在本文中,我们将讨论如何使用Bresenham方程和Polar方程绘制圆。
圆图绘制算法
在计算机屏幕上显示连续的平滑弧线并不容易,因为我们的计算机屏幕是由以矩阵形式组织的像素组成的。因此,要在计算机屏幕上画一个圆,应始终从打印的像素中选择最近的像素,以使它们形成弧形。

- 考虑以原点为中心的半径为整数的圆。
- 可以应用翻译以获取非原点为中心的圆。
- 圆的等式由下式给出:
x2 + y2 = R2
y = +/-sqrt(R2-x2)
- 给定的等式可以写成:
F(x, y)= x2+ y2-R2=0
5.
- 对称性的使用:只需要计算一个八分圆。一个人可以在其他7个八分圆中获得积分,如下所示:
- 绘图点(x,y)
- 绘图点(y,x)
- 绘图点(x,-y)
- 绘图点(-y,x)
- 绘图点(-x,-y)
- 绘图点(-y,-x)
- 绘图点(-x,y)
- 绘图点(-y,x)
使用Bresenham方程绘制圆图
布雷森汉方程式(Bresenham Equation)使用了高度对称的圆的关键特征。因此,对于整个360度圆,将其分为45度的每个八分之八部分。为此,我们的想法是使用Bresenham的Circle算法来计算45度第一个八分之一像素中像素的位置。假定圆以原点为中心。因此,对于每个像素(x,y) ,请在圆的8个八分之一圆的每个像素中绘制一个像素,如下所示:

在布雷森纳姆算法的任意(x,y)点上,我们有两个选择或者选择东部的下一个像素(x + 1,y)或东南的下一个像素(x + 1,y – 1) 。这可以通过使用决策参数d来确定:
- 如果d> 0 ,则将选择(x + 1,y – 1)作为下一个像素,因为它将更靠近圆弧。
- 否则(x + 1,y)将被选作下一个像素。
下面是布雷森纳姆方程的算法:
- F(x,y)= x 2 + y 2 = 0点在圆上。
- F(x,y)> 0点位于圆的外面。
- F(x,y)<0点位于圆内。
- 如果d> = 0,则将x更新为(x + 1)和y =(y – 1),从而得到新的d
- 如果d <0,则将x更新为(x + 1),这将给出d的新值
C
// C program for the above approach
#include
#include
#include
#include
int xo, yo, r;
// Function to display the circle using
// the above algorithm
void Display(void)
{
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// Color of printing object
glColor3f(1, 0, 0);
// Giving the size of the point
glPointSize(2);
int x = 0;
int y = r;
float p = 5 / 4 - r;
glColor3f(1, 0, 0);
// Starting of drawing the circle
glBegin(GL_POINTS);
while (y > x) {
if (p < 0) {
// Increment x to x+1
x++;
p = p + 2 * x + 1;
}
else {
// Increment x to x+1
// and decrease y to y-1
y--;
x++;
p = p + 2 * (x - y) + 1;
}
// Draw the coordinates
glVertex2d(x + xo, y + yo);
glVertex2d(-x + xo, y + yo);
glVertex2d(x + xo, -y + yo);
glVertex2d(-x + xo, -y + yo);
glVertex2d(y + yo, x + xo);
glVertex2d(-y + yo, x + xo);
glVertex2d(y + yo, -x + xo);
glVertex2d(-y + yo, -x + xo);
}
glEnd();
// Its empties all the buffer
// causing the issue
glFlush();
}
// Driver Code
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
printf("X-coordinate Y-coordinate radius:");
scanf("%d %d %d", &xo, &yo, &r);
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGB);
// Assigning the size of window
glutInitWindowSize(1000, 1000);
// Assign the position of window
// to be appeared
glutInitWindowPosition(100, 100);
// Defining the heading of the window
glutCreateWindow("GeeksforGeeks");
// Backgronnd Color
glClearColor(1, 1, 1, 1);
// limit of the coordinate points
gluOrtho2D(-500, 500, -500, 500);
// Calling the function
glutDisplayFunc(Display);
glutMainLoop();
return 0;
} C
// C program to demonstrate circle
// drawing using polar equation
#include
#include
#include
#include
float xo, yo, rad;
// Function to display the circle
void display()
{
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// Color of printing object
glColor3f(1, 1, 1);
float angle;
// Start to drawing the circle
glBegin(GL_POLYGON);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
// Change the angle
angle = i * 2 * (M_PI / 100);
glVertex2f(xo + (cos(angle) * rad),
yo + (sin(angle) * rad));
}
glEnd();
// Its empties all the buffer
// causing the issue
glFlush();
}
// Driver Code
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
glutInit(&argc, argv);
printf("Enter x y radius ");
scanf("%f %f %f", &xo, &yo, &rad);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGB);
// Assigning the size of window
glutInitWindowSize(500, 500);
// Assign the position of window
// to be appeared
glutInitWindowPosition(200, 200);
// Defining the heading of the window
glutCreateWindow("GeeksforGeeks");
// Backgronnd Color
glClearColor(0, 1, 0, 1);
// limit of the coordinate points
gluOrtho2D(-500, 500, -500, 500);
// Calling the function
glutDisplayFunc(Display);
glutMainLoop();
return 0;
} 输出:
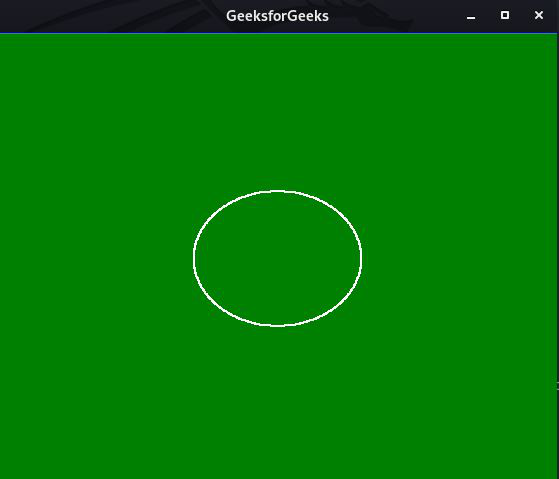
时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(1)
使用极地方程式进行圆
在Polar Equation系统中,其想法是用一只手想到一个时钟。与手从原点移开距离r (有时称为模数) ,然后将手向上(逆时针)旋转角度θ到达该点。以下是极地方程的算法:
- 初始化变量rad,center(x0,y0) ,索引值或增量值i ,并使用极坐标θ_end= 100定义一个圆。
- 如果θ_end<θ ,则退出循环。
- 找到x的值作为rad * cos(angle)和y的值作为rad * sin(angle) 。
- 绘制通过对称找到的八个点,即在当前(x,y)坐标处的中心(x0,y0)。
- 情节(x + xo,y + yo)
- 情节(-x + xo,-y + yo)
- 情节(y + xo,x + yo)
- 绘图(-y + xo,-x + yo)
- 情节(-y + xo,x + yo)
- 情节(y + xo,-x + yo)
- 绘图(-x + xo,y + yo)
- 情节(x + xo,-y + yo)
- 将角度增加i * 2 *(M_PI / 100) 。
下面是实现上述方法的程序:
C
// C program to demonstrate circle
// drawing using polar equation
#include
#include
#include
#include
float xo, yo, rad;
// Function to display the circle
void display()
{
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// Color of printing object
glColor3f(1, 1, 1);
float angle;
// Start to drawing the circle
glBegin(GL_POLYGON);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
// Change the angle
angle = i * 2 * (M_PI / 100);
glVertex2f(xo + (cos(angle) * rad),
yo + (sin(angle) * rad));
}
glEnd();
// Its empties all the buffer
// causing the issue
glFlush();
}
// Driver Code
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
glutInit(&argc, argv);
printf("Enter x y radius ");
scanf("%f %f %f", &xo, &yo, &rad);
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGB);
// Assigning the size of window
glutInitWindowSize(500, 500);
// Assign the position of window
// to be appeared
glutInitWindowPosition(200, 200);
// Defining the heading of the window
glutCreateWindow("GeeksforGeeks");
// Backgronnd Color
glClearColor(0, 1, 0, 1);
// limit of the coordinate points
gluOrtho2D(-500, 500, -500, 500);
// Calling the function
glutDisplayFunc(Display);
glutMainLoop();
return 0;
}
输出:

时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(1)