Floyd-Rivest算法是一种选择算法,用于在不同元素的数组中找到第k个最小的元素。它类似于QuickSelect算法,但在实践中具有更好的运行时间。
像QuickSelect一样,该算法也适用于分区的思想。在对数组进行分区之后,分区元素最终会在正确的排序位置结束。如果数组具有所有不同的元素,则检索第(k + 1)个最小元素与排序后检索第(k + 1)个元素相同。由于完整排序非常昂贵(需要O(N log N)来计算),因此Floyd-Rivest算法利用分区在O(N)时间内完成相同的操作。
算法:
- 如果考虑的数组S的大小足够小,则直接应用QuickSelect算法以获得第K个最小元素。该大小是算法的任意常数,作者选择该常数为600 。
- 否则,将使用随机采样选择2个枢轴-newLeftIndex和newRightIndex,以使它们具有包含第K个最大元素的最高概率。然后,递归调用该函数,并将数组的左边界和右边界设置为newLeftIndex和newRightIndex。
- 与QuickSelect一样,在对子数组进行分区之后,需要设置左右边界,使其包含最大K元素。
在围绕K划分数组后,第K个元素处于其正确的排序位置。因此,左右边界的设置方式应使所考虑的子数组包含array [k]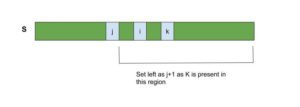

下面是上述方法的实现。
C++
// C++ implementation of the above approach.
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to return the
// sign of a number
int sign(double x)
{
if (x < 0)
return -1;
if (x > 0)
return 1;
return 0;
}
// Function to swap
// two numbers in an array.
void swap(int arr[], int i, int j)
{
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
int select(int arr[], int left,
int right, int k)
{
while (right > left) {
if (right - left > 600) {
// Choosing a small subarray
// S based on sampling.
// 600, 0.5 and 0.5
// are arbitrary constants
int n = right - left + 1;
int i = k - left + 1;
double z = log(n);
double s = 0.5 * exp(2 * z / 3);
double sd = 0.5 * sqrt(z * s
* (n - s) / n)
* sign(i - n / 2);
int newLeft = max(left,
(int)(k - i * s / n + sd));
int newRight = min(right,
(int)(k + (n - i) * s / n
+ sd));
select(arr, newLeft, newRight, k);
}
// Partition the subarray S[left..right]
// with arr[k] as pivot
int t = arr[k];
int i = left;
int j = right;
swap(arr, left, k);
if (arr[right] > t) {
swap(arr, left, right);
}
while (i < j) {
swap(arr, i, j);
i++;
j--;
while (arr[i] < t)
i++;
while (arr[j] > t)
j--;
}
if (arr[left] == t)
swap(arr, left, j);
else {
j++;
swap(arr, right, j);
}
// Adjust the left and right pointers
// to select the subarray having k
if (j <= k)
left = j + 1;
if (k <= j)
right = j - 1;
}
return arr[k];
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 7, 3, 4, 0, 1, 6 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int);
// k-th smallest element.
// In this we get the 2nd smallest element
int k = 2;
int res = select(arr, 0, n - 1, k - 1);
cout << "The " << k << "-th smallest element is "
<< res << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the above approach.
class GFG {
// Function to return
// the sign of the number
int sign(double x)
{
if (x < 0)
return -1;
if (x > 0)
return 1;
return 0;
}
// Function to swap two numbers in an array
void swap(int arr[], int i, int j)
{
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
// Function to return kth smallest number
int select(int arr[], int left,
int right, int k)
{
while (right > left) {
if (right - left > 600) {
// Choosing a small subarray
// S based on sampling.
// 600, 0.5 and 0.5 are
// arbitrary constants
int n = right - left + 1;
int i = k - left + 1;
double z = Math.log(n);
double s = 0.5 * Math.exp(2 * z / 3);
double sd = 0.5 * Math.sqrt(z * s * (n - s) / n)
* sign(i - n / 2);
int newLeft = Math.max(left,
(int)(k - i * s / n
+ sd));
int newRight = Math.min(right,
(int)(k + (n - i) * s / n
+ sd));
select(arr, newLeft, newRight, k);
}
// Partition the subarray S[left..right]
// with arr[k] as pivot
int t = arr[k];
int i = left;
int j = right;
swap(arr, left, k);
if (arr[right] > t) {
swap(arr, left, right);
}
while (i < j) {
swap(arr, i, j);
i++;
j--;
while (arr[i] < t)
i++;
while (arr[j] > t)
j--;
}
if (arr[left] == t)
swap(arr, left, j);
else {
j++;
swap(arr, right, j);
}
// Adjust the left and right
// pointers to select the subarray having k
if (j <= k)
left = j + 1;
if (k <= j)
right = j - 1;
}
return arr[k];
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] arr = new int[] { 7, 3, 4, 0, 1, 6 };
// k-th smallest element.
// In this we get the 2nd smallest element
int k = 2;
FloydRivest f = new FloydRivest();
int res = f.select(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, k - 1);
System.out.println("The " + k
+ "-th smallest element is " + res);
}
}Python3
# Python implementation of the above approach.
import math
import random
# Function to return the
# sign of the number
def sign(x):
if x>0:
return 1
elif x<0:
return -1
return 0
# Function to swap two
# numbers in an array
def swap(arr, i, j):
temp = arr[i]
arr[i] = arr[j]
arr[j] = temp
# Function to return kth smallest number
def select(arr: list, left: int,
right: int, k: int):
while right>left:
# Choosing a small subarray
# S based on sampling.
# 600, 0.5 and 0.5 are
# arbitrary constants
if right-left > 600:
n = right - left + 1
i = k - left + 1
z = math.log(n)
s = 0.5 * math.exp(2 * z / 3)
sd = 0.5 * math.sqrt(z * s * (n-s)/n) * sign(i-n / 2)
newLeft = int(max(left, k-i * s / n + sd))
newRight = int(min(right, k + (n - i) * s / n + sd))
select(arr, newLeft, newRight, k)
t = arr[k]
i = left
j = right
swap(arr, left, k)
if arr[right] > t:
swap(arr, left, right)
while it:
j = j-1
if arr[left] == t:
swap(arr, left, j)
else:
j = j + 1
swap(arr, right, j)
# Updating the left and right indices
# depending on position of k-th element
if j<= k:
left = j + 1
if k<= j:
right = j-1
return arr[k]
arr = [7, 3, 4, 0, 1, 6]
# k-th smallest element.
# In this the 2nd smallest element is returned.
k = 2
res = select(arr, 0, len(arr)-1, k-1)
print('The {}-th smallest element is {}'.format(k, res)) C#
// C# implementation of the above approach.
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to return
// the sign of the number
static int sign(double x)
{
if (x < 0)
return -1;
if (x > 0)
return 1;
return 0;
}
// Function to swap two numbers in an array
static void swap(int []arr, int i, int j)
{
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
// Function to return kth smallest number
static int select(int []arr, int left,
int right, int k)
{
int i;
while (right > left)
{
if (right - left > 600)
{
// Choosing a small subarray
// S based on sampling.
// 600, 0.5 and 0.5 are
// arbitrary constants
int n = right - left + 1;
i = k - left + 1;
double z = Math.Log(n);
double s = 0.5 * Math.Exp(2 * z / 3);
double sd = 0.5 * Math.Sqrt(z * s * (n - s) / n)
* sign(i - n / 2);
int newLeft = Math.Max(left,
(int)(k - i * s / n
+ sd));
int newRight = Math.Min(right,
(int)(k + (n - i) * s / n
+ sd));
select(arr, newLeft, newRight, k);
}
// Partition the subarray S[left..right]
// with arr[k] as pivot
int t = arr[k];
i = left;
int j = right;
swap(arr, left, k);
if (arr[right] > t)
{
swap(arr, left, right);
}
while (i < j)
{
swap(arr, i, j);
i++;
j--;
while (arr[i] < t)
i++;
while (arr[j] > t)
j--;
}
if (arr[left] == t)
swap(arr, left, j);
else
{
j++;
swap(arr, right, j);
}
// Adjust the left and right
// pointers to select the subarray having k
if (j <= k)
left = j + 1;
if (k <= j)
right = j - 1;
}
return arr[k];
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 7, 3, 4, 0, 1, 6 };
// k-th smallest element.
// In this we get the 2nd smallest element
int k = 2;
int res = select(arr, 0, arr.Length - 1, k - 1);
Console.WriteLine("The " + k + "-th smallest element is " + res);
}
}
// This code is contributed by AnkitRai01输出:
The 2-th smallest element is 1
时间复杂度:O(N)
参考:
维基百科-弗洛伊德·里维斯特
关于Floyd和Rivest的SELECT算法
维基百科-快速选择