线性函数公式
线性函数是允许在坐标平面上描述直线的过程。例如,y = 2x – 1 表示坐标平面上的直线,因此它传达了一个线性过程。由于 y 可以用 f(x) 代替,所以这个过程可以记为 f(x) = 2x – 1。
它是状态之一f(x) = mx + b ,这里 'm' 和 'b' 表示实数。它的检查类似于由 y = mx + b 提供的条形的斜率截距形状,因为线性过程表示条形,即它是图形线。这里,
'm' 是字符串的音高
'b' 是条形的 y 截距
'x' 是单独的变量
'y'(或 f(x))是条件变量
线性过程也称为代数过程。
线性函数示例
f(x) = 2x + 1
f(x) = -3x – 2
f(x) = 5
线性函数公式用于表示线性规划问题的目标函数,有助于实现利润最大化。
线性函数公式
数据以关于流程的图表形式提供,如果图表是条形图,则它是线性的。如果数据是以关于函数的代数结构状态提供的,那么如果它的形式为 f(x) = mx+b,则它是线性的。但是要查看表格中的共享数据是否描述了线性方程,我们必须这样做,
• 计算 y 值的差异
• 计算 x 轴上的差异
• 检查y 值差异与x 值差异之间的平衡是否始终稳定。
线性函数的图形
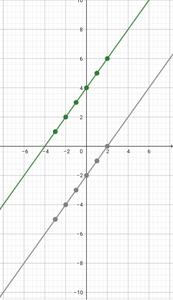
正如我们理解在图表上绘制一条线,我们需要它上面的任意两个点。如果我们发现两个点,我们只需在图上设计它们,将它们通过一条线合并并从两侧展开。线性函数f(x) = mx + b 的图是
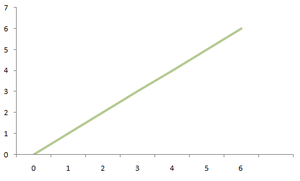
increasing line when m >0
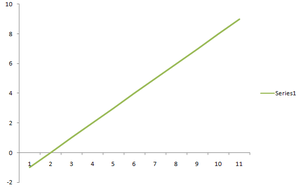
decreasing line when m < 0
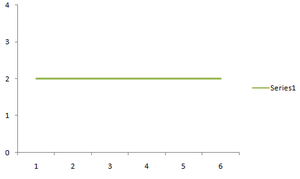
horizontal line when m = 0
通过找到两个点来绘制线性函数
要发现线性函数(线)f(x)=mx+b 上的两个精确点,请考虑 'x' 的一些意外值,并且必须替换这些值以找到 y 的连接值。
该方法由一个实例呈现,我们将在其中绘制函数f(x) = 2x + 4 。
Step1: Firstly find two points on the line by carrying some unexpected values
assume that x = 0 and x = 1
Step2: Now replace each of both the values in position to get the related y-values
Here is the table of a linear procedure y = 2x + 4
So, the two points on the line are (0, 4) and (1, 6).
Step3: Now plan the points on the graph merge them by the line and expand the line from both sides.

使用斜率和 y 截距绘制线性函数图
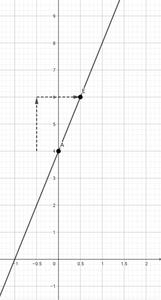
To graph a linear function , f(x)=mx+b, use its slope ‘m’ and its y-intercept ‘b’ .This procedure is explained again by graphing the same linear function f(x) = 2x + 4. Its slope is, m = 2 and its y-intercept is (0, b) = (0, 4).
Step 1: Firstly Plot the y-intercept (0, b).
Here, plot the point (0, 4).
Step2: Now document the slope as the fraction uprise/run and recognize the “uprise” and the “run”.
Here, the slope = 2 = 2/1 = uprise/run.
So uprise = 2 and run = 1.
Step3: Now uprise the y-intercept vertically by “rise” and then run horizontally by “run”. This will result in making a new point.
(Note that if “rise” is favorable, go up and if “rise” is unfavorable, go down. Also, if “run” is favorable”, go right, and if “run” is unfavorable, go left.)
Here, go up by 2 units from the y-intercept and thereby go right by 1 unit.
Step4: Now merge the points from step1 and step2 by line and expand that line on both sides.
线性函数的域和范围
线性函数的定义域是所有实数的集合,实际上,线性函数的范围也是所有自然数的集合 如图 f(x) = 2x + 3 和 g(x) = 4 - x 在相同的轴上设计。
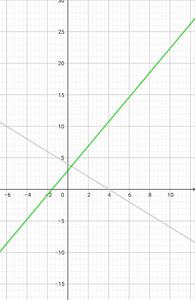
注意:对于x的所有值的绝对值所起的作用,意味着每个函数的部分是全自然数字(R)的集合。沿 x 轴检查以确保。对于 x 的每个值,我们在图上都有一个时刻。
甚至,每个过程的结果从负无穷到正无穷不等,这表示任一函数的范围也是 R。这可以通过沿 y 轴检查来验证,这显然表明每个图上都有一个矩对于每个 y 值。因此,当斜率 m ≠ 0 时,
•线性函数的部分= R
•线性函数的范围= R
Note:
(i) When the slope, m = 0, then the linear function f(x) = b is a horizontal line and in this case, the fields = R and the scope = {b}.
(ii) The fields and scope of a linear function in R as extended as the issue has not cited any exact field or scope.
线性函数的逆
线性函数f(x) = ax + b 的逆由函数f -1 (x) 表示,使得 f(f -1 (x)) = f -1 (f(x)) = x。
查看线性函数逆的方法是通过一个实例来介绍的,我们将在该实例中找到函数f(x) = 2x + 4 的逆。
Step1: Write y instead of f(x)
So, equation y = 2x + 4
Step2: Now interchange the variable x and y
Then we have x = 2y + 4
Step3: Solve the above equation to get y
x – 4 = 2y
y = (x – 4)/2
Step4: Replace y by f-1(x) and it is the inverse function of f(x).
f-1(x) = (x – 4)/2
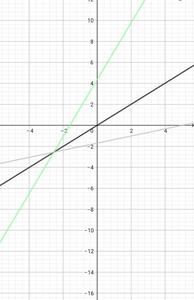
Note:- that the f(x) and f-1(x)are always symmetric with respect to the line y=x. Let us plot the linear function f(x) = 2x + 5 and its inverse f-1(x) = (x – 4)/2 and see whether they are symmetric about y = x or not . Also when (x, y) lies on f(x) , then (y, x) lies on f-1(x). For example, in the following graph (-1, 2) lies on f(x) where as (2, -1) lies on f-1(x).
分段线性函数
周期性地,线性函数可能无法通过其栖息地进行统一描述。它可以用两条更好的路线来描述,因为它的栖息地以两种或多种方法分开。在这些变化中,它被理解为分段线性函数。让我们来个样本。
示例问题
问题 1:找到具有两个点 (-2, 17) 和 (1, 26) 的线性函数。
解决方案:
The given points are (x1, y1)= (-2, 17) and (x2, y2) = (1, 26)
Step1: Firstly find the slope of the function using the slope formula:
m = (y₂ – y₁) / (x₂ – x₁) = (26 – 17) / (1 – (-2)) = 9/3 = 3.
Step2: Now find the equation of linear function using the point slope form
y – y₁ = m (x – x₁)
y – 17 = 3 (x – (-2))
y – 17 = 4 (x + 2)
y – 17 = 4x + 8
y = 4x + 25
So, the equation of linear function is, f(x) = 4x + 25
问题2:判断后续表中的后续数据是否描述了一个线性函数。x y 0 2(0) + 4 = 4 1 2(1) + 4 = 6
解决方案:
We have to compute the differences in the x-values, differences in the y-values, and the ratio by (difference in y/difference in x) and have to see whether this ratio is constant or not. 3 ⇣+2 5 16 ⇣+8 23 5 ⇣+2 7 23 ⇣+8 31 7 ⇣+4 11 31 ⇣+16 47 11 ⇣+2 13 47 ⇣+8 55X Y Difference in X/Difference in Y ⇒ 8/2 = 4 ⇒ 8/2 = 4 ⇒ 16/4 = 4 ⇒ 8/2 = 4
Since all the numbers in the last column are equal to constant, the given table represents the linear function.
问题 3:绘制图形 y = 3x + 2 是一个线性方程
解决方案:
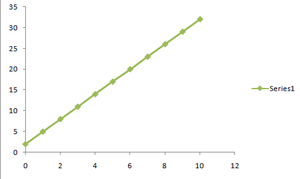
When x increases, y increases thrice as fast, so we need 3x.
When x is 0, y is already 2. So +2 is also needed.
And so: y = 3x + 2
Here are some example values:x y = 3x + 2 1 3 × 1 + 2 = 5 2 3 × 2 + 2 = 8 3 3 × 3 + 2 = 11
问题 4:绘制以下方程 3x + 2y - 4 = 0 的图形
解决方案:
It is in the form Ax + By + C = 0 where:
A = 3
B = 2
C = −4
问题 5:绘制以下分段线性函数的图形。
- f(x) = x + 4, x∈ [-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2]
- f(x) = 1x – 2, x∈ [-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2]
解决方案:
The piece wise linear function indicates both the parts of its domain. Let us find the endpoint in each of the case.
- When f(x) = x + 4
| X | Y |
| -3 | -3 + 4 = 1 |
| -2 | -2 + 4 = 2 |
| -1 | -1 + 4 = 3 |
| 0 | 0 + 4 = 4 |
| 1 | 1 + 4 = 5 |
| 2 | 2 + 4 = 6 |
- When f(x) =1x-2
| X | Y |
| -3 | 1(-3) – 2 = -5 |
| -2 | 1(-2) – 2 = -4 |
| -1 | 1(-1) – 2 = -3 |
| 0 | 1(0) – 2 = -2 |
| 1 | 1(1) – 2 = -1 |
| 2 | 1(2) – 2 = 0 |
The corresponding graph is shown below.