彼得森图问题
下面的图 G 被称为彼得森图,它的顶点已经从 0 到 9 编号。一些字母也被分配给 G 的顶点,如下图所示:
让我们考虑图 G 中的游走 W,它由 L 个顶点 W1、W2、...、WL 组成。如果沿 W 写的字母序列等于 S,则由 L 个字母 'A' - 'E' 组成的字符串S 由 walk W 实现。沿 W 行走时可以多次访问顶点。
例如,S = 'ABBECCD' 由 W = (0, 1, 6, 9, 7, 2, 3) 实现。确定在图 G 中是否存在实现给定字符串S 的游走 W,如果是,则找到按字典顺序排列的最少这样的游走。输入的唯一行包含一个字符串S。如果没有实现 S 的 walk W,则输出 -1 否则,您应该输出实现 S 的字典顺序最少的 walk W。
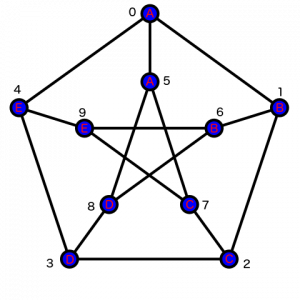
例子:
Input : s = 'ABB'
Output: 016
Explanation: As we can see in the graph
the path from ABB is 016.
Input : s = 'AABE'
Output :-1
Explanation: As there is no path that
exists, hence output is -1.我们应用广度优先搜索来访问图的每个顶点。
C++
// C++ program to find the
// path in Peterson graph
#include
using namespace std;
// path to be checked
char S[100005];
// adjacency matrix.
bool adj[10][10];
// resulted path - way
char result[100005];
// we are applying breadth first search
// here
bool findthepath(char* S, int v)
{
result[0] = v + '0';
for (int i = 1; S[i]; i++) {
// first traverse the outer graph
if (adj[v][S[i] - 'A'] || adj[S[i] -
'A'][v]) {
v = S[i] - 'A';
}
// then traverse the inner graph
else if (adj[v][S[i] - 'A' + 5] ||
adj[S[i] - 'A' + 5][v]) {
v = S[i] - 'A' + 5;
}
// if the condition failed to satisfy
// return false
else
return false;
result[i] = v + '0';
}
return true;
}
// driver code
int main()
{
// here we have used adjacency matrix to make
// connections between the connected nodes
adj[0][1] = adj[1][2] = adj[2][3] = adj[3][4] =
adj[4][0] = adj[0][5] = adj[1][6] = adj[2][7] =
adj[3][8] = adj[4][9] = adj[5][7] = adj[7][9] =
adj[9][6] = adj[6][8] = adj[8][5] = true;
// path to be checked
char S[] = "ABB";
if (findthepath(S, S[0] - 'A') ||
findthepath(S, S[0] - 'A' + 5)) {
cout << result;
} else {
cout << "-1";
}
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find the
// path in Peterson graph
class GFG
{
// path to be checked
static char []S = new char[100005];
// adjacency matrix.
static boolean [][]adj = new boolean[10][10];
// resulted path - way
static char[] result = new char[100005];
// we are applying breadth first search
// here
static boolean findthepath(char[] S, int v)
{
result[0] = (char) (v + '0');
for (int i = 1; i<(int)S.length; i++)
{
// first traverse the outer graph
if (adj[v][S[i] - 'A'] ||
adj[S[i] - 'A'][v])
{
v = S[i] - 'A';
}
// then traverse the inner graph
else if (adj[v][S[i] - 'A' + 5] ||
adj[S[i] - 'A' + 5][v])
{
v = S[i] - 'A' + 5;
}
// if the condition failed to satisfy
// return false
else
return false;
result[i] = (char) (v + '0');
}
return true;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// here we have used adjacency matrix to make
// connections between the connected nodes
adj[0][1] = adj[1][2] = adj[2][3] = adj[3][4] =
adj[4][0] = adj[0][5] = adj[1][6] = adj[2][7] =
adj[3][8] = adj[4][9] = adj[5][7] = adj[7][9] =
adj[9][6] = adj[6][8] = adj[8][5] = true;
// path to be checked
char S[] = "ABB".toCharArray();
if (findthepath(S, S[0] - 'A') ||
findthepath(S, S[0] - 'A' + 5))
{
System.out.print(result);
}
else
{
System.out.print("-1");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-JiPython3
# Python3 program to find the
# path in Peterson graph
# path to be checked
# adjacency matrix.
adj = [[False for i in range(10)] for j in range(10)]
# resulted path - way
result = [0]
# we are applying breadth first search
# here
def findthepath(S, v):
result[0] = v
for i in range(1, len(S)):
# first traverse the outer graph
if (adj[v][ord(S[i]) - ord('A')] or
adj[ord(S[i]) - ord('A')][v]):
v = ord(S[i]) - ord('A')
# then traverse the inner graph
else if (adj[v][ord(S[i]) - ord('A') + 5] or
adj[ord(S[i]) - ord('A') + 5][v]):
v = ord(S[i]) - ord('A') + 5
# if the condition failed to satisfy
# return false
else:
return False
result.append(v)
return True
# driver code
# here we have used adjacency matrix to make
# connections between the connected nodes
adj[0][1] = adj[1][2] = adj[2][3] = \
adj[3][4] = adj[4][0] = adj[0][5] = \
adj[1][6] = adj[2][7] = adj[3][8] = \
adj[4][9] = adj[5][7] = adj[7][9] = \
adj[9][6] = adj[6][8] = adj[8][5] = True
# path to be checked
S= "ABB"
S=list(S)
if (findthepath(S, ord(S[0]) - ord('A')) or
findthepath(S, ord(S[0]) - ord('A') + 5)):
print(*result, sep = "")
else:
print("-1")
# This code is contributed by SHUBHAMSINGH10C#
// C# program to find the
// path in Peterson graph
using System;
public class GFG
{
// adjacency matrix.
static bool [,]adj = new bool[10, 10];
// resulted path - way
static char[] result = new char[100005];
// we are applying breadth first search
// here
static bool findthepath(String S, int v)
{
result[0] = (char) (v + '0');
for (int i = 1; i < S.Length; i++)
{
// first traverse the outer graph
if (adj[v,S[i] - 'A'] ||
adj[S[i] - 'A',v])
{
v = S[i] - 'A';
}
// then traverse the inner graph
else if (adj[v,S[i] - 'A' + 5] ||
adj[S[i] - 'A' + 5,v])
{
v = S[i] - 'A' + 5;
}
// if the condition failed to satisfy
// return false
else
return false;
result[i] = (char) (v + '0');
}
return true;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// here we have used adjacency matrix to make
// connections between the connected nodes
adj[0,1] = adj[1,2] = adj[2,3] = adj[3,4] =
adj[4,0] = adj[0,5] = adj[1,6] = adj[2,7] =
adj[3,8] = adj[4,9] = adj[5,7] = adj[7,9] =
adj[9,6] = adj[6,8] = adj[8,5] = true;
// path to be checked
String S = "ABB";
if (findthepath(S, S[0] - 'A') || findthepath(S, S[0] - 'A' + 5))
{
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
else
{
Console.Write("-1");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by aashish1995输出:
016