使用 R 编程进行主成分分析
R编程中的主成分分析(PCA) 是对所有现有属性的线性分量的分析。主成分是数据集中原始预测变量的线性组合(正交变换)。它是 EDA(探索性数据分析)的一种有用技术,可让您更好地可视化具有许多变量的数据集中存在的变化。
R – 主成分分析
第一个主成分捕获数据集中的最大方差。它决定了更高可变性的方向。第二个主成分捕获数据中的剩余方差,并且与 PC1 不相关。 PC1 和 PC2 之间的相关性应该为零。因此,所有后续的主成分都遵循相同的概念。它们捕获剩余的方差,而不与之前的主成分相关。
数据集
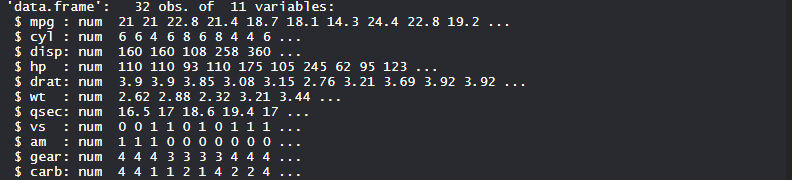
数据集mtcars (电机趋势汽车道路测试)包括 32 辆汽车的油耗和汽车设计和性能的 10 个方面。它预装了 R 中的 dplyr 包。
R
# Installing required package
install.packages("dplyr")
# Loading the package
library(dplyr)
# Importing excel file
str(mtcars)R
# Loading Data
data(mtcars)
# Apply PCA using prcomp function
# Need to scale / Normalize as
# PCA depends on distance measure
my_pca <- prcomp(mtcars, scale = TRUE,
center = TRUE, retx = T)
names(my_pca)
# Summary
summary(my_pca)
my_pca
# View the principal component loading
# my_pca$rotation[1:5, 1:4]
my_pca$rotation
# See the principal components
dim(my_pca$x)
my_pca$x
# Plotting the resultant principal components
# The parameter scale = 0 ensures that arrows
# are scaled to represent the loadings
biplot(my_pca, main = "Biplot", scale = 0)
# Compute standard deviation
my_pca$sdev
# Compute variance
my_pca.var <- my_pca$sdev ^ 2
my_pca.var
# Proportion of variance for a scree plot
propve <- my_pca.var / sum(my_pca.var)
propve
# Plot variance explained for each principal component
plot(propve, xlab = "principal component",
ylab = "Proportion of Variance Explained",
ylim = c(0, 1), type = "b",
main = "Scree Plot")
# Plot the cumulative proportion of variance explained
plot(cumsum(propve),
xlab = "Principal Component",
ylab = "Cumulative Proportion of Variance Explained",
ylim = c(0, 1), type = "b")
# Find Top n principal component
# which will atleast cover 90 % variance of dimension
which(cumsum(propve) >= 0.9)[1]
# Predict mpg using first 4 new Principal Components
# Add a training set with principal components
train.data <- data.frame(disp = mtcars$disp, my_pca$x[, 1:4])
# Running a Decision tree algporithm
## Installing and loading packages
install.packages("rpart")
install.packages("rpart.plot")
library(rpart)
library(rpart.plot)
rpart.model <- rpart(disp ~ .,
data = train.data, method = "anova")
rpart.plot(rpart.model)输出:
使用 R 语言使用数据集进行主成分分析
我们对包含 32 个汽车品牌和 10 个变量的mtcars进行主成分分析。
R
# Loading Data
data(mtcars)
# Apply PCA using prcomp function
# Need to scale / Normalize as
# PCA depends on distance measure
my_pca <- prcomp(mtcars, scale = TRUE,
center = TRUE, retx = T)
names(my_pca)
# Summary
summary(my_pca)
my_pca
# View the principal component loading
# my_pca$rotation[1:5, 1:4]
my_pca$rotation
# See the principal components
dim(my_pca$x)
my_pca$x
# Plotting the resultant principal components
# The parameter scale = 0 ensures that arrows
# are scaled to represent the loadings
biplot(my_pca, main = "Biplot", scale = 0)
# Compute standard deviation
my_pca$sdev
# Compute variance
my_pca.var <- my_pca$sdev ^ 2
my_pca.var
# Proportion of variance for a scree plot
propve <- my_pca.var / sum(my_pca.var)
propve
# Plot variance explained for each principal component
plot(propve, xlab = "principal component",
ylab = "Proportion of Variance Explained",
ylim = c(0, 1), type = "b",
main = "Scree Plot")
# Plot the cumulative proportion of variance explained
plot(cumsum(propve),
xlab = "Principal Component",
ylab = "Cumulative Proportion of Variance Explained",
ylim = c(0, 1), type = "b")
# Find Top n principal component
# which will atleast cover 90 % variance of dimension
which(cumsum(propve) >= 0.9)[1]
# Predict mpg using first 4 new Principal Components
# Add a training set with principal components
train.data <- data.frame(disp = mtcars$disp, my_pca$x[, 1:4])
# Running a Decision tree algporithm
## Installing and loading packages
install.packages("rpart")
install.packages("rpart.plot")
library(rpart)
library(rpart.plot)
rpart.model <- rpart(disp ~ .,
data = train.data, method = "anova")
rpart.plot(rpart.model)
输出:
- 毕情节
- 生成的主成分绘制为Biplot 。比例值 0 表示箭头按比例表示载荷。
- 解释每个主成分的方差
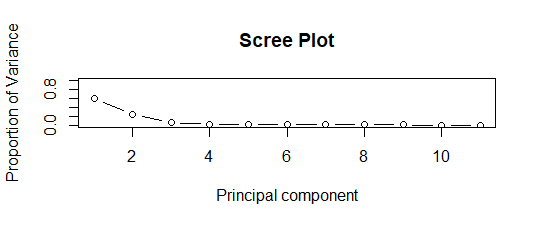
- 碎石图表示方差和主成分的比例。在 2 个主成分以下,有一个最大比例的方差,如图所示。
- 累计方差比例
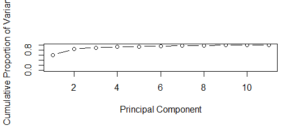
- 碎石图表示方差和主成分的累积比例。在 2 个主成分之上,有一个最大的累积方差比例,如图所示。
- 决策树模型
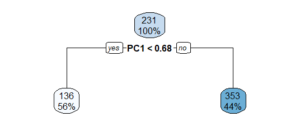
- 建立决策树模型以使用数据集中的其他变量和使用 ANOVA 方法来预测disp 。绘制决策树图并显示信息。