微分方程用于描述许多物理现象。它们帮助我们观察现实生活中发生的事情,并将其以数学形式表示。在此级别上,我们主要关注线性和一阶微分方程。如果y的所有导数仅出现一次幂,则“ y”中的微分方程为线性。因此,它具有以下形式:y的所有导数仅出现在一次幂上。它的形式如下
![]()
允许系数仅取决于自变量。注意,该顺序可以任意大。我们将看一下精确的微分方程。这些方程是一阶微分方程。
精确的微分方程
它是一阶微分方程,看起来像
M(x,y)dx + N(x,y)dy = 0
它有一个特殊的函数I(x,y),它的偏导数可以代替M和N,例如,
![]()
解决这些方程式意味着找到函数I(x,y)=C。
检查方程是否正确:
假设有一个求解函数I(x,y)。然后,
![]()
![]()
他们最终应该一样。因此,要检查方程是否正确,只需计算这些偏导数即可。因此,既然我们已经检查了方程的正确性,我们将继续寻找该方程的解。
计算精确微分方程的解:
通用解可以通过以下两种方式之一进行计算:
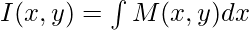 (以x为自变量)
(以x为自变量) 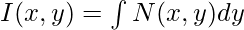 (以y为自变量)
(以y为自变量)
这样,一般的解决方案就变成了
I(x,y)= C
样本问题
问题1:求解:(3x 2 y 3 – 5x 4 )dx +(y + 3x 3 y 2 )dy = 0
解决方案:
Here, M(x, y) = 3x2y3 – 5x4 and N(x, y) = y + 3x3y2
First check if this equation is exact or not,
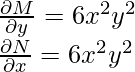
Since both of these are same, the equation is exact.
Now let’s find the solution of this equation,
I
Notice that we are writing f(y) in place constant of integration “C”, because we had y as a fixed parameter while integrating it, but we know that is a variable, so we need to calculate f(y).
We know, 
Let’s plug in f(y) in the general solution,
![]()
This is the general solution for this exact differential equation.
问题2:针对以下问题求解微分方程:
(x 2 + 3y 2 )dy + 2xydx = 0
解决方案:
M(x, y) = 2xy, N(x, y)=x2+3y2
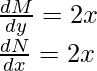
Therefore, the equation is exact.
Solution of this equation: I(x, y)=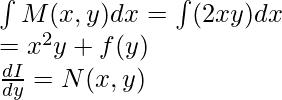
Substituting I(x, y) obtained:

Put the value of f(y) in I(x, y):
I(x, y)= x2y+y3+C
This is the general solution for the exact differential equation.
问题3:求解y dx +(2y + xe y )dy = 0
解决方案:
M(x, y) = ey, N(x, y) = (2y+xey)
Solving ![]()
![]()
Hence, the given equation is exact equation.
Solution of the equation: I(x, y) = ![]()
It is known that dI/dy = N(x, y)
Substituting I(x, y):

Therefore, the solution for the exact equation obtained is,
I(x, y) = xey + y2 + C
整合因子
这也是求解线性微分方程的另一种方法。
![]()
上式表示线性一阶微分方程。 P和Q是x的常数或函数。以下步骤概述了如何使用积分因子求解这种形式的一阶线性方程。
步骤1:以形式写给定的微分方程![]() ,其中P和Q只是常数或x的函数。
,其中P和Q只是常数或x的函数。
步骤2:找出整合因素![]()
步骤3:将微分方程的解写为![]()
Note: In case, the first-order differential equation is in the form ![]() , where P1 and Q1 are constants or functions of y only. Then
, where P1 and Q1 are constants or functions of y only. Then ![]() and the solution of the differential equation is given by
and the solution of the differential equation is given by ![]()
样本问题
问题1:找到以下方程式的一般解,
![]()
解决方案:
The equation matches the form given above, so here P = -1 and Q = cosx.
Therefore, ![]()
Multiplying both sides of the equation by I.F.
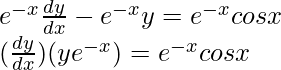
Integrating both sides of the equation by I.F, we get
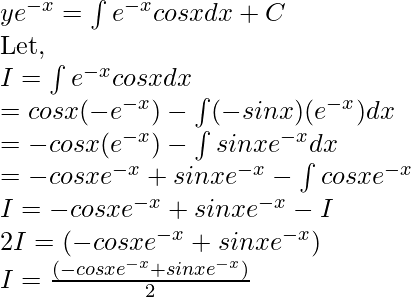
Putting this value in the original equation,
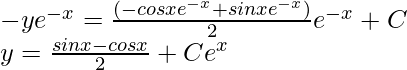
This is the general solution of the given differential equation.
问题2:找到微分方程的一般解,
![]()
解决方案:
P= -3/(x+1), Q=(x+1)4
First, find the I.F.,
I.F.=
Multiply by Integrating factor on both sides:
![]()
Integrate both sides:
![]()
Hence, the general equation is:
y = (x+1)3(0.5x2+x+c)
问题3:微分方程的一般解是?
![]()
解决方案:
First, find the I.F’
P = 3/x, Q = ex/x3
I.F = ![]()
Therefore, I.F = x3
Multiply Integrating factor on both sides,
![]()
Integrate both sides,

特殊整合因素
到目前为止,我们已经了解了关于精确微分方程的所有知识以及如何求解它们,但是有时我们会遇到某些方程“几乎精确”但不是精确的微分方程,因为它们不是精确的,而是通过做一些事而由精确微分方程形成的。他们的变化。如果我们可以追溯并再次使方程式精确,则该问题将很容易解决。
为了追溯到精确积分因子,可将方程式与一个称为“特殊积分因子”的乘积相乘。 ![]() 或者
或者![]() (取决于问题陈述)。
(取决于问题陈述)。
仅使用x的积分因子
假设给定的几乎精确的方程M(x,y)dx + N(x,y)dy = 0 [几乎精确]
让我们乘以特殊的积分因子![]()
![]() ×M(x,y)dx +
×M(x,y)dx + ![]() ×N(x,y)dy = 0
×N(x,y)dy = 0
现在,为了使上述方程式精确,必须具有以下值: ![]() 特殊积分因子的公式,
特殊积分因子的公式,
问题:求解微分方程,(1 + y 2 )dx + xydy = 0
解决方案:
To begin with, we first need to check the exactness of the differential equation
dM/dy = 2y, dN/dx = y
Now, as the equation is not exact, we need to find out the integration factor that is needed to be adjusted in the equation to make it exact.
(dM/dy- dN/dx) = 2y-y = y
1/N{dM/dy- dN/dx}=y/(xy)= 1\x
Here, we figured that the equation depends on x only.
Therefore, the integrating factor is ![]()
![]()
Separate the variables and integrate both sides,
![]()
![]()
We obtained the value of integrating factor, multiply this with our original equation
(x+xy2)dx + x2ydy=0
Checking for exactness again,
dM/dy= 2xy, dN/dx= 2xy
Integrate M and N as usual,
M(x, y)= ![]()
Substitute to determine f(y)
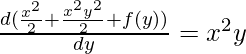
It follows f(y)=C where, C is a Constant.
Therefore, the general solution becomes,
![]()
仅使用y的积分因子
同样,可以通过将几乎精确的方程乘以特殊的积分因子来获得精确方程![]() ,公式为
,公式为
问题:求解微分方程,(2y 2 + 2y + 4x 2 )dx +(2xy + x)dy = 0
解决方案:
To begin with, we need to check if the following equation is exact or not,
dM/dy = (4y +2), dN/dx = (2y +1)
dM/dy ≠ dN/dx {the equation is not exact}
In order to find the Integrating factor, solve the value of ![]()
![]() =1/x
=1/x
Since the value obtained is purely a function of x, we can conclude that the special integrating factor is ![]()
![]() = elnx= x
= elnx= x
Multiply the special integrating factor with the original equation,
x[(2y2+2y+4x2)dx + (2xy +x) dy]=0
(2xy2+2xy+4x3)dx + (2x2y +x2) dy=0
Finding the exactness of the differential equation obtained,
dM/dy=(4xy+2x), dN/dx=(4xy+2x)
Now we can integrate M and N as usual,
![]()
![]()
Therefore, Solution: x2y2+x2y+x4=C