给定凸多边形的 N个点的坐标。任务是检查给定点(X, Y) 是否位于多边形内。
例子:
Input: N = 7, Points: {(1, 1), (2, 1), (3, 1), (4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4)}, Query: X = 3, Y = 2
Below is the image of plotting of the given points: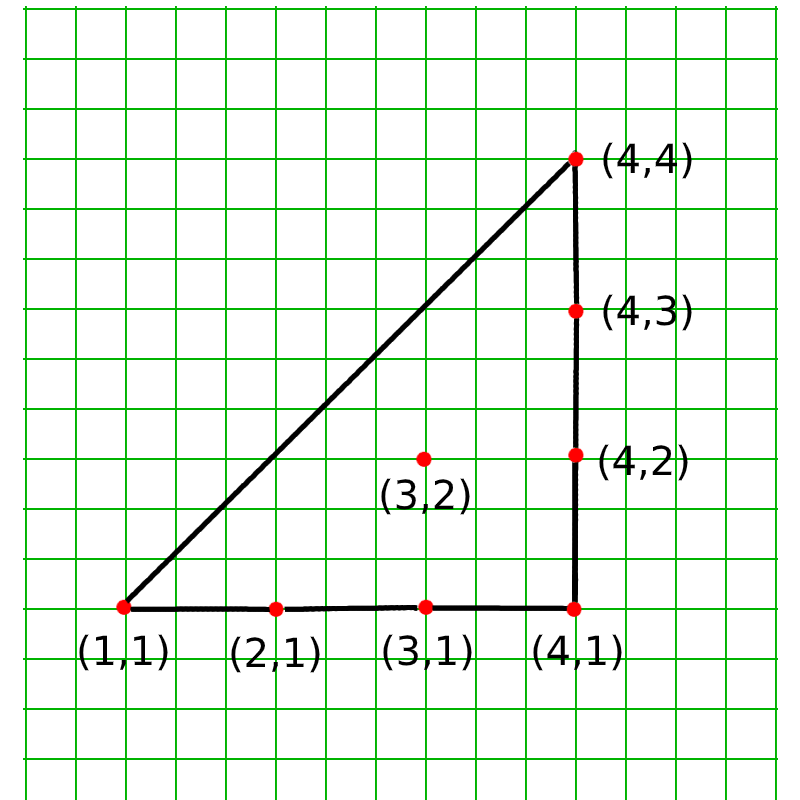
Output: YES
Input: N = 7, Points: {(1, 1), (2, 1), (3, 1), (4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4)}, Query: X = 3, Y = 9
Output: NO
方法:想法是使用格雷厄姆扫描算法来查找给定点是否位于凸多边形内。以下是一些观察结果:
- 假设点(X, Y)是凸多边形点集中的一个点。如果在这组点上使用 Graham 扫描算法,将获得另一组点,它构成了凸包。
- 如果点(X, Y)位于多边形内,则它不会位于凸包上,因此不会出现在新生成的凸包的点集中。
- 如果点(X, Y)位于多边形之外,则它将位于形成的凸包上,因此将出现在新生成的凸包的点集中。
以下是解决问题的步骤:
- 按照其横坐标值的递增顺序对给定点和查询点进行排序。如果任意两个点的横坐标值(x 坐标)相同,则根据它们的纵坐标值对它们进行排序。
- 设置左下点作为开始点和右上点作为凸包的终点。
- 迭代所有点并找出点,形成凸多边形,位于顺时针方向的起点和终点之间。将这些点存储在一个向量中。
- 迭代所有点并找出点,形成凸多边形,逆时针方向位于起点和终点之间。将这些点存储在向量中。
- 检查向量中是否存在查询点,则该点位于凸包之外。所以返回“否” 。
- 如果向量中不存在该点,则该点位于凸包打印“Yes”内。
下面是基于上述方法的实现:
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Sorting Function to sort points
bool cmp(pair& a,
pair& b)
{
if (a.first == b.first)
return a.second < b.second;
return a.first < b.first;
}
// Function To Check Clockwise
// Orientation
int cw(pair& a,
pair& b,
pair& c)
{
int p = a.first * (b.second - c.second)
+ b.first * (c.second - a.second)
+ c.first * (a.second - b.second);
return p < 0ll;
}
// Function To Check Counter
// Clockwise Orientation
int ccw(pair& a,
pair& b,
pair& c)
{
int p = a.first * (b.second - c.second)
+ b.first * (c.second - a.second)
+ c.first * (a.second - b.second);
return p > 0ll;
}
// Graham Scan algorithm to find Convex
// Hull from given points
vector > convexHull(
vector >& v)
{
// Sort the points
sort(v.begin(),
v.end(), cmp);
int n = v.size();
if (n <= 3)
return v;
// Set starting and ending points as
// left bottom and top right
pair p1 = v[0];
pair p2 = v[n - 1];
// Vector to store points in
// upper half and lower half
vector > up, down;
// Insert StartingEnding Points
up.push_back(p1);
down.push_back(p1);
// Iterate over points
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (i == n - 1 || !ccw(p1, v[i], p2)) {
while (up.size() > 1
&& ccw(up[up.size() - 2],
up[up.size() - 1],
v[i])) {
// Exclude this point
// if we can form better
up.pop_back();
}
up.push_back(v[i]);
}
if (i == n - 1 || !cw(p1, v[i], p2)) {
while (down.size() > 1
&& cw(down[down.size() - 2],
down[down.size() - 1],
v[i])) {
// Exclude this point
// if we can form better
down.pop_back();
}
down.push_back(v[i]);
}
}
// Combine upper and lower half
for (int i = down.size() - 2;
i > 0; i--)
up.push_back(down[i]);
// Remove duplicate points
up.resize(unique(up.begin(),
up.end())
- up.begin());
// Return the points on Convex Hull
return up;
}
// Function to find if point lies inside
// a convex polygon
bool isInside(vector > points,
pair query)
{
// Include the query point in the
// polygon points
points.push_back(query);
// Form a convex hull from the points
points = convexHull(points);
// Iterate over the points
// of convex hull
for (auto x : points) {
// If the query point lies
// on the convex hull
// then it wasn't inside
if (x == query)
return false;
}
// Otherwise it was Inside
return true;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Points of the polygon
// given in any order
int n = 7;
vector > points;
points = { { 1, 1 }, { 2, 1 }, { 3, 1 },
{ 4, 1 }, { 4, 2 }, { 4, 3 },
{ 4, 4 } };
// Query Points
pair query = { 3, 2 };
// Check if its inside
if (isInside(points, query)) {
cout << "YES" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "NO" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出:
YES
时间复杂度: O(N * log(N))
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。