Propan-2-Ol 公式 – 结构、性质、用途、示例问题
Propan-2-Ol属于醇类,因为名字中的Ol可以说很容易。它基本上是仲醇,其中 OH 基团仅与一个氢存在的碳原子相连。让我们来看看这种仲醇的结构、性质和用途。
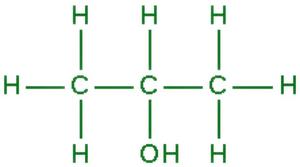
Propan-2-Ol 的结构
异丙醇的 IUPAC 名称。它是最简单的仲醇,是与羟基相连的异丙基。

化学式: CH 3 -CHOH-CH 3
Propan-2-Ol 的制备
- 生物过程
糖尿病酮症酸中毒过程会产生非常少量的 2-丙醇。
- 补水
这个过程可以使用劣质丙烯。这些过程主要产生丙-2-醇(即仲醇)而不是1-丙醇(即伯醇),因为向丙烯中添加水或硫酸遵循马尔科夫尼科夫规则。
CH3CHCH2 + H2O + H2SO4 ⇢ (CH3)2CHOH
2-丙醇的物理性质
- 它是一种无色易燃化合物。它还具有强烈的酒精气味。与乙醇或甲醇不同,propan-2-ol 不与盐溶液混溶,可以通过添加盐(如氯化钠)从水溶液中分离出来。
- 摩尔质量: 60.096 g/mol。
- 密度: 0.786 g/cc
- 沸点: 82.6 °C(180.7 °F;355.8 K)
- 溶解性:溶于水。
化学性质和反应
- 氧化
Propan-2-Ol 被铬酸 (H 2 CrO 4 )氧化并形成丙酮。这是一个脱氢过程。
(CH3)2CHOH ⇢ (CH3)2CO + H2 ⇡
- 脱水
使用443K 的浓 H 2 SO 4或使用440K 的浓 H 3 PO 4对 Propan-2-ol 进行脱水,生成丙烯和水。
(CH3)2CHOH ⇢ CH2=CH-CH3 + H2O
- 卤化
用三溴化磷生成2-溴丙烷。
(CH3)2CHOH ⇢ (CH3)2CHBr
- 其他
Propan-2-Ol 通常用作 Meerwein-Ponndorf-Verley 还原和其他转移氢化反应中的溶剂和氢化物来源。
propan-2-ol 的用途
- 医疗用途:主要用于外用酒精、洗手液、消毒剂。
- 溶剂:最好用作溶剂。与乙醇相比,它蒸发迅速,几乎没有留下任何痕迹,并且相对无毒。
- 实验室使用:它比甲醛等其他防腐剂相对无毒。因此,它比其他人更常用。
- 清洗:用作油类、眼镜、DVD等的清洗液。
示例问题
问题1:丙醇和propan-2-ol在结构上有什么区别?
回答:
The main and basic difference is propanol is a primary alcohol i.e. -OH group is linked with the 1st carbon molecule and propan-2-ol is secondary alcohol i.e. -OH group linked with the 2nd carbon molecule. Propanol is also structurally different because of its primary alcohol thus it makes it less stable than the propan-2-ol.
问题2:propan-2-ol 可以形成共沸物吗?
回答:
Propan-2-ol forms an azeotrope with water, which gives a boiling point of 80.37 °C (176.67 °F) and a composition of 87.7% by mass (91% by volume) propan-2-ol.
问题3:丙-2-醇氧化反应的主要机理是什么?
回答:
In the oxidation reaction, propan-2-ol reacts with oxidizing agent and forms propan-2-one. Here basically secondary alcohol like propan-2-ol is oxidized into ketone. In the sodium, potassium dichromate solution with sulfuric acid or chromic acid gives propan-2-one with a chromium compound. And the hydrogen molecule of secondary carbon and hydroxyl group form water with the [O] of an oxidizing agent. After the removal of two hydrogen molecules, it generates ketone.
问题4:马尔科夫尼科夫规则是什么?
回答:
Markovnikov’s rule is when a protic acid (HX) is added to an asymmetric alkene, alkyne, the acidic hydrogen attaches itself to the carbon having a greater number of hydrogen substituents whereas the halide group attaches itself to the carbon atom which has a greater number of alkyl substituents.
问题5:在propan-2-ol的生产中,马尔科夫尼科夫法则是如何执行的?
回答:
Simply Markovnikov’s rule is hydrogen is added to the carbon with the most hydrogens and halide is added to the carbon with the least hydrogens. To form propan-2-ol from propane Markovnikov’s rule is implemented. When the alkene bond breaks and -OH join with carbon has the least hydrogen i.e. formation of propan-2-ol.
问题 6:为什么 2-丙醇常用作溶剂?
回答:
Propan-2-ol dissolves a wide range of non-polar compounds. It evaporates quickly and the types of available grades tend to not leave behind oil traces when used as a cleaning fluid, unlike some other common solvents. It is also relatively non-toxic. Thus, it is used widely as a solvent.
问题 7:写下一个带有醇基的三碳分子位置异构体的简单例子。
回答:
Propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol are the positional isomers that have the same molecular formula but differ from the position of the -OH group.