使用 Tree Rerooting 技术从每个节点到所有其他节点的路径长度总和
对于无向树中的每个节点,使用 Tree Rerooting 技术找到从它到所有其他节点的路径长度总和。
Rerooting is a dynamic programming technique in trees. Using this a property dp[i] on tree is calculated, when the tree is rooted at i.
例子:
Input: Consider the tree shown in the image:
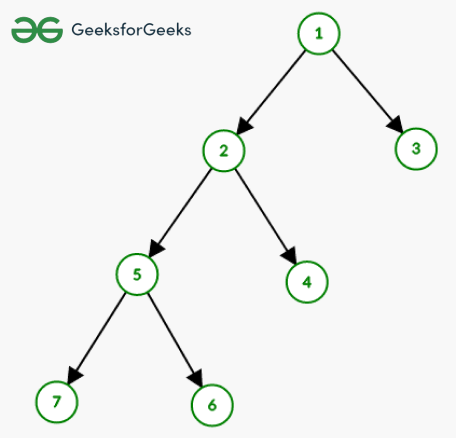
tree rooted at 1 (arrow represent paths from root to other nodes)
Output: 12 9 17 14 10 15 15
Explanation: for node i : i1 + i2 + i3 . . . in, where ij is length of path from i to j
For node 1 : 0 + 1 + 1 + 2 + 2 + 3 + 3 = 12
For node 2 : 1 + 0 + 2 + 1 + 1 + 2 + 2 = 9
For node 3 : 1 + 2 + 0 + 3 + 3 + 4 + 4 = 17
For node 4 : 2 + 1 + 3 + 0 + 2 + 3 + 3 = 14
For node 5 : 2 + 1 + 3 + 2 + 0 + 1 + 1 = 10
For node 6 : 3 + 2 + 4 + 3 + 1 + 0 + 2 = 15
For node 7 : 3 + 2 + 4 + 3 + 1 + 2 + 0 = 15
朴素的方法:这种方法基于对动态规划的以下观察。
考虑下图以了解动态规划中的转换:
Illustration:
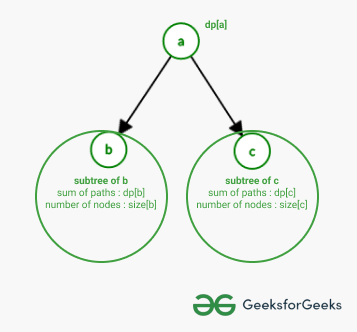
tree dp for sum of path lengths
Note: dp[node] in figure denotes the sum of paths from node to all its subtrees.
Now Consider child ‘b’ of node ‘a’,
- Size of subtree ‘b’, size[b] and the sum of lengths of paths for subtree ‘b’ is given as dp[b].
- Consider all the paths which start at ‘a’ and end at some node in subtree of ‘b’.
- Every path can be broken down as follows: path(a, x) = edge(a, b) + path(b, x)
- As lengths of all paths of form path(b, x) is already covered in dp[b], only the edge(a, b) needs to be added for all nodes ‘x’ in subtree of ‘b’.
- That means size[b] needs to be added to dp[b], hence the contribution of subtree ‘b’ to dp[a] is (dp[b] + size[b]).
过渡如下:
Transition :
for (child of node):
dp[node] += dp[child] + size[child]
按照下面提到的步骤来实施该方法:
- 对于每个节点执行以下操作:
- 将树根在该节点,并如上所述找到dp
- 由于树以'node'为根,所有其他节点都将位于其子树中。所以dp[node]将是'node'的必需答案。
C++
// C++ code to implement above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Dfs computes dp, answer for each node
// with respect to its subtree it also
// computes size of each subtree
void dfs(int node, int par,
vector >& g,
vector& size, vector& dp)
{
// Initialise given subtree with dp = 0
// [as there is no paths currently] and
// size 1, because tehre is only
// one node in subtree
size[node] = 1;
dp[node] = 0;
for (auto nebr : g[node]) {
// For every neighbour of node
// which is not its parent
// 1. compute size and dp for
// nebr by dfs
// 2. update size and dp for node,
// based on nebr
// See explanation to understand
// the dp transition
if (nebr != par) {
dfs(nebr, node, g, size, dp);
size[node] += size[nebr];
dp[node] += dp[nebr] +
size[nebr];
}
}
}
// Creates a edge between a and b,
// given graph g
void edge(int a, int b,
vector >& g)
{
// Convert into 0-based indexing
a--;
b--;
// Push b to adjacency list of a
// and vice versa because given
// tree is undirected
g[a].push_back(b);
g[b].push_back(a);
}
// Function to get the sum of paths
vector pathSum(vector > &g,
int N)
{
vector dp(N), ans(N), size(N);
// For root 'r'
// 1. compute dp for tree rooted at 'r'
// 2. as all nodes belong to some
// subtree of root, answer will be
// equal to dp
for (int r = 0; r < N; ++r) {
dfs(r, -1, g, size, dp);
ans[r] = dp[r];
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int N = 7;
vector > g(N);
edge(1, 2, g);
edge(1, 3, g);
edge(2, 4, g);
edge(2, 5, g);
edge(5, 6, g);
edge(5, 7, g);
vector res = pathSum(g, N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
cout << res[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java code to implement above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int N = 7;
static int dp[] = new int[N];
static int ans[] = new int[N];
static int size[] = new int[N];
// Dfs computes dp, answer for each node
// with respect to its subtree it also
// computes size of each subtree
static void dfs(int node, int par, Vector []g)
{
// Initialise given subtree with dp = 0
// [as there is no paths currently] and
// size 1, because tehre is only
// one node in subtree
size[node] = 1;
dp[node] = 0;
for (int nebr : g[node]) {
// For every neighbour of node
// which is not its parent
// 1. compute size and dp for
// nebr by dfs
// 2. update size and dp for node,
// based on nebr
// See explanation to understand
// the dp transition
if (nebr != par) {
dfs(nebr, node, g);
size[node] += size[nebr];
dp[node] += dp[nebr] +
size[nebr];
}
}
}
// Creates a edge between a and b,
// given graph g
static void edge(int a, int b,
Vector [] g)
{
// Convert into 0-based indexing
a--;
b--;
// Push b to adjacency list of a
// and vice versa because given
// tree is undirected
g[a].add(b);
g[b].add(a);
}
// Function to get the sum of paths
static int[] pathSum(Vector []g)
{
// For root 'r'
// 1. compute dp for tree rooted at 'r'
// 2. as all nodes belong to some
// subtree of root, answer will be
// equal to dp
for (int r = 0; r < N; ++r) {
dfs(r, -1, g);
ans[r] = dp[r];
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Vector []g = new Vector[N];
for (int i = 0; i < g.length; i++)
g[i] = new Vector();
edge(1, 2, g);
edge(1, 3, g);
edge(2, 4, g);
edge(2, 5, g);
edge(5, 6, g);
edge(5, 7, g);
int[] res = pathSum(g);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
System.out.print(res[i]+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar C#
// C# code to implement above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static int N = 7;
static int[] dp = new int[N];
static int[] ans = new int[N];
static int[] size = new int[N];
// Dfs computes dp, answer for each node
// with respect to its subtree it also
// computes size of each subtree
static void dfs(int node, int par, List[] g)
{
// Initialise given subtree with dp = 0
// [as there is no paths currently] and
// size 1, because tehre is only
// one node in subtree
size[node] = 1;
dp[node] = 0;
foreach (int nebr in g[node])
{
// For every neighbour of node
// which is not its parent
// 1. compute size and dp for
// nebr by dfs
// 2. update size and dp for node,
// based on nebr
// See explanation to understand
// the dp transition
if (nebr != par)
{
dfs(nebr, node, g);
size[node] += size[nebr];
dp[node] += dp[nebr] +
size[nebr];
}
}
}
// Creates a edge between a and b,
// given graph g
static void edge(int a, int b,
List[] g)
{
// Convert into 0-based indexing
a--;
b--;
// Push b to adjacency list of a
// and vice versa because given
// tree is undirected
g[a].Add(b);
g[b].Add(a);
}
// Function to get the sum of paths
static int[] pathSum(List[] g)
{
// For root 'r'
// 1. compute dp for tree rooted at 'r'
// 2. as all nodes belong to some
// subtree of root, answer will be
// equal to dp
for (int r = 0; r < N; ++r)
{
dfs(r, -1, g);
ans[r] = dp[r];
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
List[] g = new List[N];
for (int i = 0; i < g.Length; i++)
g[i] = new List();
edge(1, 2, g);
edge(1, 3, g);
edge(2, 4, g);
edge(2, 5, g);
edge(5, 6, g);
edge(5, 7, g);
int[] res = pathSum(g);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
Console.Write(res[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// This code is contributed by Saurabh Jaiswal C++
// C++ code to implement above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// The function dfs0 computes dp,
// answer for each node with respect to
// its subtree it also computes
// size of each subtree
void dfs0(int node, int par,
vector >& g,
vector& dp, vector& size)
{
// Initialise given subtree with dp = 0
// as there is no paths currently and
// size 1, because there is only
// one node in subtree
dp[node] = 0;
size[node] = 1;
for (auto nebr : g[node]) {
// For every neighbour of node
// which is not its parent
// 1. compute size and dp for
// nebr by dfs
// 2. update size and dp for node,
// based on nebr
// See explanation to understand
// the dp transition
if (par != nebr) {
dfs0(nebr, node, g, dp, size);
size[node] += size[nebr];
dp[node] += size[nebr] +
dp[nebr];
}
}
}
// Rerooting the tree from 'from' to 'to'
void reroot(int from, int to,
vector& dp,
vector& size)
{
// 'to' is no longer a child of 'from'
dp[from] -= size[to] + dp[to];
size[from] -= size[to];
// 'from' is now a child of 'to'
size[to] += size[from];
dp[to] += size[from] + dp[from];
}
void dfs1(int node, int par,
vector >& g,
vector& dp, vector& ans,
vector& size)
{
// Current dfs considers 'node' as root
// so currently dp[node]
// will be the answer
ans[node] = dp[node];
// For all neighbours which are
// not parent of node
for (auto nebr : g[node]) {
if (par != nebr) {
// Reroot the tree to 'nebr'
reroot(node, nebr, dp, size);
// Compute ans for 'nebr'
// as a root of tree with dfs
dfs1(nebr, node, g, dp, ans,
size);
// reroot the tree back
// to 'node'
reroot(nebr, node, dp, size);
}
}
}
// Creates a edge between a and b,
// given graph g
void edge(int a, int b,
vector >& g)
{
// Convert into 0-based indexing
a--;
b--;
// push b to adjacency list
// of a and vice versa
// because given tree is undirected
g[a].push_back(b);
g[b].push_back(a);
}
// Function to calculate sum of paths
vector pathSum(vector > &g,
int N)
{
vector dp(N), ans(N), size(N);
// Compute answer for each subtree
// with tree rooted at 0
dfs0(0, -1, g, dp, size);
// Compute answer for each node
// as root of tree, rerooting
dfs1(0, -1, g, dp, ans, size);
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int N = 7;
vector > g(N);
edge(1, 2, g);
edge(1, 3, g);
edge(2, 4, g);
edge(2, 5, g);
edge(5, 6, g);
edge(5, 7, g);
vector res = pathSum(g, N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
cout << res[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java code to implement above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int N = 7;
static int dp[] = new int[N];
static int ans[] = new int[N];
static int size[] = new int[N];
// The function dfs0 computes dp,
// answer for each node with respect to
// its subtree it also computes
// size of each subtree
static void dfs0(int node, int par, Vector []g)
{
// Initialise given subtree with dp = 0
// as there is no paths currently and
// size 1, because there is only
// one node in subtree
dp[node] = 0;
size[node] = 1;
for (int nebr : g[node]) {
// For every neighbour of node
// which is not its parent
// 1. compute size and dp for
// nebr by dfs
// 2. update size and dp for node,
// based on nebr
// See explanation to understand
// the dp transition
if (par != nebr) {
dfs0(nebr, node, g);
size[node] += size[nebr];
dp[node] += size[nebr] +
dp[nebr];
}
}
}
// Rerooting the tree from 'from' to 'to'
static void reroot(int from, int to)
{
// 'to' is no longer a child of 'from'
dp[from] -= size[to] + dp[to];
size[from] -= size[to];
// 'from' is now a child of 'to'
size[to] += size[from];
dp[to] += size[from] + dp[from];
}
static void dfs1(int node, int par,Vector []g)
{
// Current dfs considers 'node' as root
// so currently dp[node]
// will be the answer
ans[node] = dp[node];
// For all neighbours which are
// not parent of node
for (int nebr : g[node]) {
if (par != nebr) {
// Reroot the tree to 'nebr'
reroot(node, nebr);
// Compute ans for 'nebr'
// as a root of tree with dfs
dfs1(nebr, node, g);
// reroot the tree back
// to 'node'
reroot(nebr, node);
}
}
}
// Creates a edge between a and b,
// given graph g
static void edge(int a, int b,
Vector [] g)
{
// Convert into 0-based indexing
a--;
b--;
// push b to adjacency list
// of a and vice versa
// because given tree is undirected
g[a].add(b);
g[b].add(a);
}
// Function to calculate sum of paths
static int[] pathSum(Vector []g)
{
// Compute answer for each subtree
// with tree rooted at 0
dfs0(0, -1, g);
// Compute answer for each node
// as root of tree, rerooting
dfs1(0, -1, g);
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 7;
Vector []g = new Vector[N];
for (int i = 0; i < g.length; i++)
g[i] = new Vector();
edge(1, 2, g);
edge(1, 3, g);
edge(2, 4, g);
edge(2, 5, g);
edge(5, 6, g);
edge(5, 7, g);
int[] res = pathSum(g);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
System.out.print(res[i]+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
// This code contributed by shikhasingrajput C#
// C# code to implement above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG{
static int N = 7;
static int []dp = new int[N];
static int []ans = new int[N];
static int []size = new int[N];
// The function dfs0 computes dp,
// answer for each node with respect to
// its subtree it also computes
// size of each subtree
static void dfs0(int node, int par, List []g)
{
// Initialise given subtree with dp = 0
// as there is no paths currently and
// size 1, because there is only
// one node in subtree
dp[node] = 0;
size[node] = 1;
foreach (int nebr in g[node]) {
// For every neighbour of node
// which is not its parent
// 1. compute size and dp for
// nebr by dfs
// 2. update size and dp for node,
// based on nebr
// See explanation to understand
// the dp transition
if (par != nebr) {
dfs0(nebr, node, g);
size[node] += size[nebr];
dp[node] += size[nebr] +
dp[nebr];
}
}
}
// Rerooting the tree from 'from' to 'to'
static void reroot(int from, int to)
{
// 'to' is no longer a child of 'from'
dp[from] -= size[to] + dp[to];
size[from] -= size[to];
// 'from' is now a child of 'to'
size[to] += size[from];
dp[to] += size[from] + dp[from];
}
static void dfs1(int node, int par,List []g)
{
// Current dfs considers 'node' as root
// so currently dp[node]
// will be the answer
ans[node] = dp[node];
// For all neighbours which are
// not parent of node
foreach (int nebr in g[node]) {
if (par != nebr) {
// Reroot the tree to 'nebr'
reroot(node, nebr);
// Compute ans for 'nebr'
// as a root of tree with dfs
dfs1(nebr, node, g);
// reroot the tree back
// to 'node'
reroot(nebr, node);
}
}
}
// Creates a edge between a and b,
// given graph g
static void edge(int a, int b,
List [] g)
{
// Convert into 0-based indexing
a--;
b--;
// push b to adjacency list
// of a and vice versa
// because given tree is undirected
g[a].Add(b);
g[b].Add(a);
}
// Function to calculate sum of paths
static int[] pathSum(List []g)
{
// Compute answer for each subtree
// with tree rooted at 0
dfs0(0, -1, g);
// Compute answer for each node
// as root of tree, rerooting
dfs1(0, -1, g);
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int N = 7;
List []g = new List[N];
for (int i = 0; i < g.Length; i++)
g[i] = new List();
edge(1, 2, g);
edge(1, 3, g);
edge(2, 4, g);
edge(2, 5, g);
edge(5, 6, g);
edge(5, 7, g);
int[] res = pathSum(g);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
Console.Write(res[i]+ " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar 12 9 17 14 10 15 15 时间复杂度: O(N 2 ),其中 N 是节点数。
辅助空间: O(N)
Rerooting Approach:解决方案可以通过计算一个根的答案并每次rerooting树以计算其他节点来进一步优化解决方案。
看下图来理解rerooting的概念:
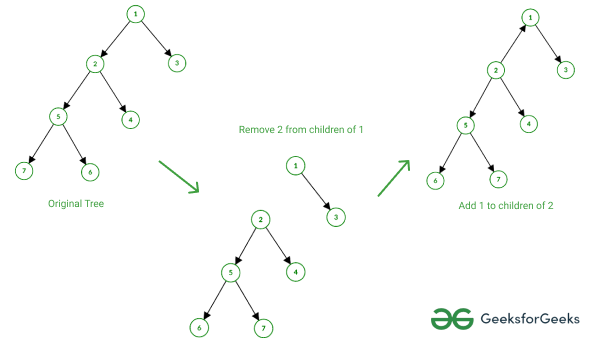
将树从 1 重新生根到 2
注意:在上图中,边是无向的,箭头只表示从根到其他节点的路径
- 在给定的图中,使用以下方法从“1”重新植根到“2”
- 从 1 的孩子中删除 2
- 2 的孩子加 1
由于没有对每个节点进行重新计算,并且重新生根只需要 O(1),因此整体时间复杂度也降低了。
C++
// C++ code to implement above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// The function dfs0 computes dp,
// answer for each node with respect to
// its subtree it also computes
// size of each subtree
void dfs0(int node, int par,
vector >& g,
vector& dp, vector& size)
{
// Initialise given subtree with dp = 0
// as there is no paths currently and
// size 1, because there is only
// one node in subtree
dp[node] = 0;
size[node] = 1;
for (auto nebr : g[node]) {
// For every neighbour of node
// which is not its parent
// 1. compute size and dp for
// nebr by dfs
// 2. update size and dp for node,
// based on nebr
// See explanation to understand
// the dp transition
if (par != nebr) {
dfs0(nebr, node, g, dp, size);
size[node] += size[nebr];
dp[node] += size[nebr] +
dp[nebr];
}
}
}
// Rerooting the tree from 'from' to 'to'
void reroot(int from, int to,
vector& dp,
vector& size)
{
// 'to' is no longer a child of 'from'
dp[from] -= size[to] + dp[to];
size[from] -= size[to];
// 'from' is now a child of 'to'
size[to] += size[from];
dp[to] += size[from] + dp[from];
}
void dfs1(int node, int par,
vector >& g,
vector& dp, vector& ans,
vector& size)
{
// Current dfs considers 'node' as root
// so currently dp[node]
// will be the answer
ans[node] = dp[node];
// For all neighbours which are
// not parent of node
for (auto nebr : g[node]) {
if (par != nebr) {
// Reroot the tree to 'nebr'
reroot(node, nebr, dp, size);
// Compute ans for 'nebr'
// as a root of tree with dfs
dfs1(nebr, node, g, dp, ans,
size);
// reroot the tree back
// to 'node'
reroot(nebr, node, dp, size);
}
}
}
// Creates a edge between a and b,
// given graph g
void edge(int a, int b,
vector >& g)
{
// Convert into 0-based indexing
a--;
b--;
// push b to adjacency list
// of a and vice versa
// because given tree is undirected
g[a].push_back(b);
g[b].push_back(a);
}
// Function to calculate sum of paths
vector pathSum(vector > &g,
int N)
{
vector dp(N), ans(N), size(N);
// Compute answer for each subtree
// with tree rooted at 0
dfs0(0, -1, g, dp, size);
// Compute answer for each node
// as root of tree, rerooting
dfs1(0, -1, g, dp, ans, size);
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int N = 7;
vector > g(N);
edge(1, 2, g);
edge(1, 3, g);
edge(2, 4, g);
edge(2, 5, g);
edge(5, 6, g);
edge(5, 7, g);
vector res = pathSum(g, N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
cout << res[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java code to implement above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int N = 7;
static int dp[] = new int[N];
static int ans[] = new int[N];
static int size[] = new int[N];
// The function dfs0 computes dp,
// answer for each node with respect to
// its subtree it also computes
// size of each subtree
static void dfs0(int node, int par, Vector []g)
{
// Initialise given subtree with dp = 0
// as there is no paths currently and
// size 1, because there is only
// one node in subtree
dp[node] = 0;
size[node] = 1;
for (int nebr : g[node]) {
// For every neighbour of node
// which is not its parent
// 1. compute size and dp for
// nebr by dfs
// 2. update size and dp for node,
// based on nebr
// See explanation to understand
// the dp transition
if (par != nebr) {
dfs0(nebr, node, g);
size[node] += size[nebr];
dp[node] += size[nebr] +
dp[nebr];
}
}
}
// Rerooting the tree from 'from' to 'to'
static void reroot(int from, int to)
{
// 'to' is no longer a child of 'from'
dp[from] -= size[to] + dp[to];
size[from] -= size[to];
// 'from' is now a child of 'to'
size[to] += size[from];
dp[to] += size[from] + dp[from];
}
static void dfs1(int node, int par,Vector []g)
{
// Current dfs considers 'node' as root
// so currently dp[node]
// will be the answer
ans[node] = dp[node];
// For all neighbours which are
// not parent of node
for (int nebr : g[node]) {
if (par != nebr) {
// Reroot the tree to 'nebr'
reroot(node, nebr);
// Compute ans for 'nebr'
// as a root of tree with dfs
dfs1(nebr, node, g);
// reroot the tree back
// to 'node'
reroot(nebr, node);
}
}
}
// Creates a edge between a and b,
// given graph g
static void edge(int a, int b,
Vector [] g)
{
// Convert into 0-based indexing
a--;
b--;
// push b to adjacency list
// of a and vice versa
// because given tree is undirected
g[a].add(b);
g[b].add(a);
}
// Function to calculate sum of paths
static int[] pathSum(Vector []g)
{
// Compute answer for each subtree
// with tree rooted at 0
dfs0(0, -1, g);
// Compute answer for each node
// as root of tree, rerooting
dfs1(0, -1, g);
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 7;
Vector []g = new Vector[N];
for (int i = 0; i < g.length; i++)
g[i] = new Vector();
edge(1, 2, g);
edge(1, 3, g);
edge(2, 4, g);
edge(2, 5, g);
edge(5, 6, g);
edge(5, 7, g);
int[] res = pathSum(g);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
System.out.print(res[i]+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
// This code contributed by shikhasingrajput
C#
// C# code to implement above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG{
static int N = 7;
static int []dp = new int[N];
static int []ans = new int[N];
static int []size = new int[N];
// The function dfs0 computes dp,
// answer for each node with respect to
// its subtree it also computes
// size of each subtree
static void dfs0(int node, int par, List []g)
{
// Initialise given subtree with dp = 0
// as there is no paths currently and
// size 1, because there is only
// one node in subtree
dp[node] = 0;
size[node] = 1;
foreach (int nebr in g[node]) {
// For every neighbour of node
// which is not its parent
// 1. compute size and dp for
// nebr by dfs
// 2. update size and dp for node,
// based on nebr
// See explanation to understand
// the dp transition
if (par != nebr) {
dfs0(nebr, node, g);
size[node] += size[nebr];
dp[node] += size[nebr] +
dp[nebr];
}
}
}
// Rerooting the tree from 'from' to 'to'
static void reroot(int from, int to)
{
// 'to' is no longer a child of 'from'
dp[from] -= size[to] + dp[to];
size[from] -= size[to];
// 'from' is now a child of 'to'
size[to] += size[from];
dp[to] += size[from] + dp[from];
}
static void dfs1(int node, int par,List []g)
{
// Current dfs considers 'node' as root
// so currently dp[node]
// will be the answer
ans[node] = dp[node];
// For all neighbours which are
// not parent of node
foreach (int nebr in g[node]) {
if (par != nebr) {
// Reroot the tree to 'nebr'
reroot(node, nebr);
// Compute ans for 'nebr'
// as a root of tree with dfs
dfs1(nebr, node, g);
// reroot the tree back
// to 'node'
reroot(nebr, node);
}
}
}
// Creates a edge between a and b,
// given graph g
static void edge(int a, int b,
List [] g)
{
// Convert into 0-based indexing
a--;
b--;
// push b to adjacency list
// of a and vice versa
// because given tree is undirected
g[a].Add(b);
g[b].Add(a);
}
// Function to calculate sum of paths
static int[] pathSum(List []g)
{
// Compute answer for each subtree
// with tree rooted at 0
dfs0(0, -1, g);
// Compute answer for each node
// as root of tree, rerooting
dfs1(0, -1, g);
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int N = 7;
List []g = new List[N];
for (int i = 0; i < g.Length; i++)
g[i] = new List();
edge(1, 2, g);
edge(1, 3, g);
edge(2, 4, g);
edge(2, 5, g);
edge(5, 6, g);
edge(5, 7, g);
int[] res = pathSum(g);
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
Console.Write(res[i]+ " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
12 9 17 14 10 15 15 时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)