📌 相关文章
- JavaFX 多重变换(1)
- JavaFX 多重变换
- JavaFX动画的颜色变换(1)
- JavaFX动画的颜色变换
- JavaFX动画的填充变换(1)
- JavaFX动画的填充变换
- JavaFX动画的path变换
- JavaFX动画的path变换(1)
- python中的z变换(1)
- JavaFX动画的pause变换(1)
- JavaFX动画的pause变换
- JavaFX动画的stroke变换
- JavaFX动画的stroke变换(1)
- JavaFX动画的sequential变换
- JavaFX动画的sequential变换(1)
- python代码示例中的z变换
- JavaFX动画的parallel变换
- JavaFX动画的parallel变换(1)
- Z变换属性(1)
- Z变换属性
- JavaFX动画的尺度变换
- JavaFX |弧与示例(1)
- JavaFX |弧与示例
- 变换 - CSS 代码示例
- Matplotlib-变换(1)
- Matplotlib-变换
- 变换元素 - CSS (1)
- CSS |变换式属性
- CSS |变换属性(1)
📜 JavaFX Shear变换
📅 最后修改于: 2020-10-14 01:53:25 🧑 作者: Mango
JavaFX剪切
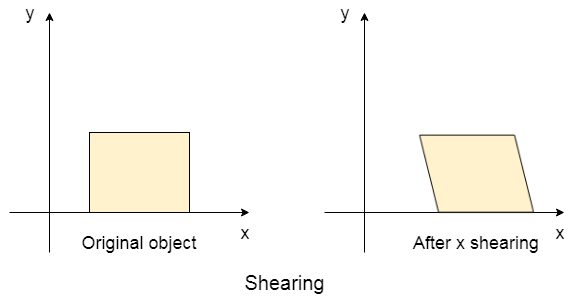
剪切是一种改变对象相对于任何轴的倾斜度的变换。有两个剪切转换,分别是X剪切和Y剪切。 X剪切变形更改X坐标值,而Y剪切更改Y坐标值。
在两种剪切中,只有一个坐标会更改值,而另一坐标保持不变。下图显示了对其应用X剪切转换后的对象。矩形的y坐标保持不变,而X坐标移动了某个因子。
在JavaFX中,类javafx.scene.transform.Shear表示剪切转换。
物产
下表描述了该类的属性以及setter方法。
| Property | Description | Setter Methods |
|---|---|---|
| pivotX | It is a double type property. It represents the X coordinate of the shear pivot point. | setPivotX(double value) |
| pivotY | It is a double type property. It represents the Y coordinate of the shear pivot point. | setPivotY(double value) |
| x | It is a double type property. It represents the multiplier by which the coordinates deviate in the positive X direction as the factor of their Y coordinate. | setX(double value) |
| y | It is a double type property. It represents the multiplier by which the coordinates deviate in the positive Y direction as the factor of their X coordinate. | setY(double value) |
建设者
该类包含三个构造函数
- public Shear():使用默认参数创建一个新的Shear实例。
- public Shear(double x,double y):创建一个具有指定偏移坐标的新实例。枢轴坐标设置为(0,0)。
- public Shear(double x,double y,double axisX,double shaftY):使用指定的偏移坐标和枢轴坐标创建一个新实例。
例:
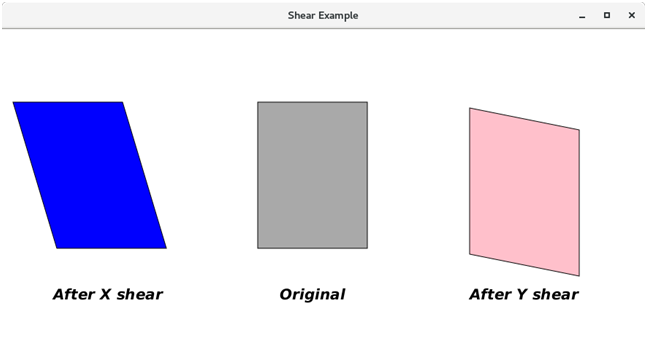
以下示例说明了剪切转换的实现。在这里,我们创建了三个矩形,分别用蓝色,深灰色和粉红色填充。深灰色矩形是原始矩形,蓝色矩形是X剪切的,粉红色矩形是Y剪切的。
package application;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.shape.Rectangle;
import javafx.scene.text.Font;
import javafx.scene.text.FontPosture;
import javafx.scene.text.FontWeight;
import javafx.scene.text.Text;
import javafx.scene.transform.Shear;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class ShearExample extends Application{
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// creating Rectangles
Rectangle rect1 = new Rectangle(60,100,150,200);
Rectangle rect2 = new Rectangle(350,100,150,200);
Rectangle rect3 = new Rectangle(640,100,150,200);
//creating Text node just for the identification
Text text1 = new Text("After X shear");
Text text2 = new Text("Original ");
Text text3 = new Text("After Y shear");
//setting the positions and the fonts for the text nodes
text1.setX(70);
text1.setY(370);
text2.setX(380);
text2.setY(370);
text3.setX(640);
text3.setY(370);
text1.setFont(Font.font("calibri",FontWeight.BOLD,FontPosture.ITALIC,20));
text2.setFont(Font.font("calibri",FontWeight.BOLD,FontPosture.ITALIC,20));
text3.setFont(Font.font("calibri",FontWeight.BOLD,FontPosture.ITALIC,20));
//setting the color and stroke for the rectangles
rect1.setFill(Color.BLUE);
rect1.setStroke(Color.BLACK);
rect2.setFill(Color.DARKGRAY);
rect2.setStroke(Color.BLACK);
rect3.setFill(Color.PINK);
rect3.setStroke(Color.BLACK);
//creating the shear transformation
Shear shearX = new Shear();
// setting properties for the shear, the Y coordinate // needs to set to (0,0) for the X-shear transformation
shearX.setPivotX(200);
shearX.setPivotY(250);
shearX.setX(0.3);
shearX.setY(0.0);
// applying the shear to first rectangle.
rect1.getTransforms().add(shearX);
//creating the shear for third rectangle
Shear shearY = new Shear();
//setting the properties for shear, X coordinate needs // to be set to (0,0) in order to implement Y-shear
shearY.setPivotX(600);
shearY.setPivotY(80);
shearY.setX(0.0);
shearY.setY(0.2);
rect3.getTransforms().add(shearY);
Group root = new Group();
root.getChildren().addAll(rect1,rect2,rect3,text1,text2,text3);
Scene scene = new Scene(root,880,420);
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
primaryStage.setTitle("Shear Example");
primaryStage.show();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}