5.51846098 -4.25744878]
Beta Std Error: [ 0.7786442 2.33126407]
Beta Covariance: [
[ 1.93150969 -4.82877433]
[ -4.82877433 17.31417201
]]
Residual Variance: 0.313892697582
Inverse Condition #: 0.146618499389
Reason(s) for Halting:
Sum of squares convergence