给定成本矩阵 cost[][] 和在 cost[][] 中的位置 (m, n),编写一个函数,返回从 (0, 0) 到达 (m, n) 的最小成本路径的成本。矩阵的每个单元格表示遍历该单元格的成本。到达路径 (m, n) 的总成本是该路径上所有成本(包括源和目的地)的总和。您只能从给定的单元格(即从给定的单元格 (i, j)、单元格 (i+1, j)、(i, j+1) 和 (i+1) , j+1) 可以遍历。您可以假设所有成本都是正整数。
例如,在下图中,到 (2, 2) 的最小成本路径是什么?
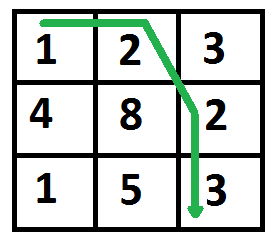
下图突出显示了成本最低的路径。路径是(0, 0) –> (0, 1) –> (1, 2) –> (2, 2)。路径的成本是 8 (1 + 2 + 2 + 3)。
1) 最优子结构
到达 (m, n) 的路径必须通过 3 个单元格之一:(m-1, n-1) 或 (m-1, n) 或 (m, n-1)。因此,达到 (m, n) 的最小成本可以写为“3 个单元的最小值加上成本 [m][n]”。
minCost(m, n) = min (minCost(m-1, n-1), minCost(m-1, n), minCost(m, n-1)) + cost[m][n]
2) 重叠子问题
以下是 MCP(最小成本路径)问题的简单递归实现。实现只是简单地遵循上面提到的递归结构。
C++
// A Naive recursive implementation
// of MCP(Minimum Cost Path) problem
#include
using namespace std;
#define R 3
#define C 3
int min(int x, int y, int z);
// Returns cost of minimum cost path
// from (0,0) to (m, n) in mat[R][C]
int minCost(int cost[R][C], int m, int n)
{
if (n < 0 || m < 0)
return INT_MAX;
else if (m == 0 && n == 0)
return cost[m][n];
else
return cost[m][n] +
min(minCost(cost, m - 1, n - 1),
minCost(cost, m - 1, n),
minCost(cost, m, n - 1));
}
// A utility function that returns
// minimum of 3 integers
int min(int x, int y, int z)
{
if (x < y)
return (x < z) ? x : z;
else
return (y < z) ? y : z;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int cost[R][C] = { { 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 8, 2 },
{ 1, 5, 3 } };
cout << minCost(cost, 2, 2) << endl;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by nikhilchhipa9 C
/* A Naive recursive implementation of MCP(Minimum Cost Path) problem */
#include
#include
#define R 3
#define C 3
int min(int x, int y, int z);
/* Returns cost of minimum cost path from (0,0) to (m, n) in mat[R][C]*/
int minCost(int cost[R][C], int m, int n)
{
if (n < 0 || m < 0)
return INT_MAX;
else if (m == 0 && n == 0)
return cost[m][n];
else
return cost[m][n] + min( minCost(cost, m-1, n-1),
minCost(cost, m-1, n),
minCost(cost, m, n-1) );
}
/* A utility function that returns minimum of 3 integers */
int min(int x, int y, int z)
{
if (x < y)
return (x < z)? x : z;
else
return (y < z)? y : z;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
int main()
{
int cost[R][C] = { {1, 2, 3},
{4, 8, 2},
{1, 5, 3} };
printf(" %d ", minCost(cost, 2, 2));
return 0;
} Java
/* A Naive recursive implementation of
MCP(Minimum Cost Path) problem */
public class GFG {
/* A utility function that returns
minimum of 3 integers */
static int min(int x, int y, int z)
{
if (x < y)
return (x < z) ? x : z;
else
return (y < z) ? y : z;
}
/* Returns cost of minimum cost path
from (0,0) to (m, n) in mat[R][C]*/
static int minCost(int cost[][], int m,
int n)
{
if (n < 0 || m < 0)
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
else if (m == 0 && n == 0)
return cost[m][n];
else
return cost[m][n] +
min( minCost(cost, m-1, n-1),
minCost(cost, m-1, n),
minCost(cost, m, n-1) );
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int cost[][] = { {1, 2, 3},
{4, 8, 2},
{1, 5, 3} };
System.out.print(minCost(cost, 2, 2));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007Python3
# A Naive recursive implementation of MCP(Minimum Cost Path) problem
R = 3
C = 3
import sys
# Returns cost of minimum cost path from (0,0) to (m, n) in mat[R][C]
def minCost(cost, m, n):
if (n < 0 or m < 0):
return sys.maxsize
elif (m == 0 and n == 0):
return cost[m][n]
else:
return cost[m][n] + min( minCost(cost, m-1, n-1),
minCost(cost, m-1, n),
minCost(cost, m, n-1) )
#A utility function that returns minimum of 3 integers */
def min(x, y, z):
if (x < y):
return x if (x < z) else z
else:
return y if (y < z) else z
# Driver program to test above functions
cost= [ [1, 2, 3],
[4, 8, 2],
[1, 5, 3] ]
print(minCost(cost, 2, 2))
# This code is contributed by
# Smitha Dinesh SemwalC#
/* A Naive recursive implementation of
MCP(Minimum Cost Path) problem */
using System;
class GFG
{
/* A utility function that
returns minimum of 3 integers */
static int min(int x,
int y, int z)
{
if (x < y)
return ((x < z) ? x : z);
else
return ((y < z) ? y : z);
}
/* Returns cost of minimum
cost path from (0,0) to
(m, n) in mat[R][C]*/
static int minCost(int [,]cost,
int m , int n)
{
if (n < 0 || m < 0)
return int.MaxValue;
else if (m == 0 && n == 0)
return cost[m, n];
else
return cost[m, n] +
min(minCost(cost, m - 1, n - 1),
minCost(cost, m - 1, n),
minCost(cost, m, n - 1) );
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int [,]cost = {{1, 2, 3},
{4, 8, 2},
{1, 5, 3}};
Console.Write(minCost(cost, 2, 2));
}
}
// This code is contributed
// by shiv_bhakt.PHP
Javascript
C++
/* Dynamic Programming implementation of MCP problem */
#include
#include
#define R 3
#define C 3
using namespace std;
int min(int x, int y, int z);
int minCost(int cost[R][C], int m, int n)
{
int i, j;
// Instead of following line, we can use int tc[m+1][n+1] or
// dynamically allocate memory to save space. The following line is
// used to keep the program simple and make it working on all compilers.
int tc[R][C];
tc[0][0] = cost[0][0];
/* Initialize first column of total cost(tc) array */
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
tc[i][0] = tc[i - 1][0] + cost[i][0];
/* Initialize first row of tc array */
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
tc[0][j] = tc[0][j - 1] + cost[0][j];
/* Construct rest of the tc array */
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
tc[i][j] = min(tc[i - 1][j - 1],
tc[i - 1][j],
tc[i][j - 1]) + cost[i][j];
return tc[m][n];
}
/* A utility function that returns minimum of 3 integers */
int min(int x, int y, int z)
{
if (x < y)
return (x < z)? x : z;
else
return (y < z)? y : z;
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
int cost[R][C] = { {1, 2, 3},
{4, 8, 2},
{1, 5, 3} };
cout << " " << minCost(cost, 2, 2);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110 C
/* Dynamic Programming implementation of MCP problem */
#include
#include
#define R 3
#define C 3
int min(int x, int y, int z);
int minCost(int cost[R][C], int m, int n)
{
int i, j;
// Instead of following line, we can use int tc[m+1][n+1] or
// dynamically allocate memory to save space. The following line is
// used to keep the program simple and make it working on all compilers.
int tc[R][C];
tc[0][0] = cost[0][0];
/* Initialize first column of total cost(tc) array */
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
tc[i][0] = tc[i-1][0] + cost[i][0];
/* Initialize first row of tc array */
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
tc[0][j] = tc[0][j-1] + cost[0][j];
/* Construct rest of the tc array */
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
tc[i][j] = min(tc[i-1][j-1],
tc[i-1][j],
tc[i][j-1]) + cost[i][j];
return tc[m][n];
}
/* A utility function that returns minimum of 3 integers */
int min(int x, int y, int z)
{
if (x < y)
return (x < z)? x : z;
else
return (y < z)? y : z;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
int main()
{
int cost[R][C] = { {1, 2, 3},
{4, 8, 2},
{1, 5, 3} };
printf(" %d ", minCost(cost, 2, 2));
return 0;
} Java
/* Java program for Dynamic Programming implementation
of Min Cost Path problem */
import java.util.*;
class MinimumCostPath
{
/* A utility function that returns minimum of 3 integers */
private static int min(int x, int y, int z)
{
if (x < y)
return (x < z)? x : z;
else
return (y < z)? y : z;
}
private static int minCost(int cost[][], int m, int n)
{
int i, j;
int tc[][]=new int[m+1][n+1];
tc[0][0] = cost[0][0];
/* Initialize first column of total cost(tc) array */
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
tc[i][0] = tc[i-1][0] + cost[i][0];
/* Initialize first row of tc array */
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
tc[0][j] = tc[0][j-1] + cost[0][j];
/* Construct rest of the tc array */
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
tc[i][j] = min(tc[i-1][j-1],
tc[i-1][j],
tc[i][j-1]) + cost[i][j];
return tc[m][n];
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void main(String args[])
{
int cost[][]= {{1, 2, 3},
{4, 8, 2},
{1, 5, 3}};
System.out.println(minCost(cost,2,2));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Pankaj KumarPython
# Dynamic Programming Python implementation of Min Cost Path
# problem
R = 3
C = 3
def minCost(cost, m, n):
# Instead of following line, we can use int tc[m+1][n+1] or
# dynamically allocate memoery to save space. The following
# line is used to keep te program simple and make it working
# on all compilers.
tc = [[0 for x in range(C)] for x in range(R)]
tc[0][0] = cost[0][0]
# Initialize first column of total cost(tc) array
for i in range(1, m+1):
tc[i][0] = tc[i-1][0] + cost[i][0]
# Initialize first row of tc array
for j in range(1, n+1):
tc[0][j] = tc[0][j-1] + cost[0][j]
# Construct rest of the tc array
for i in range(1, m+1):
for j in range(1, n+1):
tc[i][j] = min(tc[i-1][j-1], tc[i-1][j], tc[i][j-1]) + cost[i][j]
return tc[m][n]
# Driver program to test above functions
cost = [[1, 2, 3],
[4, 8, 2],
[1, 5, 3]]
print(minCost(cost, 2, 2))
# This code is contributed by Bhavya JainC#
// C# program for Dynamic Programming implementation
// of Min Cost Path problem
using System;
class GFG
{
// A utility function that
// returns minimum of 3 integers
private static int min(int x, int y, int z)
{
if (x < y)
return (x < z)? x : z;
else
return (y < z)? y : z;
}
private static int minCost(int [,]cost, int m, int n)
{
int i, j;
int [,]tc=new int[m+1,n+1];
tc[0,0] = cost[0,0];
/* Initialize first column of total cost(tc) array */
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
tc[i, 0] = tc[i - 1, 0] + cost[i, 0];
/* Initialize first row of tc array */
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
tc[0, j] = tc[0, j - 1] + cost[0, j];
/* Construct rest of the tc array */
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
tc[i, j] = min(tc[i - 1, j - 1],
tc[i - 1, j],
tc[i, j - 1]) + cost[i, j];
return tc[m, n];
}
// Driver program
public static void Main()
{
int [,]cost= {{1, 2, 3},
{4, 8, 2},
{1, 5, 3}};
Console.Write(minCost(cost,2,2));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007.PHP
Javascript
C++
#include
#define endl "\n"
using namespace std;
const int row = 3;
const int col = 3;
int minCost(int cost[row][col]) {
// for 1st column
for (int i=1 ; i|
Java
// Java program for the
// above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int row = 3;
static int col = 3;
static int minCost(int cost[][])
{
// for 1st column
for (int i = 1; i < row; i++)
{
cost[i][0] += cost[i - 1][0];
}
// for 1st row
for (int j = 1; j < col; j++)
{
cost[0][j] += cost[0][j - 1];
}
// for rest of the 2d matrix
for (int i = 1; i < row; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < col; j++)
{
cost[i][j] += Math.min(cost[i - 1][j - 1],
Math.min(cost[i - 1][j],
cost[i][j - 1]));
}
}
// Returning the value in
// last cell
return cost[row - 1][col - 1];
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int cost[][] = {{1, 2, 3},
{4, 8, 2},
{1, 5, 3} };
System.out.print(minCost(cost) + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit KatiyarPython3
# Python3 program for the
# above approach
def minCost(cost, row, col):
# For 1st column
for i in range(1, row):
cost[i][0] += cost[i - 1][0]
# For 1st row
for j in range(1, col):
cost[0][j] += cost[0][j - 1]
# For rest of the 2d matrix
for i in range(1, row):
for j in range(1, col):
cost[i][j] += (min(cost[i - 1][j - 1],
min(cost[i - 1][j],
cost[i][j - 1])))
# Returning the value in
# last cell
return cost[row - 1][col - 1]
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
row = 3
col = 3
cost = [ [ 1, 2, 3 ],
[ 4, 8, 2 ],
[ 1, 5, 3 ] ]
print(minCost(cost, row, col));
# This code is contributed by Amit KatiyarC#
// C# program for the
// above approach
using System;
class GFG{
static int row = 3;
static int col = 3;
static int minCost(int [,]cost)
{
// for 1st column
for (int i = 1; i < row; i++)
{
cost[i, 0] += cost[i - 1, 0];
}
// for 1st row
for (int j = 1; j < col; j++)
{
cost[0, j] += cost[0, j - 1];
}
// for rest of the 2d matrix
for (int i = 1; i < row; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < col; j++)
{
cost[i,j] += Math.Min(cost[i - 1,
j - 1],
Math.Min(cost[i - 1, j],
cost[i, j - 1]));
}
}
// Returning the value in
// last cell
return cost[row - 1, col - 1];
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int [,]cost = {{1, 2, 3},
{4, 8, 2},
{1, 5, 3} };
Console.Write(minCost(cost) + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-JiJavascript
C++
/* Minimum Cost Path using Dijkstra’s shortest path
algorithm with Min Heap by dinglizeng */
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
/* define the number of rows and the number of columns */
#define R 4
#define C 5
/* 8 possible moves */
int dx[] = {1,-1, 0, 0, 1, 1,-1,-1};
int dy[] = {0, 0, 1,-1, 1,-1, 1,-1};
/* The data structure to store the coordinates of \\
the unit square and the cost of path from the top left. */
struct Cell{
int x;
int y;
int cost;
};
/* The compare class to be used by a Min Heap.
* The greater than condition is used as this
is for a Min Heap based on priority_queue.
*/
class mycomparison
{
public:
bool operator() (const Cell &lhs, const Cell &rhs) const
{
return (lhs.cost > rhs.cost);
}
};
/* To verify whether a move is within the boundary. */
bool isSafe(int x, int y){
return x >= 0 && x < R && y >= 0 && y < C;
}
/* This solution is based on Dijkstra’s shortest path algorithm
* For each unit square being visited, we examine all
possible next moves in 8 directions,
* calculate the accumulated cost of path for each
next move, adjust the cost of path of the adjacent
units to the minimum as needed.
* then add the valid next moves into a Min Heap.
* The Min Heap pops out the next move with the minimum
accumulated cost of path.
* Once the iteration reaches the last unit at the lower
right corner, the minimum cost path will be returned.
*/
int minCost(int cost[R][C], int m, int n) {
/* the array to store the accumulated cost
of path from top left corner */
int dp[R][C];
/* the array to record whether a unit
square has been visited */
bool visited[R][C];
/* Initialize these two arrays, set path cost
to maximum integer value, each unit as not visited */
for(int i = 0; i < R; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < C; j++) {
dp[i][j] = INT_MAX;
visited[i][j] = false;
}
}
/* Define a reverse priority queue.
* Priority queue is a heap based implementation.
* The default behavior of a priority queue is
to have the maximum element at the top.
* The compare class is used in the definition of the Min Heap.
*/
priority_queue, mycomparison> pq;
/* initialize the starting top left unit with the
cost and add it to the queue as the first move. */
dp[0][0] = cost[0][0];
pq.push({0, 0, cost[0][0]});
while(!pq.empty()) {
/* pop a move from the queue, ignore the units
already visited */
Cell cell = pq.top();
pq.pop();
int x = cell.x;
int y = cell.y;
if(visited[x][y]) continue;
/* mark the current unit as visited */
visited[x][y] = true;
/* examine all non-visited adjacent units in 8 directions
* calculate the accumulated cost of path for
each next move from this unit,
* adjust the cost of path for each next adjacent
units to the minimum if possible.
*/
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
int next_x = x + dx[i];
int next_y = y + dy[i];
if(isSafe(next_x, next_y) && !visited[next_x][next_y]) {
dp[next_x][next_y] = min(dp[next_x][next_y],
dp[x][y] + cost[next_x][next_y]);
pq.push({next_x, next_y, dp[next_x][next_y]});
}
}
}
/* return the minimum cost path at the lower
right corner */
return dp[m][n];
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
int main()
{
int cost[R][C] = { {1, 8, 8, 1, 5},
{4, 1, 1, 8, 1},
{4, 2, 8, 8, 1},
{1, 5, 8, 8, 1} };
printf(" %d ", minCost(cost, 3, 4));
return 0;
} 8需要注意的是,上述函数一次又一次地计算相同的子问题。看下面的递归树,有很多节点出现了不止一次。这种朴素的递归解决方案的时间复杂度是指数级的,而且速度非常慢。
mC refers to minCost()
mC(2, 2)
/ | \
/ | \
mC(1, 1) mC(1, 2) mC(2, 1)
/ | \ / | \ / | \
/ | \ / | \ / | \
mC(0,0) mC(0,1) mC(1,0) mC(0,1) mC(0,2) mC(1,1) mC(1,0) mC(1,1) mC(2,0)因此,MCP 问题具有动态规划问题的两个性质(参见this 和this)。与其他典型的动态规划 (DP) 问题一样,通过以自底向上的方式构造临时数组 tc[][] 可以避免相同子问题的重新计算。
C++
/* Dynamic Programming implementation of MCP problem */
#include
#include
#define R 3
#define C 3
using namespace std;
int min(int x, int y, int z);
int minCost(int cost[R][C], int m, int n)
{
int i, j;
// Instead of following line, we can use int tc[m+1][n+1] or
// dynamically allocate memory to save space. The following line is
// used to keep the program simple and make it working on all compilers.
int tc[R][C];
tc[0][0] = cost[0][0];
/* Initialize first column of total cost(tc) array */
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
tc[i][0] = tc[i - 1][0] + cost[i][0];
/* Initialize first row of tc array */
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
tc[0][j] = tc[0][j - 1] + cost[0][j];
/* Construct rest of the tc array */
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
tc[i][j] = min(tc[i - 1][j - 1],
tc[i - 1][j],
tc[i][j - 1]) + cost[i][j];
return tc[m][n];
}
/* A utility function that returns minimum of 3 integers */
int min(int x, int y, int z)
{
if (x < y)
return (x < z)? x : z;
else
return (y < z)? y : z;
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
int cost[R][C] = { {1, 2, 3},
{4, 8, 2},
{1, 5, 3} };
cout << " " << minCost(cost, 2, 2);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
C
/* Dynamic Programming implementation of MCP problem */
#include
#include
#define R 3
#define C 3
int min(int x, int y, int z);
int minCost(int cost[R][C], int m, int n)
{
int i, j;
// Instead of following line, we can use int tc[m+1][n+1] or
// dynamically allocate memory to save space. The following line is
// used to keep the program simple and make it working on all compilers.
int tc[R][C];
tc[0][0] = cost[0][0];
/* Initialize first column of total cost(tc) array */
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
tc[i][0] = tc[i-1][0] + cost[i][0];
/* Initialize first row of tc array */
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
tc[0][j] = tc[0][j-1] + cost[0][j];
/* Construct rest of the tc array */
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
tc[i][j] = min(tc[i-1][j-1],
tc[i-1][j],
tc[i][j-1]) + cost[i][j];
return tc[m][n];
}
/* A utility function that returns minimum of 3 integers */
int min(int x, int y, int z)
{
if (x < y)
return (x < z)? x : z;
else
return (y < z)? y : z;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
int main()
{
int cost[R][C] = { {1, 2, 3},
{4, 8, 2},
{1, 5, 3} };
printf(" %d ", minCost(cost, 2, 2));
return 0;
}
Java
/* Java program for Dynamic Programming implementation
of Min Cost Path problem */
import java.util.*;
class MinimumCostPath
{
/* A utility function that returns minimum of 3 integers */
private static int min(int x, int y, int z)
{
if (x < y)
return (x < z)? x : z;
else
return (y < z)? y : z;
}
private static int minCost(int cost[][], int m, int n)
{
int i, j;
int tc[][]=new int[m+1][n+1];
tc[0][0] = cost[0][0];
/* Initialize first column of total cost(tc) array */
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
tc[i][0] = tc[i-1][0] + cost[i][0];
/* Initialize first row of tc array */
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
tc[0][j] = tc[0][j-1] + cost[0][j];
/* Construct rest of the tc array */
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
tc[i][j] = min(tc[i-1][j-1],
tc[i-1][j],
tc[i][j-1]) + cost[i][j];
return tc[m][n];
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void main(String args[])
{
int cost[][]= {{1, 2, 3},
{4, 8, 2},
{1, 5, 3}};
System.out.println(minCost(cost,2,2));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Pankaj Kumar
Python
# Dynamic Programming Python implementation of Min Cost Path
# problem
R = 3
C = 3
def minCost(cost, m, n):
# Instead of following line, we can use int tc[m+1][n+1] or
# dynamically allocate memoery to save space. The following
# line is used to keep te program simple and make it working
# on all compilers.
tc = [[0 for x in range(C)] for x in range(R)]
tc[0][0] = cost[0][0]
# Initialize first column of total cost(tc) array
for i in range(1, m+1):
tc[i][0] = tc[i-1][0] + cost[i][0]
# Initialize first row of tc array
for j in range(1, n+1):
tc[0][j] = tc[0][j-1] + cost[0][j]
# Construct rest of the tc array
for i in range(1, m+1):
for j in range(1, n+1):
tc[i][j] = min(tc[i-1][j-1], tc[i-1][j], tc[i][j-1]) + cost[i][j]
return tc[m][n]
# Driver program to test above functions
cost = [[1, 2, 3],
[4, 8, 2],
[1, 5, 3]]
print(minCost(cost, 2, 2))
# This code is contributed by Bhavya Jain
C#
// C# program for Dynamic Programming implementation
// of Min Cost Path problem
using System;
class GFG
{
// A utility function that
// returns minimum of 3 integers
private static int min(int x, int y, int z)
{
if (x < y)
return (x < z)? x : z;
else
return (y < z)? y : z;
}
private static int minCost(int [,]cost, int m, int n)
{
int i, j;
int [,]tc=new int[m+1,n+1];
tc[0,0] = cost[0,0];
/* Initialize first column of total cost(tc) array */
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
tc[i, 0] = tc[i - 1, 0] + cost[i, 0];
/* Initialize first row of tc array */
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
tc[0, j] = tc[0, j - 1] + cost[0, j];
/* Construct rest of the tc array */
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
tc[i, j] = min(tc[i - 1, j - 1],
tc[i - 1, j],
tc[i, j - 1]) + cost[i, j];
return tc[m, n];
}
// Driver program
public static void Main()
{
int [,]cost= {{1, 2, 3},
{4, 8, 2},
{1, 5, 3}};
Console.Write(minCost(cost,2,2));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007.
PHP
Javascript
8DP 实现的时间复杂度为 O(mn),这比 Naive Recursive 实现要好得多。
空间优化:想法是使用相同的给定数组来存储子问题的解决方案。
C++
#include
#define endl "\n"
using namespace std;
const int row = 3;
const int col = 3;
int minCost(int cost[row][col]) {
// for 1st column
for (int i=1 ; i|
Java
// Java program for the
// above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int row = 3;
static int col = 3;
static int minCost(int cost[][])
{
// for 1st column
for (int i = 1; i < row; i++)
{
cost[i][0] += cost[i - 1][0];
}
// for 1st row
for (int j = 1; j < col; j++)
{
cost[0][j] += cost[0][j - 1];
}
// for rest of the 2d matrix
for (int i = 1; i < row; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < col; j++)
{
cost[i][j] += Math.min(cost[i - 1][j - 1],
Math.min(cost[i - 1][j],
cost[i][j - 1]));
}
}
// Returning the value in
// last cell
return cost[row - 1][col - 1];
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int cost[][] = {{1, 2, 3},
{4, 8, 2},
{1, 5, 3} };
System.out.print(minCost(cost) + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar
蟒蛇3
# Python3 program for the
# above approach
def minCost(cost, row, col):
# For 1st column
for i in range(1, row):
cost[i][0] += cost[i - 1][0]
# For 1st row
for j in range(1, col):
cost[0][j] += cost[0][j - 1]
# For rest of the 2d matrix
for i in range(1, row):
for j in range(1, col):
cost[i][j] += (min(cost[i - 1][j - 1],
min(cost[i - 1][j],
cost[i][j - 1])))
# Returning the value in
# last cell
return cost[row - 1][col - 1]
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
row = 3
col = 3
cost = [ [ 1, 2, 3 ],
[ 4, 8, 2 ],
[ 1, 5, 3 ] ]
print(minCost(cost, row, col));
# This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar
C#
// C# program for the
// above approach
using System;
class GFG{
static int row = 3;
static int col = 3;
static int minCost(int [,]cost)
{
// for 1st column
for (int i = 1; i < row; i++)
{
cost[i, 0] += cost[i - 1, 0];
}
// for 1st row
for (int j = 1; j < col; j++)
{
cost[0, j] += cost[0, j - 1];
}
// for rest of the 2d matrix
for (int i = 1; i < row; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < col; j++)
{
cost[i,j] += Math.Min(cost[i - 1,
j - 1],
Math.Min(cost[i - 1, j],
cost[i, j - 1]));
}
}
// Returning the value in
// last cell
return cost[row - 1, col - 1];
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int [,]cost = {{1, 2, 3},
{4, 8, 2},
{1, 5, 3} };
Console.Write(minCost(cost) + "\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
8替代解决方案
我们也可以使用 Dijkstra 的最短路径算法。下面是该方法的实现:
C++
/* Minimum Cost Path using Dijkstra’s shortest path
algorithm with Min Heap by dinglizeng */
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
/* define the number of rows and the number of columns */
#define R 4
#define C 5
/* 8 possible moves */
int dx[] = {1,-1, 0, 0, 1, 1,-1,-1};
int dy[] = {0, 0, 1,-1, 1,-1, 1,-1};
/* The data structure to store the coordinates of \\
the unit square and the cost of path from the top left. */
struct Cell{
int x;
int y;
int cost;
};
/* The compare class to be used by a Min Heap.
* The greater than condition is used as this
is for a Min Heap based on priority_queue.
*/
class mycomparison
{
public:
bool operator() (const Cell &lhs, const Cell &rhs) const
{
return (lhs.cost > rhs.cost);
}
};
/* To verify whether a move is within the boundary. */
bool isSafe(int x, int y){
return x >= 0 && x < R && y >= 0 && y < C;
}
/* This solution is based on Dijkstra’s shortest path algorithm
* For each unit square being visited, we examine all
possible next moves in 8 directions,
* calculate the accumulated cost of path for each
next move, adjust the cost of path of the adjacent
units to the minimum as needed.
* then add the valid next moves into a Min Heap.
* The Min Heap pops out the next move with the minimum
accumulated cost of path.
* Once the iteration reaches the last unit at the lower
right corner, the minimum cost path will be returned.
*/
int minCost(int cost[R][C], int m, int n) {
/* the array to store the accumulated cost
of path from top left corner */
int dp[R][C];
/* the array to record whether a unit
square has been visited */
bool visited[R][C];
/* Initialize these two arrays, set path cost
to maximum integer value, each unit as not visited */
for(int i = 0; i < R; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < C; j++) {
dp[i][j] = INT_MAX;
visited[i][j] = false;
}
}
/* Define a reverse priority queue.
* Priority queue is a heap based implementation.
* The default behavior of a priority queue is
to have the maximum element at the top.
* The compare class is used in the definition of the Min Heap.
*/
priority_queue, mycomparison> pq;
/* initialize the starting top left unit with the
cost and add it to the queue as the first move. */
dp[0][0] = cost[0][0];
pq.push({0, 0, cost[0][0]});
while(!pq.empty()) {
/* pop a move from the queue, ignore the units
already visited */
Cell cell = pq.top();
pq.pop();
int x = cell.x;
int y = cell.y;
if(visited[x][y]) continue;
/* mark the current unit as visited */
visited[x][y] = true;
/* examine all non-visited adjacent units in 8 directions
* calculate the accumulated cost of path for
each next move from this unit,
* adjust the cost of path for each next adjacent
units to the minimum if possible.
*/
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
int next_x = x + dx[i];
int next_y = y + dy[i];
if(isSafe(next_x, next_y) && !visited[next_x][next_y]) {
dp[next_x][next_y] = min(dp[next_x][next_y],
dp[x][y] + cost[next_x][next_y]);
pq.push({next_x, next_y, dp[next_x][next_y]});
}
}
}
/* return the minimum cost path at the lower
right corner */
return dp[m][n];
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
int main()
{
int cost[R][C] = { {1, 8, 8, 1, 5},
{4, 1, 1, 8, 1},
{4, 2, 8, 8, 1},
{1, 5, 8, 8, 1} };
printf(" %d ", minCost(cost, 3, 4));
return 0;
}
7与以最小路径成本寻找节点的全扫描相比,在该解决方案中使用反向优先级队列可以降低时间复杂度。 DP实现的整体时间复杂度为O(mn),不考虑使用中的优先级队列,比Naive Recursive实现要好很多。
?list=PLqM7alHXFySEQDk2MDfbwEdjd2svVJH9p
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。