两个节点之间的单色路径数
给定一个无向彩色图(边是彩色的),具有源顶点's'和目标顶点'd',打印从给定's'到'd'的路径数,使得路径是单色的(路径中的边具有相同的颜色)。
边缘是彩色的,这里颜色用数字表示。最多,不同颜色的数量将是边缘的数量。 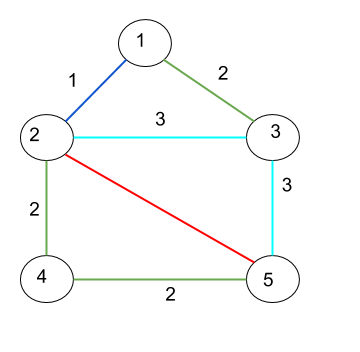
Input : Graph
u, v, color
1, 2, 1
1, 3, 2
2, 3, 3
2, 4, 2
2, 5, 4
3, 5, 3
4, 5, 2
source = 2 destination = 5
Output : 3
Explanation : There are three paths from 2 to 5
2 -> 5 with color red
2 -> 3 - > 5 with color sky blue
2 -> 4 - > 5 with color green
算法 :
1、对源节点的邻居节点进行dfs遍历。
2、源节点和邻居节点之间的颜色已知,如果DFS遍历也有相同的颜色,则继续,否则停止该路径。
3. 到达目的节点后,count 加 1。
注意:颜色数总是小于边数。
C++
// C++ code to find unicolored paths
#include
using namespace std;
const int MAX_V = 100;
int color[MAX_V];
bool vis[MAX_V];
// Graph class represents an undirected graph
// using adjacency list representation
class Graph
{
// vertices, edges, adjancy list
int V;
int E;
vector > adj[MAX_V];
// function used by UniColorPaths
// DFS traversal o from x to y
void dfs(int x, int y, int z);
// Constructor
public:
Graph(int V, int E);
// function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int v, int w, int z);
// finds paths between a and b having
// same color edges
int UniColorPaths(int a, int b);
};
Graph::Graph(int V, int E)
{
this -> V = V;
this -> E = E;
}
void Graph::addEdge(int a, int b, int c)
{
adj[a].push_back({b, c}); // Add b to a’s list.
adj[b].push_back({a, c}); // Add c to b’s list.
}
void Graph::dfs(int x, int y, int col)
{
if (vis[x])
return;
vis[x] = 1;
// mark this as a possible color to reach s to d
if (x == y)
{
color[col] = 1;
return;
}
// if the next edge is also of same color
for (int i = 0; i < int(adj[x].size()); i++)
if (adj[x][i].second == col)
dfs(adj[x][i].first, y, col);
}
// function that finds paths between a and b
// such that all edges are same colored
// It uses recursive dfs()
int Graph::UniColorPaths(int a, int b)
{
// dfs on nodes directly connected to source
for (int i = 0; i < int(adj[a].size()); i++)
{
dfs(a, b, adj[a][i].second);
// to visit again visited nodes
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
}
int cur = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= E; i++)
cur += color[i];
return (cur);
}
// driver code
int main()
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
Graph g(5, 7);
g.addEdge(1, 2, 1);
g.addEdge(1, 3, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 3, 3);
g.addEdge(2, 4, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 5, 4);
g.addEdge(3, 5, 3);
g.addEdge(4, 5, 2);
int s = 2; // source
int d = 5; // destination
cout << "Number of unicolored paths : ";
cout << g.UniColorPaths(s, d) << endl;
return 0;
} Python3
# Python3 code to find unicolored paths
MAX_V = 100
color = [0] * MAX_V
vis = [0] * MAX_V
# Graph class represents a undirected graph
# using adjacency list representation
class Graph:
def __init__(self, V, E):
self.V = V
self.E = E
self.adj = [[] for i in range(MAX_V)]
# Function used by UniColorPaths
# DFS traversal o from x to y
def dfs(self, x, y, col):
if vis[x]:
return
vis[x] = 1
# mark this as a possible color to reach s to d
if x == y:
color[col] = 1
return
# if the next edge is also of same color
for i in range(0, len(self.adj[x])):
if self.adj[x][i][1] == col:
self.dfs(self.adj[x][i][0], y, col)
def addEdge(self, a, b, c):
self.adj[a].append((b, c)) # Add b to a’s list.
self.adj[b].append((a, c)) # Add c to b’s list.
# Function that finds paths between a
# and b such that all edges are same
# colored. It uses recursive dfs()
def UniColorPaths(self, a, b):
global vis
# dfs on nodes directly connected to source
for i in range(0, len(self.adj[a])):
self.dfs(a, b, self.adj[a][i][1])
# to visit again visited nodes
vis = [0] * len(vis)
cur = 0
for i in range(0, self.E + 1):
cur += color[i]
return cur
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Create a graph given in the above diagram
g = Graph(5, 7)
g.addEdge(1, 2, 1)
g.addEdge(1, 3, 2)
g.addEdge(2, 3, 3)
g.addEdge(2, 4, 2)
g.addEdge(2, 5, 4)
g.addEdge(3, 5, 3)
g.addEdge(4, 5, 2)
s = 2 # source
d = 5 # destination
print("Number of unicolored paths : ", end = "")
print(g.UniColorPaths(s, d))
# This code is contributed by Rituraj Jain输出:
Number of unicolored paths : 3
时间复杂度: O(E * (E + V))