贪婪是一种算法范式,它一步一步地建立解决方案,总是选择下一个提供最明显和最直接利益的解决方案。贪婪算法用于优化问题。如果问题具有以下属性,则可以使用Greedy解决最优化问题:在每一步中,我们都可以做出目前看上去最好的选择,并且可以得出完整问题的最优解决方案。
如果贪婪算法可以解决问题,那么它通常会成为解决该问题的最佳方法,因为贪婪算法通常比动态编程等其他技术更有效率。但是贪婪算法不能总是被应用。例如,分数贪婪背包问题(请参阅此)可以使用Greedy来解决,但是0-1背包无法使用Greedy来解决。
以下是贪婪算法的一些标准算法。
1) Kruskal的最小生成树(MST) :在Kruskal的算法中,我们通过一一挑选边来创建MST。贪婪的选择是选择迄今为止不会造成MST周期变化的最小重量边。
2) Prim的最小生成树:同样在Prim的算法中,我们通过一一挑选边来创建MST。我们维护两组:一组已经包含在MST中的顶点和一组尚未包含的顶点。贪婪的选择是选择连接两组的最小重量边。
3) Dijkstra的最短路径: Dijkstra的算法与Prim的算法非常相似。一条最短的路径树逐渐建立起来。我们维护两组:一组已经包含在树中的顶点和一组尚未包含的顶点。贪婪的选择是选择连接两个集合的边,并且该边在从源到包含尚未包含顶点的集合的最小权重路径上。
4) Huffman编码: Huffman编码是一种无损压缩技术。它将可变长度的位代码分配给不同的字符。贪婪的选择是将最小位长度的代码分配给最频繁的字符。
有时也会使用贪婪算法来获得Hard优化问题的近似值。例如,旅行推销员问题是NP-Hard问题。此问题的贪婪选择是在每个步骤中,从当前城市中选择最近的未访问城市。这种解决方案并不总是能产生最佳的最佳解决方案,但可以用来获得近似最佳的解决方案。
让我们将活动选择问题视为贪婪算法的第一个示例。以下是问题陈述。
您将获得n个活动的开始和结束时间。假设一个人一次只能从事一项活动,请选择一个人可以执行的最大活动数。
例子:
Example 1 : Consider the following 3 activities sorted by
by finish time.
start[] = {10, 12, 20};
finish[] = {20, 25, 30};
A person can perform at most two activities. The
maximum set of activities that can be executed
is {0, 2} [ These are indexes in start[] and
finish[] ]
Example 2 : Consider the following 6 activities
sorted by by finish time.
start[] = {1, 3, 0, 5, 8, 5};
finish[] = {2, 4, 6, 7, 9, 9};
A person can perform at most four activities. The
maximum set of activities that can be executed
is {0, 1, 3, 4} [ These are indexes in start[] and
finish[] ]贪婪的选择是始终选择下一个活动的结束时间在其余活动中最少的下一个活动,并且开始时间大于或等于先前选择的活动的结束时间。我们可以根据活动的结束时间对其进行排序,以便我们始终将下一个活动视为最短结束时间活动。
1)根据活动的完成时间对活动进行排序
2)从排序的数组中选择第一个活动并打印。
3)对已排序数组中的剩余活动执行以下操作。
……. a)如果此活动的开始时间大于或等于先前选择的活动的结束时间,则选择此活动并打印。
在下面的C实现中,假定已经根据活动的完成时间对活动进行了排序。
C++
// C++ program for activity selection problem.
// The following implementation assumes that the activities
// are already sorted according to their finish time
#include
using namespace std;
// Prints a maximum set of activities that can be done by a single
// person, one at a time.
// n --> Total number of activities
// s[] --> An array that contains start time of all activities
// f[] --> An array that contains finish time of all activities
void printMaxActivities(int s[], int f[], int n)
{
int i, j;
cout <<"Following activities are selected "<< endl;
// The first activity always gets selected
i = 0;
cout <<" "<< i;
// Consider rest of the activities
for (j = 1; j < n; j++)
{
// If this activity has start time greater than or
// equal to the finish time of previously selected
// activity, then select it
if (s[j] >= f[i])
{
cout <<" " << j;
i = j;
}
}
}
// driver program to test above function
int main()
{
int s[] = {1, 3, 0, 5, 8, 5};
int f[] = {2, 4, 6, 7, 9, 9};
int n = sizeof(s)/sizeof(s[0]);
printMaxActivities(s, f, n);
return 0;
}
//this code contributed by shivanisinghss2110 C
// C program for activity selection problem.
// The following implementation assumes that the activities
// are already sorted according to their finish time
#include
// Prints a maximum set of activities that can be done by a single
// person, one at a time.
// n --> Total number of activities
// s[] --> An array that contains start time of all activities
// f[] --> An array that contains finish time of all activities
void printMaxActivities(int s[], int f[], int n)
{
int i, j;
printf ("Following activities are selected n");
// The first activity always gets selected
i = 0;
printf("%d ", i);
// Consider rest of the activities
for (j = 1; j < n; j++)
{
// If this activity has start time greater than or
// equal to the finish time of previously selected
// activity, then select it
if (s[j] >= f[i])
{
printf ("%d ", j);
i = j;
}
}
}
// driver program to test above function
int main()
{
int s[] = {1, 3, 0, 5, 8, 5};
int f[] = {2, 4, 6, 7, 9, 9};
int n = sizeof(s)/sizeof(s[0]);
printMaxActivities(s, f, n);
return 0;
} Java
// The following implementation assumes that the activities
// are already sorted according to their finish time
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class ActivitySelection
{
// Prints a maximum set of activities that can be done by a single
// person, one at a time.
// n --> Total number of activities
// s[] --> An array that contains start time of all activities
// f[] --> An array that contains finish time of all activities
public static void printMaxActivities(int s[], int f[], int n)
{
int i, j;
System.out.print("Following activities are selected : n");
// The first activity always gets selected
i = 0;
System.out.print(i+" ");
// Consider rest of the activities
for (j = 1; j < n; j++)
{
// If this activity has start time greater than or
// equal to the finish time of previously selected
// activity, then select it
if (s[j] >= f[i])
{
System.out.print(j+" ");
i = j;
}
}
}
// driver program to test above function
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int s[] = {1, 3, 0, 5, 8, 5};
int f[] = {2, 4, 6, 7, 9, 9};
int n = s.length;
printMaxActivities(s, f, n);
}
}C#
// The following implementation assumes
// that the activities are already sorted
// according to their finish time
using System;
class GFG
{
// Prints a maximum set of activities
// that can be done by a single
// person, one at a time.
// n --> Total number of activities
// s[] --> An array that contains start
// time of all activities
// f[] --> An array that contains finish
// time of all activities
public static void printMaxActivities(int[] s,
int[] f, int n)
{
int i, j;
Console.Write("Following activities are selected : ");
// The first activity always gets selected
i = 0;
Console.Write(i + " ");
// Consider rest of the activities
for (j = 1; j < n; j++)
{
// If this activity has start time greater than or
// equal to the finish time of previously selected
// activity, then select it
if (s[j] >= f[i])
{
Console.Write(j + " ");
i = j;
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int[] s = {1, 3, 0, 5, 8, 5};
int[] f = {2, 4, 6, 7, 9, 9};
int n = s.Length;
printMaxActivities(s, f, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed
// by ChitraNayalPython
"""The following implementation assumes that the activities
are already sorted according to their finish time"""
"""Prints a maximum set of activities that can be done by a
single person, one at a time"""
# n --> Total number of activities
# s[]--> An array that contains start time of all activities
# f[] --> An array that contains finish time of all activities
def printMaxActivities(s , f ):
n = len(f)
print "The following activities are selected"
# The first activity is always selected
i = 0
print i,
# Consider rest of the activities
for j in xrange(n):
# If this activity has start time greater than
# or equal to the finish time of previously
# selected activity, then select it
if s[j] >= f[i]:
print j,
i = j
# Driver program to test above function
s = [1 , 3 , 0 , 5 , 8 , 5]
f = [2 , 4 , 6 , 7 , 9 , 9]
printMaxActivities(s , f)
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar SinghPHP
Total number of activities
// s[] --> An array that contains start
// time of all activities
// f[] --> An array that contains finish
// time of all activities
function printMaxActivities($s, $f, $n)
{
echo "Following activities are selected " . "\n";
// The first activity always gets selected
$i = 0;
echo $i . " ";
// Consider rest of the activities
for ($j = 1; $j < $n; $j++)
{
// If this activity has start time greater
// than or equal to the finish time of
// previously selected activity, then select it
if ($s[$j] >= $f[$i])
{
echo $j . " ";
$i = $j;
}
}
}
// Driver Code
$s = array(1, 3, 0, 5, 8, 5);
$f = array(2, 4, 6, 7, 9, 9);
$n = sizeof($s);
printMaxActivities($s, $f, $n);
// This code is contributed
// by Akanksha Rai
?>Javascript
C++
// C++ program for activity selection problem
// when input activities may not be sorted.
#include
using namespace std;
// A job has a start time, finish time and profit.
struct Activitiy
{
int start, finish;
};
// A utility function that is used for sorting
// activities according to finish time
bool activityCompare(Activitiy s1, Activitiy s2)
{
return (s1.finish < s2.finish);
}
// Returns count of the maximum set of activities that can
// be done by a single person, one at a time.
void printMaxActivities(Activitiy arr[], int n)
{
// Sort jobs according to finish time
sort(arr, arr+n, activityCompare);
cout << "Following activities are selected n";
// The first activity always gets selected
int i = 0;
cout << "(" << arr[i].start << ", " << arr[i].finish << "), ";
// Consider rest of the activities
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++)
{
// If this activity has start time greater than or
// equal to the finish time of previously selected
// activity, then select it
if (arr[j].start >= arr[i].finish)
{
cout << "(" << arr[j].start << ", "
<< arr[j].finish << "), ";
i = j;
}
}
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
Activitiy arr[] = {{5, 9}, {1, 2}, {3, 4}, {0, 6},
{5, 7}, {8, 9}};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
printMaxActivities(arr, n);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for activity selection problem
// when input activities may not be sorted.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// A job has a start time, finish time and profit.
class Activity
{
int start, finish;
// Constructor
public Activity(int start, int finish)
{
this.start = start;
this.finish = finish;
}
}
// class to define user defined comparator
class Compare
{
// A utility function that is used for sorting
// activities according to finish time
static void compare(Activity arr[], int n)
{
Arrays.sort(arr, new Comparator()
{
@Override
public int compare(Activity s1, Activity s2)
{
return s1.finish - s2.finish;
}
});
}
}
// Driver class
class GFG {
// Returns count of the maximum set of activities that
// can
// be done by a single person, one at a time.
static void printMaxActivities(Activity arr[], int n)
{
// Sort jobs according to finish time
Compare obj = new Compare();
obj.compare(arr, n);
System.out.println(
"Following activities are selected :");
// The first activity always gets selected
int i = 0;
System.out.print("(" + arr[i].start + ", "
+ arr[i].finish + "), ");
// Consider rest of the activities
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++)
{
// If this activity has start time greater than
// or equal to the finish time of previously
// selected activity, then select it
if (arr[j].start >= arr[i].finish)
{
System.out.print("(" + arr[j].start + ", "
+ arr[j].finish + "), ");
i = j;
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 6;
Activity arr[] = new Activity[n];
arr[0] = new Activity(5, 9);
arr[1] = new Activity(1, 2);
arr[2] = new Activity(3, 4);
arr[3] = new Activity(0, 6);
arr[4] = new Activity(5, 7);
arr[5] = new Activity(8, 9);
printMaxActivities(arr, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Dharanendra L V. Python3
''' Python program for activity selection problem
when input activities may not be sorted.'''
def MaxActivities(arr, n):
selected = []
# Sort jobs according to finish time
Activity.sort(key = lambda x : x[1])
# The first activity always gets selected
i = 0
selected.append(arr[i])
for j in range(1, n):
'''If this activity has start time greater than or
equal to the finish time of previously selected
activity, then select it'''
if arr[j][0] >= arr[i][1]:
selected.append(arr[j])
i = j
return selected
# Driver code
Activity = [[5, 9], [1, 2], [3, 4], [0, 6],[5, 7], [8, 9]]
n = len(Activity)
selected = MaxActivities(Activity, n)
print("Following activities are selected :")
print(selected)
# This cde is contributed by kshitijjainmCPP
// C++ program for activity selection problem
// when input activities may not be sorted.
#include
using namespace std;
void SelectActivities(vectors,vectorf){
// Vector to store results.
vector>ans;
// Minimum Priority Queue to sort activities in ascending order of finishing time (f[i]).
priority_queue,vector>,greater>>p;
for(int i=0;i= end){
start = itr.second;
end = itr.first;
ans.push_back(make_pair(start,end));
}
}
cout << "Following Activities should be selected. " << endl << endl;
for(auto itr=ans.begin();itr!=ans.end();itr++){
cout << "Activity started at: " << (*itr).first << " and ends at " << (*itr).second << endl;
}
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
vectors = {1, 3, 0, 5, 8, 5};
vectorf = {2, 4, 6, 7, 9, 9};
SelectActivities(s,f);
return 0;
} Java
// java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Pair class
static class Pair {
int first;
int second;
Pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
static void SelectActivities(int s[], int f[])
{
// Vector to store results.
ArrayList ans = new ArrayList<>();
// Minimum Priority Queue to sort activities in
// ascending order of finishing time (f[i]).
PriorityQueue p = new PriorityQueue<>(
(p1, p2) -> p1.first - p2.first);
for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
// Pushing elements in priority queue where the
// key is f[i]
p.add(new Pair(f[i], s[i]));
}
Pair it = p.poll();
int start = it.second;
int end = it.first;
ans.add(new Pair(start, end));
while (!p.isEmpty()) {
Pair itr = p.poll();
if (itr.second >= end) {
start = itr.second;
end = itr.first;
ans.add(new Pair(start, end));
}
}
System.out.println(
"Following Activities should be selected. \n");
for (Pair itr : ans) {
System.out.println(
"Activity started at: " + itr.first
+ " and ends at " + itr.second);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int s[] = { 1, 3, 0, 5, 8, 5 };
int f[] = { 2, 4, 6, 7, 9, 9 };
// Function call
SelectActivities(s, f);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Kingash. Following activities are selected n0 1 3 4 “贪婪选择”如何根据完成时间对“活动”进行分类?
让给定的活动集为S = {1,2,3,.. n},并按结束时间对活动进行排序。贪婪的选择是始终选择活动1。活动1为何总是提供最佳解决方案之一。我们可以证明,如果存在另一个溶液B的第一个活性不是1,那么还有一个溶液A的大小与第一个活性相同。假设由B选择的第一个活动为k,则始终存在A = {B – {k}} U {1}。(请注意,B中的活动是独立的,并且k在所有活动中的时间最短。因为k不是1,finish(k)> = finish(1))。
当给定活动未排序时,如何实施?
我们为活动创建一个结构/类。我们按完成时间对所有活动进行排序(请参阅C++ STL中的排序)。一旦我们对活动进行了排序,我们将应用与上面相同的算法。
下图说明了上述方法:
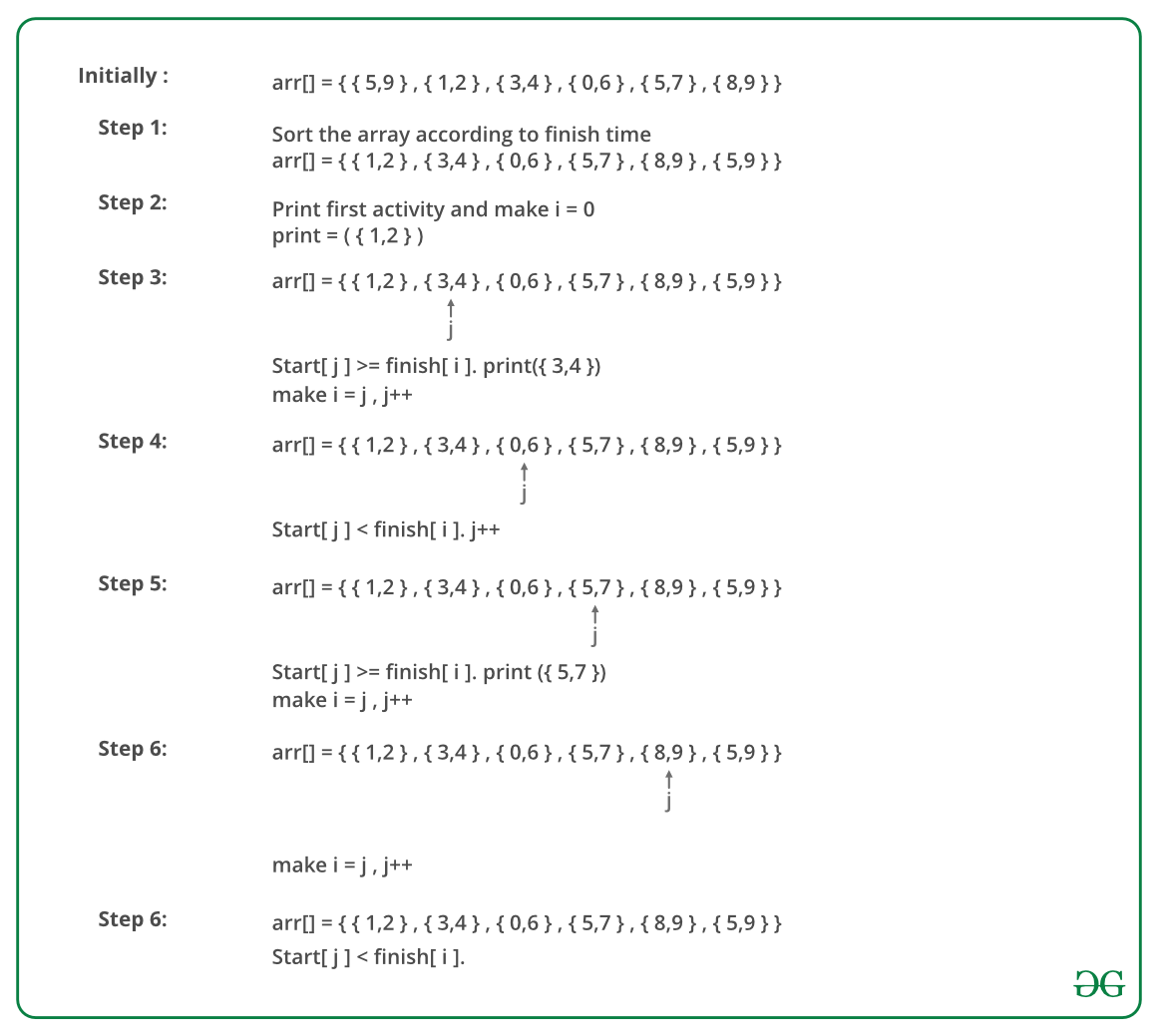
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for activity selection problem
// when input activities may not be sorted.
#include
using namespace std;
// A job has a start time, finish time and profit.
struct Activitiy
{
int start, finish;
};
// A utility function that is used for sorting
// activities according to finish time
bool activityCompare(Activitiy s1, Activitiy s2)
{
return (s1.finish < s2.finish);
}
// Returns count of the maximum set of activities that can
// be done by a single person, one at a time.
void printMaxActivities(Activitiy arr[], int n)
{
// Sort jobs according to finish time
sort(arr, arr+n, activityCompare);
cout << "Following activities are selected n";
// The first activity always gets selected
int i = 0;
cout << "(" << arr[i].start << ", " << arr[i].finish << "), ";
// Consider rest of the activities
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++)
{
// If this activity has start time greater than or
// equal to the finish time of previously selected
// activity, then select it
if (arr[j].start >= arr[i].finish)
{
cout << "(" << arr[j].start << ", "
<< arr[j].finish << "), ";
i = j;
}
}
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
Activitiy arr[] = {{5, 9}, {1, 2}, {3, 4}, {0, 6},
{5, 7}, {8, 9}};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
printMaxActivities(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for activity selection problem
// when input activities may not be sorted.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// A job has a start time, finish time and profit.
class Activity
{
int start, finish;
// Constructor
public Activity(int start, int finish)
{
this.start = start;
this.finish = finish;
}
}
// class to define user defined comparator
class Compare
{
// A utility function that is used for sorting
// activities according to finish time
static void compare(Activity arr[], int n)
{
Arrays.sort(arr, new Comparator()
{
@Override
public int compare(Activity s1, Activity s2)
{
return s1.finish - s2.finish;
}
});
}
}
// Driver class
class GFG {
// Returns count of the maximum set of activities that
// can
// be done by a single person, one at a time.
static void printMaxActivities(Activity arr[], int n)
{
// Sort jobs according to finish time
Compare obj = new Compare();
obj.compare(arr, n);
System.out.println(
"Following activities are selected :");
// The first activity always gets selected
int i = 0;
System.out.print("(" + arr[i].start + ", "
+ arr[i].finish + "), ");
// Consider rest of the activities
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++)
{
// If this activity has start time greater than
// or equal to the finish time of previously
// selected activity, then select it
if (arr[j].start >= arr[i].finish)
{
System.out.print("(" + arr[j].start + ", "
+ arr[j].finish + "), ");
i = j;
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 6;
Activity arr[] = new Activity[n];
arr[0] = new Activity(5, 9);
arr[1] = new Activity(1, 2);
arr[2] = new Activity(3, 4);
arr[3] = new Activity(0, 6);
arr[4] = new Activity(5, 7);
arr[5] = new Activity(8, 9);
printMaxActivities(arr, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Dharanendra L V.
Python3
''' Python program for activity selection problem
when input activities may not be sorted.'''
def MaxActivities(arr, n):
selected = []
# Sort jobs according to finish time
Activity.sort(key = lambda x : x[1])
# The first activity always gets selected
i = 0
selected.append(arr[i])
for j in range(1, n):
'''If this activity has start time greater than or
equal to the finish time of previously selected
activity, then select it'''
if arr[j][0] >= arr[i][1]:
selected.append(arr[j])
i = j
return selected
# Driver code
Activity = [[5, 9], [1, 2], [3, 4], [0, 6],[5, 7], [8, 9]]
n = len(Activity)
selected = MaxActivities(Activity, n)
print("Following activities are selected :")
print(selected)
# This cde is contributed by kshitijjainm
输出:
Following activities are selected
(1, 2), (3, 4), (5, 7), (8, 9),时间复杂度:如果可能无法对输入活动进行排序,则需要O(n log n)时间。假设输入活动始终被排序,则需要O(n)时间。
使用STL,我们可以解决以下问题:
CPP
// C++ program for activity selection problem
// when input activities may not be sorted.
#include
using namespace std;
void SelectActivities(vectors,vectorf){
// Vector to store results.
vector>ans;
// Minimum Priority Queue to sort activities in ascending order of finishing time (f[i]).
priority_queue,vector>,greater>>p;
for(int i=0;i= end){
start = itr.second;
end = itr.first;
ans.push_back(make_pair(start,end));
}
}
cout << "Following Activities should be selected. " << endl << endl;
for(auto itr=ans.begin();itr!=ans.end();itr++){
cout << "Activity started at: " << (*itr).first << " and ends at " << (*itr).second << endl;
}
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
vectors = {1, 3, 0, 5, 8, 5};
vectorf = {2, 4, 6, 7, 9, 9};
SelectActivities(s,f);
return 0;
}
Java
// java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Pair class
static class Pair {
int first;
int second;
Pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
static void SelectActivities(int s[], int f[])
{
// Vector to store results.
ArrayList ans = new ArrayList<>();
// Minimum Priority Queue to sort activities in
// ascending order of finishing time (f[i]).
PriorityQueue p = new PriorityQueue<>(
(p1, p2) -> p1.first - p2.first);
for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
// Pushing elements in priority queue where the
// key is f[i]
p.add(new Pair(f[i], s[i]));
}
Pair it = p.poll();
int start = it.second;
int end = it.first;
ans.add(new Pair(start, end));
while (!p.isEmpty()) {
Pair itr = p.poll();
if (itr.second >= end) {
start = itr.second;
end = itr.first;
ans.add(new Pair(start, end));
}
}
System.out.println(
"Following Activities should be selected. \n");
for (Pair itr : ans) {
System.out.println(
"Activity started at: " + itr.first
+ " and ends at " + itr.second);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int s[] = { 1, 3, 0, 5, 8, 5 };
int f[] = { 2, 4, 6, 7, 9, 9 };
// Function call
SelectActivities(s, f);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Kingash.