给定一个权重可能为负的加权有向图,使用约翰逊算法找到图中每对顶点之间的最短路径。
Johnson 算法的详细解释已在前一篇文章中讨论过。
参考:Johnson 的 All-pairs 最短路径算法。
这篇文章的重点是约翰逊算法的实现。
算法:
- 让给定的图为 G。向图中添加一个新顶点 s,将新顶点的边添加到 G 的所有顶点。让修改后的图为 G’。
- 以 s 作为源在 G’ 上运行 Bellman-Ford 算法。让 Bellman-Ford 计算的距离为 h[0], h[1], .. h[V-1]。如果我们发现负权重循环,则返回。请注意,新顶点 s 不能创建负权重循环,因为 s 没有边。所有的边都来自 s。
- 重新加权原始图的边缘。对于每条边 (u, v),将新权重分配为“原始权重 + h[u] – h[v]”。
- 删除添加的顶点 s 并对每个顶点运行 Dijkstra 算法。
例子:
让我们考虑下图。
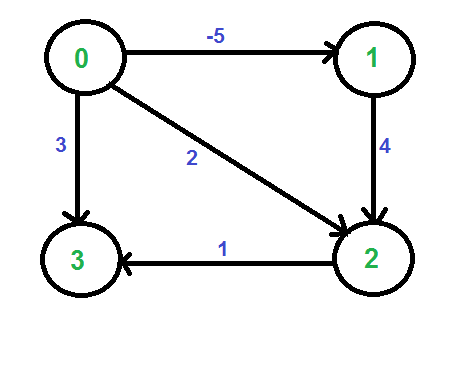
我们添加一个源 s 并将来自 s 的边添加到原始图的所有顶点。在下图中,s 是 4。
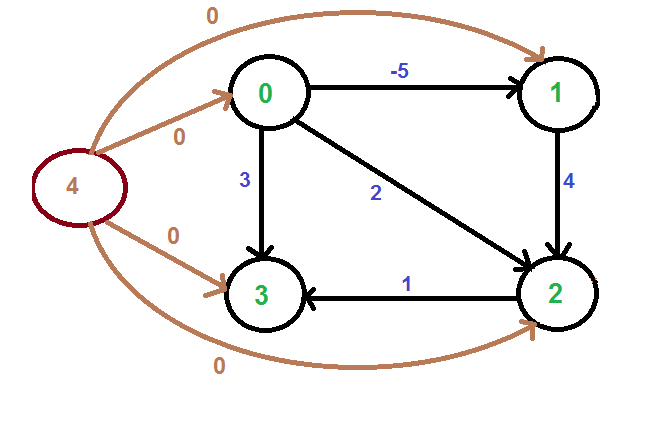
我们使用 Bellman-Ford 算法计算从 4 到所有其他顶点的最短距离。 4到0、1、2、3的最短距离分别为0、-5、-1、0,即h[] = {0, -5, -1, 0}。获得这些距离后,我们移除源顶点 4 并使用以下公式重新加权边缘。 w(u, v) = w(u, v) + h[u] – h[v]。
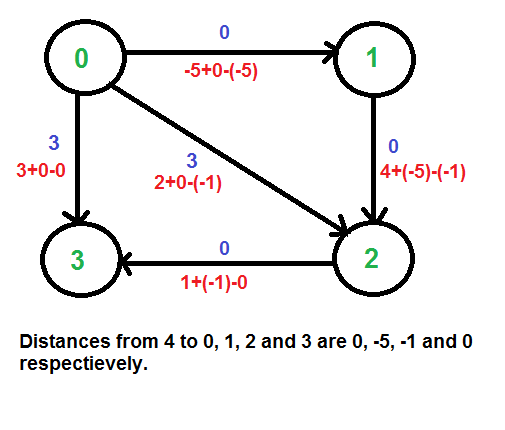
由于现在所有的权重都是正的,我们可以为每个顶点运行 Dijkstra 最短路径算法作为源。
下面是上述方法的实现
# Implementation of Johnson's algorithm in Python3
# Import function to initialize the dictionary
from collections import defaultdict
MAX_INT = float('Inf')
# Returns the vertex with minimum
# distance from the source
def minDistance(dist, visited):
(minimum, minVertex) = (MAX_INT, 0)
for vertex in range(len(dist)):
if minimum > dist[vertex] and visited[vertex] == False:
(minimum, minVertex) = (dist[vertex], vertex)
return minVertex
# Dijkstra Algorithm for Modified
# Graph (removing negative weights)
def Dijkstra(graph, modifiedGraph, src):
# Number of vertices in the graph
num_vertices = len(graph)
# Dictionary to check if given vertex is
# already included in the shortest path tree
sptSet = defaultdict(lambda : False)
# Shortest distance of all vertices from the source
dist = [MAX_INT] * num_vertices
dist[src] = 0
for count in range(num_vertices):
# The current vertex which is at min Distance
# from the source and not yet included in the
# shortest path tree
curVertex = minDistance(dist, sptSet)
sptSet[curVertex] = True
for vertex in range(num_vertices):
if ((sptSet[vertex] == False) and
(dist[vertex] > (dist[curVertex] +
modifiedGraph[curVertex][vertex])) and
(graph[curVertex][vertex] != 0)):
dist[vertex] = (dist[curVertex] +
modifiedGraph[curVertex][vertex]);
# Print the Shortest distance from the source
for vertex in range(num_vertices):
print ('Vertex ' + str(vertex) + ': ' + str(dist[vertex]))
# Function to calculate shortest distances from source
# to all other vertices using Bellman-Ford algorithm
def BellmanFord(edges, graph, num_vertices):
# Add a source s and calculate its min
# distance from every other node
dist = [MAX_INT] * (num_vertices + 1)
dist[num_vertices] = 0
for i in range(num_vertices):
edges.append([num_vertices, i, 0])
for i in range(num_vertices):
for (src, des, weight) in edges:
if((dist[src] != MAX_INT) and
(dist[src] + weight < dist[des])):
dist[des] = dist[src] + weight
# Don't send the value for the source added
return dist[0:num_vertices]
# Function to implement Johnson Algorithm
def JohnsonAlgorithm(graph):
edges = []
# Create a list of edges for Bellman-Ford Algorithm
for i in range(len(graph)):
for j in range(len(graph[i])):
if graph[i][j] != 0:
edges.append([i, j, graph[i][j]])
# Weights used to modify the original weights
modifyWeights = BellmanFord(edges, graph, len(graph))
modifiedGraph = [[0 for x in range(len(graph))] for y in
range(len(graph))]
# Modify the weights to get rid of negative weights
for i in range(len(graph)):
for j in range(len(graph[i])):
if graph[i][j] != 0:
modifiedGraph[i][j] = (graph[i][j] +
modifyWeights[i] - modifyWeights[j]);
print ('Modified Graph: ' + str(modifiedGraph))
# Run Dijkstra for every vertex as source one by one
for src in range(len(graph)):
print ('\nShortest Distance with vertex ' +
str(src) + ' as the source:\n')
Dijkstra(graph, modifiedGraph, src)
# Driver Code
graph = [[0, -5, 2, 3],
[0, 0, 4, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0]]
JohnsonAlgorithm(graph)
输出:
Modified Graph: [[0, 0, 3, 3], [0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0]]
Shortest Distance with vertex 0 as the source:
Vertex 0: 0
Vertex 1: 0
Vertex 2: 0
Vertex 3: 0
Shortest Distance with vertex 1 as the source:
Vertex 0: inf
Vertex 1: 0
Vertex 2: 0
Vertex 3: 0
Shortest Distance with vertex 2 as the source:
Vertex 0: inf
Vertex 1: inf
Vertex 2: 0
Vertex 3: 0
Shortest Distance with vertex 3 as the source:
Vertex 0: inf
Vertex 1: inf
Vertex 2: inf
Vertex 3: 0
时间复杂度:上述算法的时间复杂度为![]() 正如 Dijkstra 算法所采用的
正如 Dijkstra 算法所采用的![]() 为邻接矩阵。请注意,通过使用邻接表而不是邻接矩阵来表示图可以使上述算法更加高效。
为邻接矩阵。请注意,通过使用邻接表而不是邻接矩阵来表示图可以使上述算法更加高效。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。