使用 Floyd Warshall 检测负循环
我们得到一个有向图。我们需要计算图是否有负循环。负循环是循环的总和为负的循环。
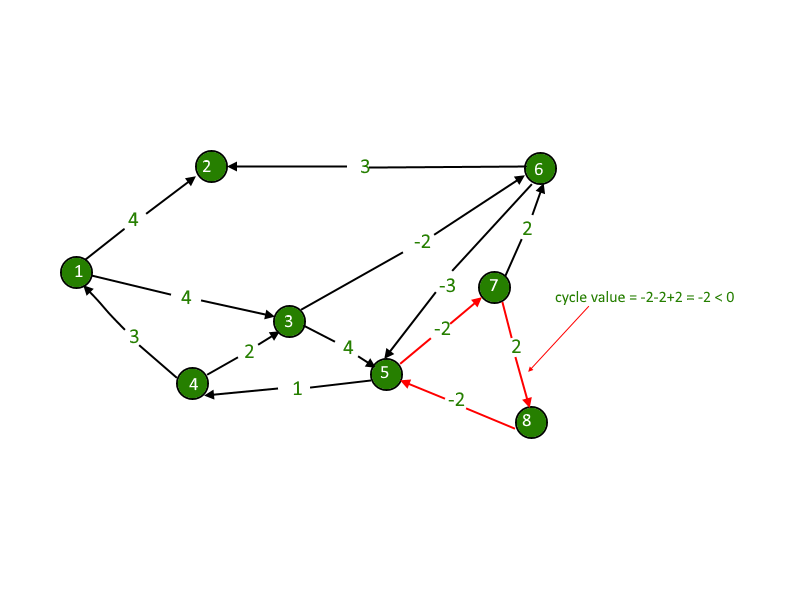
在图形的各种应用中都可以找到负权重。例如,如果我们遵循路径,我们可能会获得一些优势,而不是为路径支付成本。
例子:
Input : 4 4
0 1 1
1 2 -1
2 3 -1
3 0 -1
Output : Yes
The graph contains a negative cycle.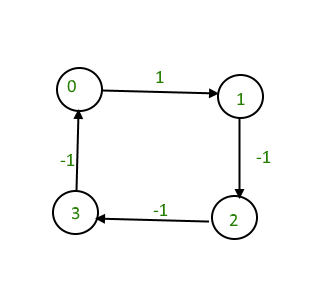
我们已经讨论了这个问题的基于贝尔曼福特算法的解决方案。
在这篇文章中,讨论了基于 Floyd Warshall 算法的解决方案,该解决方案适用于连通图和不连通图。
任何节点与其自身的距离始终为零。但在某些情况下,如本例中,当我们从 4 进一步遍历到 1 时,距离为 -2,即 1 到 1 的距离将变为 -2。这是我们的问题,我们只需要检查节点与自身的距离,如果结果为负,我们将检测所需的负循环。
C++
// C++ Program to check if there is a negative weight
// cycle using Floyd Warshall Algorithm
#include
using namespace std;
// Number of vertices in the graph
#define V 4
/* Define Infinite as a large enough value. This
value will be used for vertices not connected
to each other */
#define INF 99999
// A function to print the solution matrix
void printSolution(int dist[][V]);
// Returns true if graph has negative weight cycle
// else false.
bool negCyclefloydWarshall(int graph[][V])
{
/* dist[][] will be the output matrix that will
finally have the shortest
distances between every pair of vertices */
int dist[V][V], i, j, k;
/* Initialize the solution matrix same as input
graph matrix. Or we can say the initial values
of shortest distances are based on shortest
paths considering no intermediate vertex. */
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
for (j = 0; j < V; j++)
dist[i][j] = graph[i][j];
/* Add all vertices one by one to the set of
intermediate vertices.
---> Before start of a iteration, we have shortest
distances between all pairs of vertices such
that the shortest distances consider only the
vertices in set {0, 1, 2, .. k-1} as intermediate
vertices.
----> After the end of a iteration, vertex no. k is
added to the set of intermediate vertices and
the set becomes {0, 1, 2, .. k} */
for (k = 0; k < V; k++)
{
// Pick all vertices as source one by one
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
// Pick all vertices as destination for the
// above picked source
for (j = 0; j < V; j++)
{
// If vertex k is on the shortest path from
// i to j, then update the value of dist[i][j]
if (dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] < dist[i][j])
dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j];
}
}
}
// If distance of any vertex from itself
// becomes negative, then there is a negative
// weight cycle.
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (dist[i][i] < 0)
return true;
return false;
}
// driver program
int main()
{
/* Let us create the following weighted graph
1
(0)----------->(1)
/|\ |
| |
-1 | | -1
| \|/
(3)<-----------(2)
-1 */
int graph[V][V] = { {0 , 1 , INF , INF},
{INF , 0 , -1 , INF},
{INF , INF , 0 , -1},
{-1 , INF , INF , 0}};
if (negCyclefloydWarshall(graph))
cout << "Yes";
else
cout << "No";
return 0;
} Java
// Java Program to check if there is a negative weight
// cycle using Floyd Warshall Algorithm
class GFG
{
// Number of vertices in the graph
static final int V = 4;
/* Define Infinite as a large enough value. This
value will be used for vertices not connected
to each other */
static final int INF = 99999;
// Returns true if graph has negative weight cycle
// else false.
static boolean negCyclefloydWarshall(int graph[][])
{
/* dist[][] will be the output matrix that will
finally have the shortest
distances between every pair of vertices */
int dist[][] = new int[V][V], i, j, k;
/* Initialize the solution matrix same as input
graph matrix. Or we can say the initial values
of shortest distances are based on shortest
paths considering no intermediate vertex. */
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
for (j = 0; j < V; j++)
dist[i][j] = graph[i][j];
/* Add all vertices one by one to the set of
intermediate vertices.
---> Before start of a iteration, we have shortest
distances between all pairs of vertices such
that the shortest distances consider only the
vertices in set {0, 1, 2, .. k-1} as intermediate
vertices.
----> After the end of a iteration, vertex no. k is
added to the set of intermediate vertices and
the set becomes {0, 1, 2, .. k} */
for (k = 0; k < V; k++)
{
// Pick all vertices as source one by one
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
// Pick all vertices as destination for the
// above picked source
for (j = 0; j < V; j++)
{
// If vertex k is on the shortest path from
// i to j, then update the value of dist[i][j]
if (dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] < dist[i][j])
dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j];
}
}
}
// If distance of any vertex from itself
// becomes negative, then there is a negative
// weight cycle.
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (dist[i][i] < 0)
return true;
return false;
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
/* Let us create the following weighted graph
1
(0)----------->(1)
/|\ |
| |
-1 | | -1
| \|/
(3)<-----------(2)
-1 */
int graph[][] = { {0, 1, INF, INF},
{INF, 0, -1, INF},
{INF, INF, 0, -1},
{-1, INF, INF, 0}};
if (negCyclefloydWarshall(graph))
System.out.print("Yes");
else
System.out.print("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Anant Agarwal.Python3
# Python Program to check
# if there is a
# negative weight
# cycle using Floyd
# Warshall Algorithm
# Number of vertices
# in the graph
V = 4
# Define Infinite as a
# large enough value. This
# value will be used
#for vertices not connected
# to each other
INF = 99999
# Returns true if graph has
# negative weight cycle
# else false.
def negCyclefloydWarshall(graph):
# dist[][] will be the
# output matrix that will
# finally have the shortest
# distances between every
# pair of vertices
dist=[[0 for i in range(V+1)]for j in range(V+1)]
# Initialize the solution
# matrix same as input
# graph matrix. Or we can
# say the initial values
# of shortest distances
# are based on shortest
# paths considering no
# intermediate vertex.
for i in range(V):
for j in range(V):
dist[i][j] = graph[i][j]
''' Add all vertices one
by one to the set of
intermediate vertices.
---> Before start of a iteration,
we have shortest
distances between all pairs
of vertices such
that the shortest distances
consider only the
vertices in set {0, 1, 2, .. k-1}
as intermediate vertices.
----> After the end of a iteration,
vertex no. k is
added to the set of
intermediate vertices and
the set becomes {0, 1, 2, .. k} '''
for k in range(V):
# Pick all vertices
# as source one by one
for i in range(V):
# Pick all vertices as
# destination for the
# above picked source
for j in range(V):
# If vertex k is on
# the shortest path from
# i to j, then update
# the value of dist[i][j]
if (dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] < dist[i][j]):
dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j]
# If distance of any
# vertex from itself
# becomes negative, then
# there is a negative
# weight cycle.
for i in range(V):
if (dist[i][i] < 0):
return True
return False
# Driver code
''' Let us create the
following weighted graph
1
(0)----------->(1)
/|\ |
| |
-1 | | -1
| \|/
(3)<-----------(2)
-1 '''
graph = [ [0, 1, INF, INF],
[INF, 0, -1, INF],
[INF, INF, 0, -1],
[-1, INF, INF, 0]]
if (negCyclefloydWarshall(graph)):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
# This code is contributed
# by Anant Agarwal.C#
// C# Program to check if there
// is a negative weight cycle
// using Floyd Warshall Algorithm
using System;
namespace Cycle
{
public class GFG
{
// Number of vertices in the graph
static int V = 4;
/* Define Infinite as a large enough value. This
value will be used for vertices not connected
to each other */
static int INF = 99999;
// Returns true if graph has negative weight cycle
// else false.
static bool negCyclefloydWarshall(int [,]graph)
{
/* dist[][] will be the output matrix that will
finally have the shortest
distances between every pair of vertices */
int [,]dist = new int[V,V];
int i, j, k;
/* Initialize the solution matrix same as input
graph matrix. Or we can say the initial values
of shortest distances are based on shortest
paths considering no intermediate vertex. */
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
for (j = 0; j < V; j++)
dist[i,j] = graph[i,j];
/* Add all vertices one by one to the set of
intermediate vertices.
---> Before start of a iteration, we have shortest
distances between all pairs of vertices such
that the shortest distances consider only the
vertices in set {0, 1, 2, .. k-1} as intermediate
vertices.
----> After the end of a iteration, vertex no. k is
added to the set of intermediate vertices and
the set becomes {0, 1, 2, .. k} */
for (k = 0; k < V; k++)
{
// Pick all vertices as source one by one
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
// Pick all vertices as destination for the
// above picked source
for (j = 0; j < V; j++)
{
// If vertex k is on the shortest path from
// i to j, then update the value of dist[i][j]
if (dist[i,k] + dist[k,j] < dist[i,j])
dist[i,j] = dist[i,k] + dist[k,j];
}
}
}
// If distance of any vertex from itself
// becomes negative, then there is a negative
// weight cycle.
for (i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (dist[i,i] < 0)
return true;
return false;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
/* Let us create the following weighted graph
1
(0)----------->(1)
/|\ |
| |
-1 | | -1
| \|/
(3)<-----------(2)
-1 */
int [,]graph = { {0, 1, INF, INF},
{INF, 0, -1, INF},
{INF, INF, 0, -1},
{-1, INF, INF, 0}};
if (negCyclefloydWarshall(graph))
Console.Write("Yes");
else
Console.Write("No");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007.Javascript
输出:
Yes