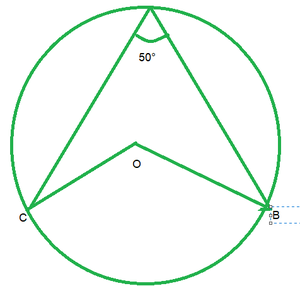
问题1.在图中,O是圆的中心。如果∠APB∠APB= 50°,找到findAOB和∠OAB。
解决方案:
∠APB=50°
By degree measure theorem
∠AOB=2APB
∠APB=2*50°=100°
since OA=OB [Radius of circle]
Then ∠OAB=∠OBA [Angles opposite to equal sides]
Let ∠OAB=x
In △OAb, by angle sum property
∠OAB+∠OBA+∠AOB=180°
x+x+100°=180°
2x=180°-100°
2x=80°
x=40°
∠OAB=∠OBA=40°
问题2。在图中,假设O是圆的中心,∠AOC= 150°。查找∠ABC。

解决方案:
∠AOC = 150°
∠AOC +reflex ∠AOC = 360° [complex angle]
150°+reflex ∠AOC = 360°
reflex ∠AOC=210°
2∠ABC=210° [By degree measure theorem]
∠ABC=210°/2=105°
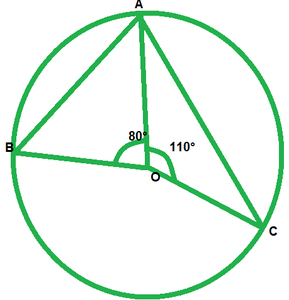
问题3。在图中,O是圆的中心。查找∠BAC。
解决方案:
We have ∠AOB=80°
And ∠AOC=110°
Therefore, ∠AOB+∠AOC+∠BOC=360° [complete angle]
80+100+∠BOC=360°
∠BOC=360°-80°-110°
∠BOC=70°
By degree measure theorem
∠BOC=2∠BAC
170=2∠BAC
∠BAC=170°/2=85°
问题4.如果O是圆的中心,请在以下每个图中找到x的值。
解决方案:
i)
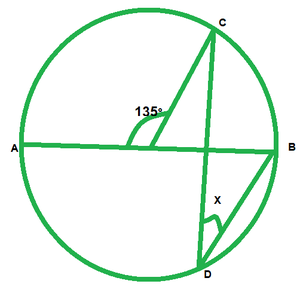
∠AOC=135°
∠AOC+BOC=185° [Linear pair of angles]
135°+∠BOC=180°
∠BOC=180°-135°=45°
By degree measure theorem
∠BOC=2∠COB
45=2x
x=45°/2=22\frac{1}{2}
ii)
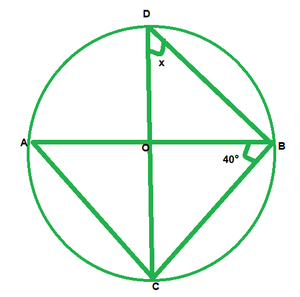
We have
∠ABC=40°
∠ACB=90° [Angle in semicircle]
In △ABC, by angle sum property
∠CAB+∠ACB+∠ABC=180°
∠CAB+90°+40°=180°
∠CAB=180°-90°-40°
∠CAB=50°
Now,
∠CDB=∠CAB [Angle is same in segment]
x=50°
iii)
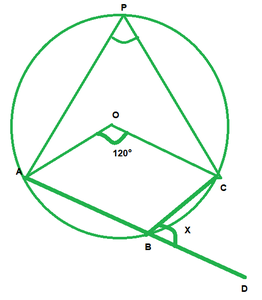
We have,
∠AOC=120°
By degree measure theorem
∠AOC=2∠APC
120°=2∠APC
∠APC=120°/2=60
∠APC+∠ABC=180° [Opposite angles of cyclic quadrilaterals]
60°+∠ABC=180°
∠ABC=180°-60°
∠ABC=120°
∠ABC+∠DBC=180° [Linear pair of angles]
120°+x=180°
x=180°-120°=60°
iv)
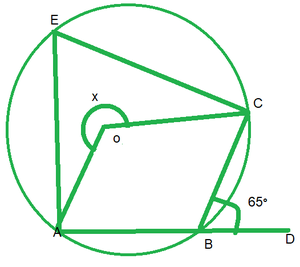
We have
∠CBD=65°
∠ABC+∠CBD=180° [Linear pair of angles]
∠ABC=65°=180°
∠ABC=180°-65°=115°
reflex ∠AOC=2∠ABC [By degree measure theorem]
x=2*115°
x=230°
v)

We have,
∠OAB=35°
Then, ∠OBA=∠OAB=35° [Angles opposite to equal radii]
In △AOB, by angle sum property
∠AOB+∠OAB+∠OBA=180°
∠AOB+35°+35°=180°
∠AOB=180°-35°=110°
∠AOB+reflex ∠AOB=360° [complex angle]
110+reflex∠AOB=360°
reflex∠AOB=360°-110°=250°
By degree measure theorem reflex∠AOB=2∠ACB
250°=2x
x=250°/2=125°
vi)
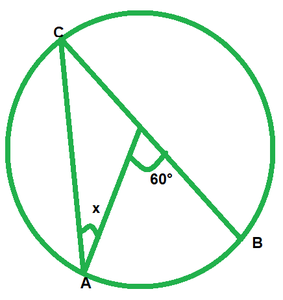
We have,
∠AOB=60
By degree measure theorem reflex
∠AOB=2∠ACB
60=2∠ACB
∠ACB=60°/2=30° [Angle opposite to equal radii]
x=30°
vii)

We have,
∠BAC=50° and ∠DBC=70°
∠BDC=∠BAC=50° [Angle in same segment]
In △BDC, by angle sum property
∠BDC+∠BCD+∠DBC=180°
50°+x+70°=180°
x=180°-50°-70°=60°
viii)
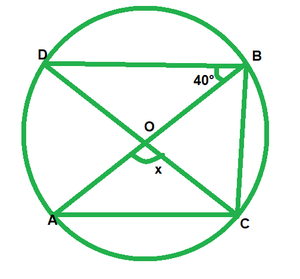
We have,
∠DBO=40° and ∠DBC=90° ——-[Angle in a semi circle]
∠DBO+∠OBC=90°
40°+∠OBC=90°
∠OBC=90°-40°=50°
By degree measure theorem
∠AOC=∠OBC
x=2*50°=100°
ix)
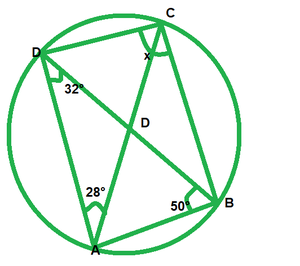
In ∆DAB, by angle sum property
∠ADB+∠DAB+∠ABD=180°
32°+∠DAB+50°=180°
∠DAB=180°-32°-50°
∠DAB=98°
Now,
∠OAB+∠DCB=180° [opposite angle of cyclic quadrilateral]
98°+x=180°
x=180°-98°=82°
x)
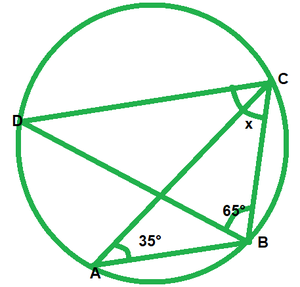
We have,
∠BAC=35°
∠BDC=∠BAC=35° [Angle in same segment]
In ∆BCD, by angle sum property
∠BDC+∠BCD+∠DBC=180°
35°+x+65°=180°
x=180°-35°-65°=80°
xi)

We have,
∠ABD=40°
∠ACD=∠ABD=40° [Angle in same segment]
In ∆PCD, by angle sum property
∠PCD+∠CPO+∠PDC=180°
40°+110°+x=180°
x=180°-150°
x=30°
xii)

Given that,
∠BAC=52°
Then ∠BDC=∠BAC=52° [Angle in same segment]
Since OD=OC
Then ∠ODC=∠OCD [ Opposite angle to equal radii]
x=52°
问题5。O是三角形ABC的外接中心,OD在BC上垂直。证明∠BOD=∠A。
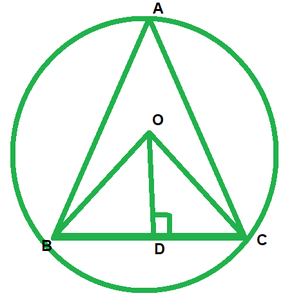
解决方案:
We have to prove that ∠BOD=∠A
since, circum center is the intersection of perpendicular bisector of each side of the the triangle. Now according to figure A,B,C are the vertices of ∆ABC
In ∆BOC, OD is perpendicular bisector of BC.
so, BD=CD
OB=OC ——–(Radius of the same circle)
And,
OD=OD —–[common]
Therefore,
∆BDO≅∆CDO (SSS concurrency criterion )
∠BOD=∠COD (by cpct)
We know that angle formed any chord of the circle at the center is twice of the angle formed at the circumference by same chord
Therefore,
∠BAC=\frac{1}{2} ∠BOC
∠BAC=\frac{1}{2}*2∠BOD
∠BAC=∠BOD
Therefore,
∠BOD=∠A
问题6。在图中,O是圆心,BO是∠ABC的平分线。证明AB = AC。
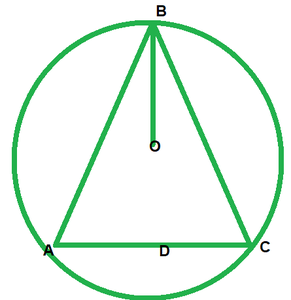
解决方案:
Given, BO is the bisector of ∠ABC
To prove: AB=BC
Proof: Since, BO is the bisector of ∠ABC.
Then, ∠ABO=∠CBO —-(i)
Since, OB=OA [Radius of circle]
Then, ∠ABO=∠DAB ——–(ii) [opposite angles to equal sides]
Since OB=OC [Radius of circle]
Then, ∠OAB=∠OCB ——–(iii) [opposite angles to equal sides]
compare equations (i), (ii) and (iii)
∠OAB=∠OCB ——-(iv)
In ∆OAB and ∆OCB
∠OAB=∠OCB [From(iv)]
∠OBA=∠OBC [Given]
OB=OB [common]
Then
∆OAB≅∆OCB [By AAS condition]
Therefore, AB=BC [CPCT]
问题7。在图中,O为圆心,证明∠x=∠y+∠z。
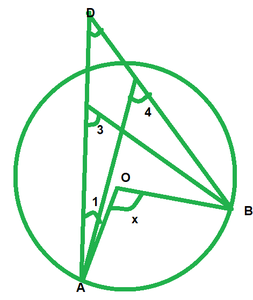
解决方案:
We have,
∠3=∠4 [Angles in same segment]
∠x=2∠3 [By degree measure theorem]
∠x=∠3+∠3⇒∠x=∠3+∠4 ——–(i) [∠3=angle 4]
But ∠y=∠3+∠1 [By exterior angle property]
⇒∠3=∠y-∠1 —-(ii)
from (i) and (ii)
∠x=∠y-∠1+∠4
∠x=∠y+∠4-∠1
∠x=∠y+∠z+∠1-∠1 [By exterior angle property]
∠x=∠y+∠z
问题8。在图中,O和O’是在B和C相交的两个圆的中心。ACD是一条直线,找到x。
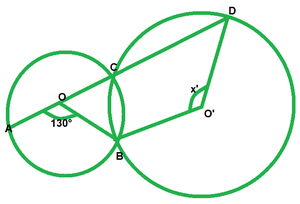
解决方案:
By degree measure theorem
∠AOB=2∠ACB
130°=2∠ACB⇒∠ACB=130°/2=65
∠ACB+∠BCD=180° [Linear pair of angles]
65°+∠BCD=180°
∠BCD=180-65=115
By degree measure theorem
reflex∠BOD=2∠BCD
reflex∠BOD=2*115°=230°
Now, reflex∠BOD+∠BOD=360° [complex angle]
230°+x=360°
x=360°-230°
x=130°
问题9。在图中,O是圆心,PQ是直径。如果∠ROS= 40°,则找到∠RTS。
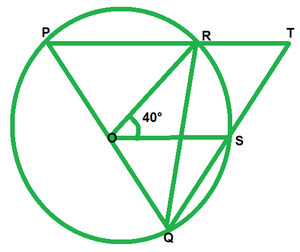
解决方案:
Since PQ is diameter
Then,
∠PRQ=90° [Angle in semi circle]
∠PRQ+∠TRQ=180° [Linear pair of angle]
90+∠TRQ=180
∠TRQ=180°-90°=90°
By degree measure theorem
∠ROS=2∠RQS
40=2∠RQS
∠RQS=40°/2=20°
In ∆RQT, by angle sum property
∠RQT+∠QRT+∠RTS=180°
20°+90°+∠RTS=180°
问题10。在图中,如果∠ACB= 40°,∠DPB= 120°,则找到∠CBD。

解决方案:
We have,
∠ACB=40°; ∠DPB=120°
∠APB=∠DCB=40° [Angle in same segment]
In ∆POB, by angle sum property
∠PDB+∠PBD+∠BPD=180°
40+∠PBD+120°=180°
∠PBD=180°-40°-120°
∠PBD=20°
∠CBD=20°
问题11:圆的和弦等于圆的半径。在小弧上的一个点以及在大弧上的一个点上找到弦对着的角度。

解决方案:
Construction: O is center and r is radius and given that chord is equal to radius of circle.
Now in ∆AOB we have
AO=OB=BA (It is given that chord is equal to radius of circle)
so, ∆AOB is an equilateral triangle
∠AOB=60°
So, ∠AOB=2∠ADB (The angle subtended by an arc of a circle at the center is double the angle subtended by it at any point on the remaining prat of the circle)
Then ∠ADB=30°
So,
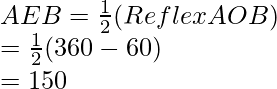
Therefore,
∠ADB=30° and ∠AEB=150°