R 编程的中心趋势
中心趋势是描述性统计的特征之一。集中趋势说明数据组如何围绕分布的中心值聚集。集中趋势执行以下措施:
- 算术平均值
- 几何平均数
- 谐波平均值
- 中位数
- 模式
算术平均值
算术平均值简称为数字的平均值,代表数据分布的中心值。它是通过将所有值相加然后除以观察总数来计算的。
公式: 
在哪里,
X indicates the arithmetic mean![]() indicates
indicates ![]() value in data vector
value in data vector
n indicates total number of observations
在 R 语言中,可以通过mean()函数计算算术平均值。
Syntax: mean(x, trim, na.rm = FALSE)
Parameters:
x: Represents object
trim: Specifies number of values to be removed from each side of object before calculating the mean. The value is between 0 to 0.5
na.rm: If TRUE then removes the NA value from x
例子:
# Defining vector
x <- c(3, 7, 5, 13, 20, 23, 39, 23, 40, 23, 14, 12, 56, 23)
# Print mean
print(mean(x))
输出:
[1] 21.5
几何平均数
几何平均值是一种平均值,通过将所有数据值相乘计算得出,因此显示了给定数据分布的集中趋势。
公式: ![由 QuickLaTeX.com 渲染 \displaystyle X = \left(\prod _{i=1}^{n}x_{i}\right)^{\frac {1}{n}}={\sqrt[{n}]{x_{1}x_{2}\cdots x_{n}}}](https://mangodoc.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/geek8geeks/Central_Tendency_in_R_Programming_3.png)
在哪里,
X indicates geometric mean![]() indicates
indicates ![]() value in data vector
value in data vector
n indicates total number of observations
prod()和length()函数有助于找到给定数字集的几何平均值,因为几何平均值没有直接函数。
Syntax:
where,
prod() function returns the product of all values present in vector x
length() function returns the length of vector x
例子:
prod(x)^(1/length(x))
输出:
# Defining vector
x <- c(1, 5, 9, 19, 25)
# Print Geometric Mean
print(prod(x)^(1 / length(x)))
谐波平均值
调和平均值是另一种类型的平均值,用作另一种集中趋势的度量。它被计算为给定值的倒数的算术平均值的倒数。
公式: 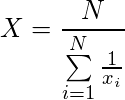
在哪里,
X indicates harmonic mean![]() indicates
indicates ![]() value in data vector
value in data vector
n indicates total number of observations
例子:
修改代码以找到给定值集的调和平均值。
[1] 7.344821
输出:
# Defining vector
x <- c(1, 5, 8, 10)
# Print Harmonic Mean
print(1 / mean(1 / x))
中位数
统计中的中位数是集中趋势的另一种度量,它代表一组给定值的中间值。
在 R 语言中,可以通过median()函数计算中位数。
Syntax: median(x, na.rm = FALSE)
Parameters:
x: It is the data vector
na.rm: If TRUE then removes the NA value from x
例子:
[1] 2.807018
输出:
# Defining vector
x <- c(3, 7, 5, 13, 20, 23, 39,
23, 40, 23, 14, 12, 56, 23)
# Print Median
median(x)
模式
一组给定值的众数是该组中重复次数最多的值。如果有两个或多个具有匹配最大频率的值,则可以存在多个模式值。
示例 1:单模值
在 R 语言中,没有计算众数的函数。因此,修改代码以找出给定值集的模式。
[1] 21.5
输出:
# Defining vector
x <- c(3, 7, 5, 13, 20, 23, 39,
23, 40, 23, 14, 12, 56,
23, 29, 56, 37, 45, 1, 25, 8)
# Generate frequency table
y <- table(x)
# Print frequency table
print(y)
# Mode of x
m <- names(y)[which(y == max(y))]
# Print mode
print(m)
示例 2:多个模式值
x
1 3 5 7 8 12 13 14 20 23 25 29 37 39 40 45 56
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4 1 1 1 1 1 1 2
[1] "23"
输出:
# Defining vector
x <- c(3, 7, 5, 13, 20, 23, 39, 23, 40,
23, 14, 12, 56, 23, 29, 56, 37,
45, 1, 25, 8, 56, 56)
# Generate frequency table
y <- table(x)
# Print frequency table
print(y)
# Mode of x
m <- names(y)[which(y == max(y))]
# Print mode
print(m)