给定图中元素属于不同连通分量的最大对
给定一个具有从0 到 (N-1)编号的N个顶点的图和一个表示图边缘的矩阵edges[][] ,任务是找出可以形成的最大对数,其中每个元素pair 属于图的不同连通分量。
例子:
Input: N = 4, edges = {{1, 2}, {2, 3}}
Output: 3
Explanation: Total nodes 4 (from 0 to 3).
There are 3 possible pairs: {0, 1}, {0, 2} and {0, 3}.
No pair between {1, 2} or {1, 3} or {2, 3} because they belong to the same connected component.
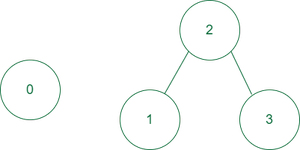
graph with given edges
Input: N = 2, edges = {0, 1}
Output: 0
Explanation: All the elements belong to the same connected component.
方法:可以通过计算连通分量的数量和每个连通分量中的节点数来解决问题。从给定的 N 个节点可以形成总共N*(N-1)/2个节点。但是,要获得所需的对数,减去每个连接组件的节点之间可以形成的对数。请按照以下步骤操作:
- 将total初始化为可能对的总数,即N*(N-1)/2 。
- 使用DFS查找不同的连接组件和每个组件:
- 找出该连接组件中的节点数并将其存储在变量中(例如cnt )。
- 减去这些节点之间可以形成的对数,即cnt*(cnt – 1)/2 。
- 访问完所有节点后, total的剩余值就是最终的答案。
下面是上述方法的实现
C++
// C++ code to implement the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// DFS function
void dfs(vector adj[], int src,
bool visited[], int& cnt)
{
visited[src] = true;
// Count number of nodes
// in current component
cnt++;
for (auto it : adj[src]) {
if (!visited[it]) {
dfs(adj, it, visited, cnt);
}
}
}
// Function to count total possible pairs
int maxPairs(int N,
vector >& edges)
{
vector adj[N];
// Building the adjacency matrix
for (int i = 0; i < edges.size(); i++) {
adj[edges[i][0]].push_back(
edges[i][1]);
adj[edges[i][1]].push_back(
edges[i][0]);
}
// Maximum total pairs
int total = N * (N - 1) / 2;
// Array to keep track of components
bool visited[N + 1] = { false };
// Loop to count total possible pairs
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (visited[i] == false) {
int cnt = 0;
dfs(adj, i, visited, cnt);
// Subtract pairs from
// the same connected component
total -= (cnt * (cnt - 1) / 2);
}
}
return total;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int N = 4;
vector > edges = { { 1, 2 },
{ 2, 3 } };
int result = maxPairs(N, edges);
cout << result;
return 0;
} Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int count = 0;
// DFS function
public static void
dfs(ArrayList > adj, int src,
boolean visited[])
{
visited[src] = true;
// Count number of nodes
// in current component
count++;
for (int it : adj.get(src)) {
if (!visited[it]) {
dfs(adj, it, visited);
}
}
}
// Function to count total possible pairs
public static int
maxPairs(int N, ArrayList > edges)
{
ArrayList > adj
= new ArrayList >();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
ArrayList temp
= new ArrayList();
adj.add(temp);
}
// Building the adjacency matrix
for (int i = 0; i < edges.size(); i++) {
ArrayList temp
= adj.get(edges.get(i).get(0));
temp.add(edges.get(i).get(1));
adj.set(edges.get(i).get(0), temp);
temp = adj.get(edges.get(i).get(1));
temp.add(edges.get(i).get(0));
adj.set(edges.get(i).get(1), temp);
}
// Maximum total pairs
int total = N * (N - 1) / 2;
// Array to keep track of components
boolean[] visited = new boolean[N + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) {
visited[i] = false;
}
// Loop to count total possible pairs
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (visited[i] == false) {
count = 0;
dfs(adj, i, visited);
// Subtract pairs from
// the same connected component
total -= (count * (count - 1) / 2);
}
}
return total;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 4;
ArrayList > edges
= new ArrayList >();
edges.add(
new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(1, 2)));
edges.add(
new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(2, 3)));
int result = maxPairs(N, edges);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Palak Gupta Python3
# python3 code to implement the approach
visited = []
cnt = 0
# DFS function
def dfs(adj, src):
global visited
global cnt
visited[src] = True
# Count number of nodes
# in current component
cnt += 1
for it in adj[src]:
if (not visited[it]):
dfs(adj, it)
# Function to count total possible pairs
def maxPairs(N, edges):
global visited
global cnt
adj = [[] for _ in range(N)]
# Building the adjacency matrix
for i in range(0, len(edges)):
adj[edges[i][0]].append(edges[i][1])
adj[edges[i][1]].append(edges[i][0])
# Maximum total pairs
total = (N * (N - 1)) // 2
# Array to keep track of components
for i in range(N + 1):
visited.append(False)
# Loop to count total possible pairs
for i in range(0, N):
if (visited[i] == False):
cnt = 0
dfs(adj, i)
# Subtract pairs from
# the same connected component
total -= ((cnt * (cnt - 1)) // 2)
return total
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
N = 4
edges = [[1, 2], [2, 3]]
result = maxPairs(N, edges)
print(result)
# This code is contributed by rakeshsahniC#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static int count = 0;
// DFS function
public static void
dfs(List> adj, int src, bool[] visited)
{
visited[src] = true;
// Count number of nodes
// in current component
count++;
foreach (int it in adj[src])
{
if (!visited[it])
{
dfs(adj, it, visited);
}
}
}
// Function to count total possible pairs
public static int
maxPairs(int N, List> edges)
{
List> adj = new List>();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
List temp = new List();
adj.Add(temp);
}
// Building the adjacency matrix
for (int i = 0; i < edges.Count; i++)
{
List temp = adj[edges[i][0]];
temp.Add(edges[i][1]);
adj[edges[i][0]] = temp;
temp = adj[edges[i][1]];
temp.Add(edges[i][0]);
adj[edges[i][1]] = temp;
}
// Maximum total pairs
int total = N * (N - 1) / 2;
// Array to keep track of components
bool[] visited = new bool[N + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++)
{
visited[i] = false;
}
// Loop to count total possible pairs
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if (visited[i] == false)
{
count = 0;
dfs(adj, i, visited);
// Subtract pairs from
// the same connected component
total -= (count * (count - 1) / 2);
}
}
return total;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int N = 4;
List> edges = new List>();
edges.Add(new List());
edges.Add(new List());
edges[0].Add(1);
edges[0].Add(2);
edges[1].Add(2);
edges[1].Add(3);
int result = maxPairs(N, edges);
Console.Write(result);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Saurabh Jaiswal Javascript
输出
3时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)