我们必须将对象绕给定的枢轴点旋转给定的角度,然后打印新的坐标。
例子:
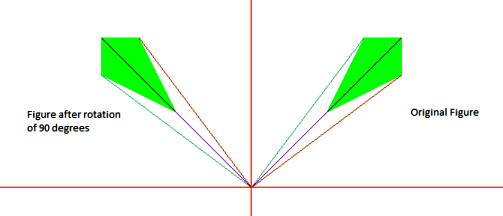
Input : {(100, 100), (150, 200), (200, 200),
(200, 150)} is to be rotated about
(0, 0) by 90 degrees
Output : (-100, 100), (-200, 150), (-200, 200), (-150, 200)
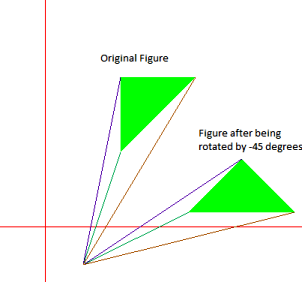
Input : {(100, 100), (100, 200), (200, 200)}
is to be rotated about (50, -50) by
-45 degrees
Output : (191.421, 20.7107), (262.132, 91.4214),
(332.843, 20.7107)
为了旋转对象,我们需要分别旋转图形的每个顶点。
将点P(x,y)绕原点旋转角度A后,我们得到一个点P’(x’,y’)。 x’和y’的值可以如下计算:
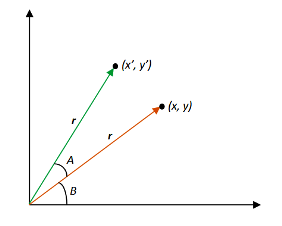
我们知道,
x = rcosB,y = rsinB
x’= rcos(A + B)= r(cosAcosB – sinAsinB)= rcosB cosA – rsinB sinA = xcosA – ysinA
y’= rsin(A + B)= r(sinAcosB + cosAsinB)= rcosB sinA + rsinB cosA = xsinA + ycosA
旋转矩阵方程式:-
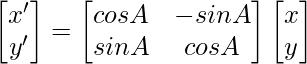
C
// C program to rotate an object by
// a given angle about a given point
#include
#include
// Using macros to convert degree to radian
// and call sin() and cos() as these functions
// take input in radians
#define SIN(x) sin(x * 3.141592653589 / 180)
#define COS(x) cos(x * 3.141592653589 / 180)
// To rotate an object
void rotate(float a[][2], int n, int x_pivot, int y_pivot,
int angle)
{
int i = 0;
while (i < n) {
// Shifting the pivot point to the origin
// and the given points accordingly
int x_shifted = a[i][0] - x_pivot;
int y_shifted = a[i][1] - y_pivot;
// Calculating the rotated point co-ordinates
// and shifting it back
a[i][0] = x_pivot
+ (x_shifted * COS(angle)
- y_shifted * SIN(angle));
a[i][1] = y_pivot
+ (x_shifted * SIN(angle)
+ y_shifted * COS(angle));
printf("(%f, %f) ", a[i][0], a[i][1]);
i++;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// 1st Example
// The following figure is to be
// rotated about (0, 0) by 90 degrees
int size1 = 4; // No. of vertices
// Vertex co-ordinates must be in order
float points_list1[][2] = { { 100, 100 },
{ 150, 200 },
{ 200, 200 },
{ 200, 150 } };
rotate(points_list1, size1, 0, 0, 90);
// 2nd Example
// The following figure is to be
// rotated about (50, -50) by -45 degrees
/*int size2 = 3;//No. of vertices
float points_list2[][2] = {{100, 100}, {100, 200},
{200, 200}};
rotate(points_list2, size2, 50, -50, -45);*/
return 0;
} CPP
// C++ program to rotate an object by
// a given angle about a given point
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// Using macros to convert degree to radian
// and call sin() and cos() as these functions
// take input in radians
#define SIN(x) sin(x * 3.141592653589 / 180)
#define COS(x) cos(x * 3.141592653589 / 180)
// To rotate an object given as order set of points in a[]
// (x_pivot, y_pivot)
void rotate(float a[][2], int n, int x_pivot, int y_pivot,
int angle)
{
int i = 0;
while (i < n) {
// Shifting the pivot point to the origin
// and the given points accordingly
int x_shifted = a[i][0] - x_pivot;
int y_shifted = a[i][1] - y_pivot;
// Calculating the rotated point co-ordinates
// and shifting it back
a[i][0] = x_pivot
+ (x_shifted * COS(angle)
- y_shifted * SIN(angle));
a[i][1] = y_pivot
+ (x_shifted * SIN(angle)
+ y_shifted * COS(angle));
cout << "(" << a[i][0] << ", " << a[i][1] << ") ";
i++;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// 1st Example
// The following figure is to be
// rotated about (0, 0) by 90 degrees
int size1 = 4; // No. of vertices
// Vertex co-ordinates must be in order
float points_list1[][2] = { { 100, 100 },
{ 150, 200 },
{ 200, 200 },
{ 200, 150 } };
rotate(points_list1, size1, 0, 0, 90);
// 2nd Example
// The following figure is to be
// rotated about (50, -50) by -45 degrees
/*int size2 = 3;//No. of vertices
float points_list2[][2] = {{100, 100}, {100, 200},
{200, 200}};
rotate(points_list2, size2, 50, -50, -45);*/
return 0;
} 输出:
(-100, 100), (-200, 150), (-200, 200), (-150, 200)
参考:旋转矩阵