先决条件– ERP系统的演进
1.物料需求计划(MRP):
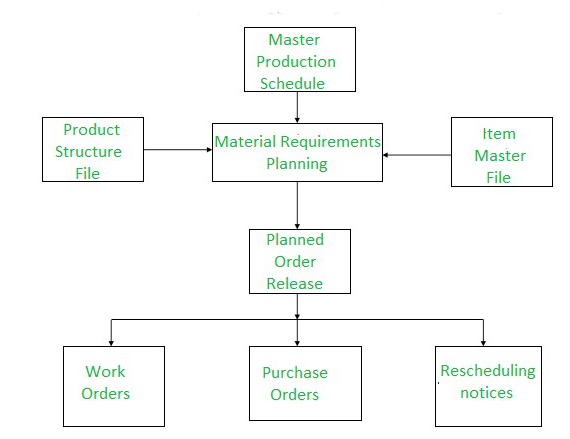
开发于1970年代,可以管理任何组织需要的原材料,即公司需要的原材料都存储在数据库中。此外,它还告诉您任何材料的短缺。物料需求计划是工业生产计划和计划中广泛使用的方法。
MRP的函数是提供物料可用性,即用于按时生产需求数量。此过程涉及监视库存和需求,从而自动创建用于采购或生产的采购建议。 MRP的主要目标是确定所需的材料,所需的数量以及所需的时间。这是要素材料清单,并强调实际资产。
2.制造资源计划(MRP II):
制造资源计划开发于1980年代,是对管理整个制造公司的闭环MRP的扩展。该系统提供了对所有功能区域有用的信息,并鼓励跨功能的交互。在这种情况下,制造单位下的任务是自动化的或与之相关的,因此最终的产量应提高。
它通过提供和订购有希望的功能来支持销售和市场营销。它是基础广泛的资源协调系统,在计划过程中涉及公司的其他领域,例如营销,财务和人力资源。

MRP和MRP II之间的区别:
| MRP | MRP II |
|---|---|
| Stands for Material Requirements Planning. | Stands for Manufacturing Resource Planning. |
| Developed in 1970s. | Developed in 1980s. |
| Widely used approach for production planning and scheduling in industry. | Provides an information that is useful to all functional areas and encourages cross-functional interactions. |
| Aims at releasing and managing manufacturing orders and purchasing requisitions. | Aims to control relevant material flows and production capacity while also taking into account the relationship between these material flows and the required capacity. |
| MRP is simply about ensuring the materials which are available to manufacture a specific part in a specific volume. | It take care of all other aspects of a job including ordering, tracking inventory and ensuring capacity. |
| It takes inputs all in order to make sure you have the right amount of materials/labor/machinery on hand at any given time to satisfy the market or your company production goals. | MRP II uses additional data from accounting records and sales for further analysis and forecasting of manufacturing requirements. |