相对速度公式
假设我们乘坐公共汽车旅行,比方说,另一辆公共汽车超过我们。我们不会感觉到超车公共汽车的实际速度,就像站在路边看着它的人所感觉到的那样。如果两辆公共汽车以相同的速度向同一方向移动,则一辆公共汽车上的人会观察到另一辆公共汽车上的人处于静止状态,即使两者都在运动。如果两辆公共汽车的方向相反,那么乘客会观察到更大的速度,大于他们各自的速度。在所有这些情况下,我们测量相对速度。因此,
The relative is the velocity of one body with respect to another body. It is measured as the rate of change of position of a body with respect to another body.
在数学中,相对速度是两个物体之间速度的矢量差。
什么是相对速度?
一个物体相对于另一个物体的速度称为第一个物体相对于第二个物体的相对速度。
相对速度 = 第一个物体的速度 - 第二个物体的速度
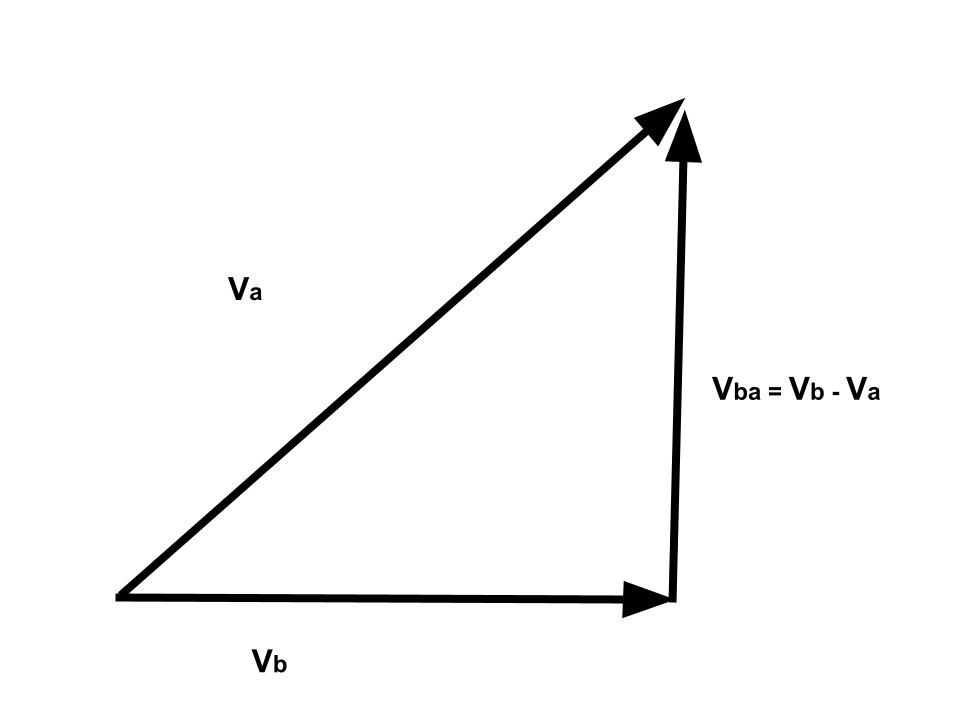
If Va and Vb represent the velocities of two bodies A and B respectively at any instant, then, the relative velocity of A with respect to B is represented by Vab.
Then, Vab = Va – Vb ……(1)
Similarly, the relative velocity of B with respect to A is given by,
Vba = Vb – Va ……(2)
So, from the equations (1) and (2), we can write
Vba = – Vab
This implies that
Relative velocity of A with respect to B = – Relative velocity of B with respect to A
Henceforth, the magnitude of both relative velocities are equal to each other.
- 速度和相对速度之间的差异:速度和相对速度之间的差异在于速度是相对于相对于不同点的参考点测量的。而相对速度是在物体相对于绝对框架静止或移动的框架中测量的。
- 相对速度的维数单位:相对速度的维数单位类似于速度的单位,可表示为- [ M 0 L 1 T -1 ]。
案例 1:两个物体在相同方向上以相等的速度运动的相对速度。
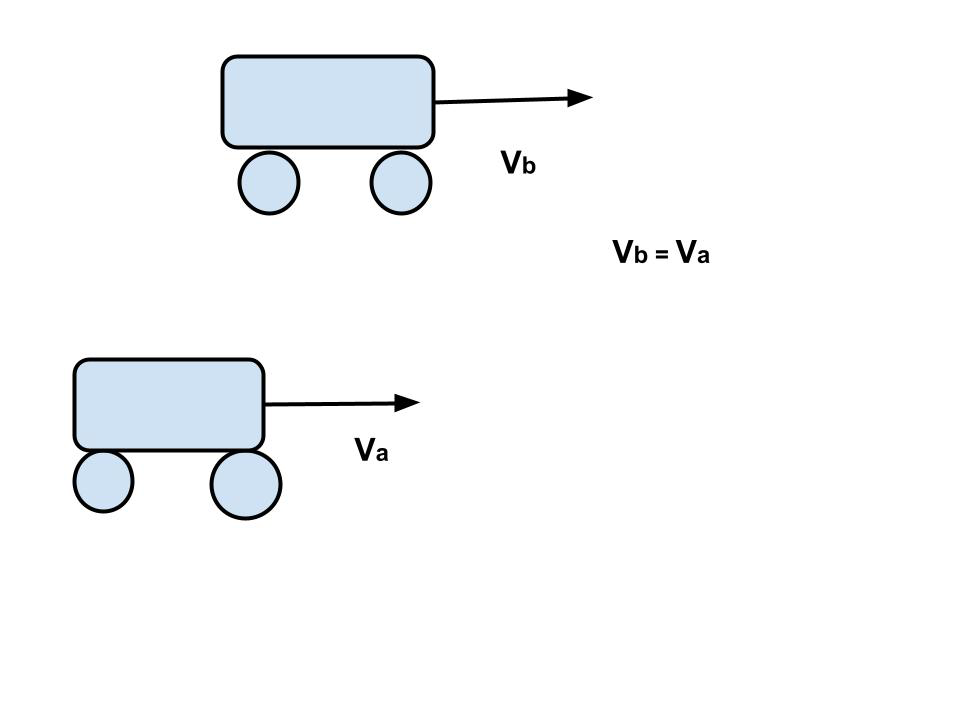
现在让我们考虑关于相对运动的四种不同情况。在第一种情况下,让我们假设两辆汽车 A 和 B 以相等的速度(Va = Vb)以相同的方向移动。对于坐在 A 中的人来说,如果他暂时忘记了他自己在运动的事实,那么 B 车似乎是静止的。因此 B 相对于 A 的速度为零。
V ba = V b – V a = 0 (因为 V a =V b )
类似地,在一个人坐在汽车 B 并观察汽车 A 的情况下,A 相对于 B 的相对速度也为零。
V ab = V a – V b = 0 (如 V a =V b )
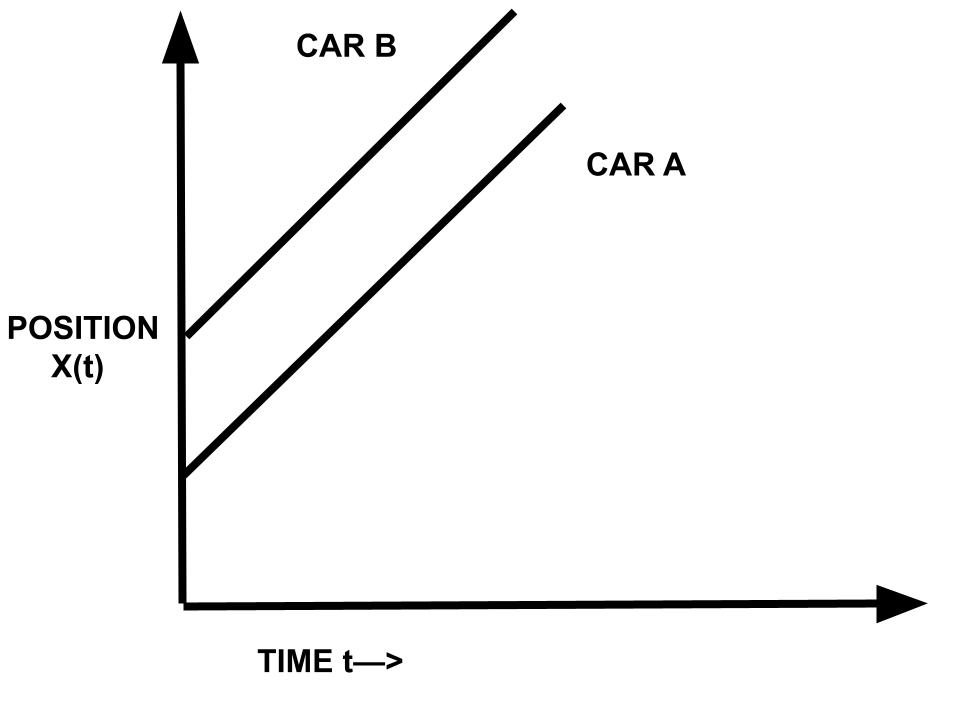
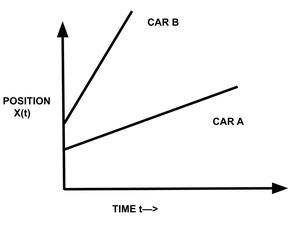
因此,如果 V b – V a = 0,则意味着两辆车沿同一方向行驶,并且它们之间始终保持相同的距离。所以它们的位置-时间图是两条平行的直线。
案例 2:两个物体的相对速度,从同一点开始,以不相等的速度沿同一方向移动。
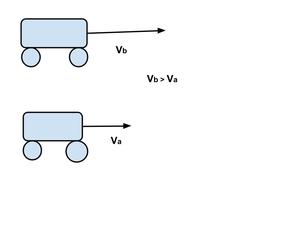
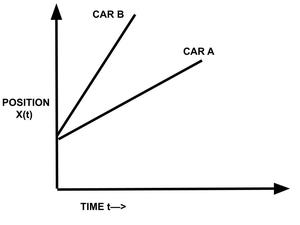
在这种情况下,让汽车 A 以速度 Va 移动,汽车 B(从同一点或 X 1 (0)=X 2 (0) 开始)以更大的速度 V b沿相同方向移动。然后,A车里的人感觉公交车B正在以速度远离他,
V ba = V b – V a
对于 B 车上的观察者来说,A 车似乎以一定速度返回,
V ab = V a -V b = – (V b – V a )
A 相对于 B 的速度 = - (B 相对于 A 的速度)
也就是说,A 相对于 B 的速度是 B 相对于 A 的速度的负值。
案例 3:两个物体从不同位置开始并以不相等的速度沿相同方向运动的相对速度
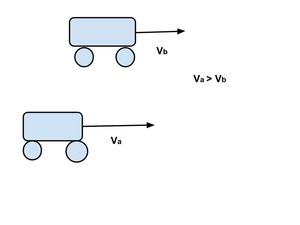
这里,V a > V b 。如果 A 车速度较快并在 B 车后面移动,则 A 车将在某个时刻超越 B 车,两车的位置-时间图将在一点相交
V ab =V a -V b ≠0且
V ba =V b -V a ≠0 因为 V a > V b
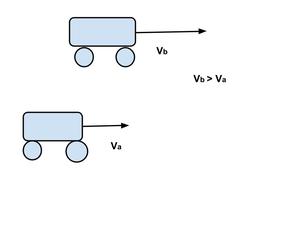
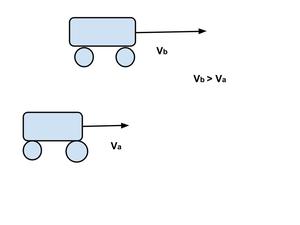
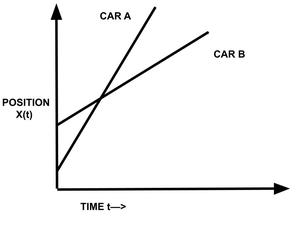
并且 V b > V a 。如果速度较大的汽车(在这种情况下是汽车 B)正在向前移动,则没有机会超越另一辆汽车 A,因此位置-时间图不会相交,两条线彼此远离,如图所示图形
V ab =V a -V b ≠0且
V ba =V b -V a ≠0 因为 V b > V a
显然,如果V b – V a ≠ 0,则意味着两辆车的速度不同。它们的位置-时间图是倾斜于时间轴的直线,其中一个比另一个更陡峭。
案例 4:两个物体沿相反方向运动的相对速度
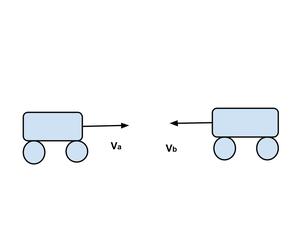

如图所示,如果两辆车的运动方向相反,则 V ba或 V ab的相对速度为
V ba =V b -(-V a ) = V b +V a ,
相似地,
V ab =V a -(-V b ) = V a +V b
要么
V ab =V ba =V a +V b
这意味着,当两辆车 A 和 B 沿相反方向移动时,每辆车似乎都相对于另一辆车跑得非常快。
示例问题
问题 1:公共汽车 A 以 40 m/s 的速度向北行驶,公共汽车 B 以 60 m/s 的速度向南行驶。什么是相对速度?
解决方案:
Speed of bus A= Va = 40 m/s (towards north)
Speed of bus B= Vb = 60 m/s (towards south)
As both the buses are moving in opposite direction, so relative velocity is:
Vab = Va – (-Vb)
= 40 – (-60)
= 100 m/s
问题 2:两辆相距不远的卡车开始以 1 m/s 和 2 m/s 的速度沿着笔直的道路相互移动。他们接近对方的速度是多少?
解决方案:
Let us consider that “A” denotes any truck at rest, “B” denotes first truck and “C” denotes second truck. The equation of relative velocity for this case is :
⇒ Vca = Vba + Vbc
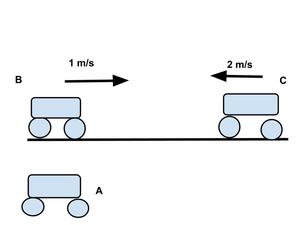
Vba = Vb-Va =1-0=1m/s ,
Vca= Vba + Vbc=-2-0=-2m/s
Vba = 1 m/s and Vca= − 2 m/s
Using,
Vca = Vba + Vcb
− 2 = 1 + Vcb
Vcb = − 2 − 1
= − 3 m/s
It means that the truck “C” is approaching “B” with a speed of -3 m/s along the straight road. Or, it means that the truck “B” is approaching “C” with a speed of 3 m/s along the straight road. We, therefore, say that the two trucks move towards each other each with a relative speed of 3 m/s.
问题 3:两辆汽车,最初相距 900 m,开始以 1 m/s 和 2 m/s 的速度沿着笔直的道路相互移动。他们什么时候见面?
解决方案:
The relative velocity of two cars (say 1 and 2) is: V21 = V2-V1
Let us consider that the direction V1 is moving in a positive direction.
Here, V1 = 1 m/s and V2 = -2 m/s. So, relative velocity of two cars (of 2 w.r.t 1) is : ⇒ V21 = − 2 − 1 = − 3 m / s
This means that car “2” is approaching car “1” with a speed of -3 m/s along the straight road.
Similarly, car “1” is approaching car “2” with a speed of 3 m/s along the straight road. Therefore,
So can say that two cars are approaching at a speed of 3 m/s. Now, let the two cars meet after time:
t = Displacement ⁄ Relative velocity
= 900/3 = 30 sec.
问题 4: 坐在以 36 km/h-1 行驶的火车窗边的女孩多久会看到一列以 18 km/h 的速度从相反方向经过的火车?慢行列车的长度为 90 m。
解决方案:
Given : Velocity of train = Vt = 36 Km/h = 36 × 5/18 m/s = 10 m/s
Velocity of passenger moving in opposite direction = Vp = 18 Km/h = 18 × 5/18 m/s = 5 m/s
The relative velocity of the slow-moving train with respect to the girl is Vtp = Vt – (-Vp) = Vt + Vp
Vtp = (10 + 5) m/s = 15 m/s.
As the girl will watch the full length of the other train, to find the time taken to watch the full train:
Using relative speed = distance / time
15 = 90/t
t = 90/15
= 6 sec
问题 5:一个女孩以 3 公里/小时的速度沿直线移动,发现雨滴在垂直方向以 4 公里/小时的速度下落。求雨滴落到地面的角度。
解决方案:
Let the girl be moving in the x-direction. Let us also denote girl with “A” and raindrop with “B”. we need to know the direction of raindrop with respect to ground=Vb.
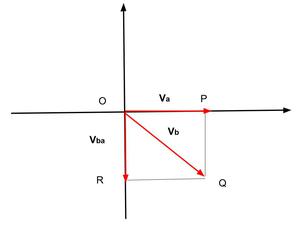
Here Given
Va=3km/hr , Vb =? , Vba =4km/hr
Using equation, Vba = Vb-Va
So V=Va+Vba
In ΔOQR, Angle with which rain drop hits the ground = ∠QOR = θ
So tanθ= Va/Vba
tanθ=3/4
Hence,
θ= tan-1(3/4)
or
θ = 37°
问题 6:从一个点出发的公共汽车以 3 m/s 的速度向东行驶。从该点出发的另一辆公共汽车以一定速度向北行驶。 4米/秒。求一个相对于另一个的相对速度的大小。
解决方案:
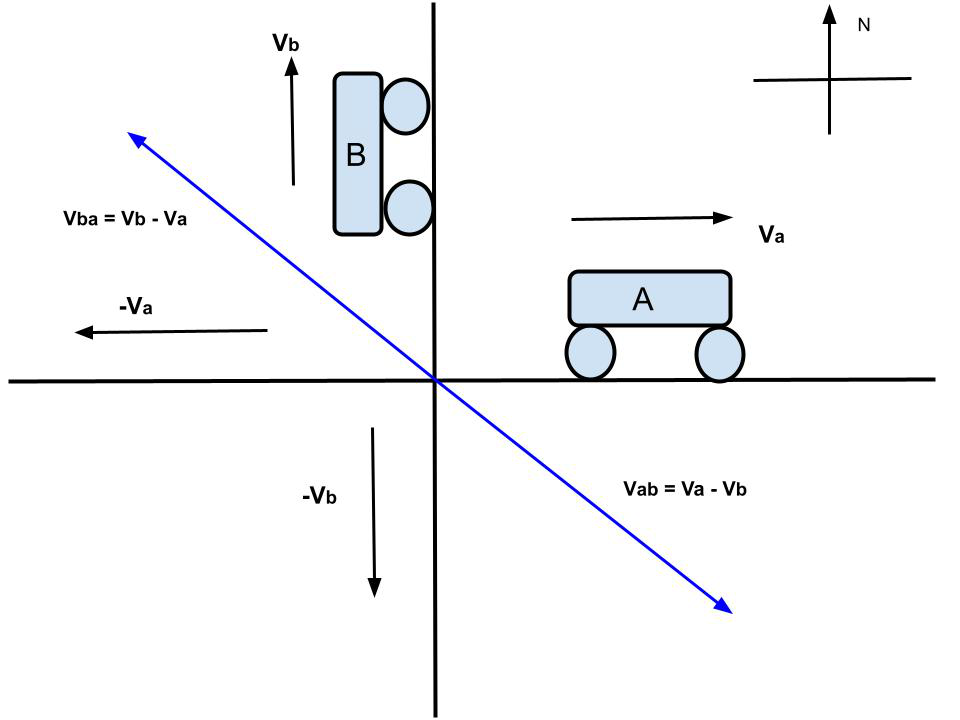
Given that,
The Bus-A moves towards East with velocity = Va = 3 m/s
And Bus-B moves towards North with velocity = Vb =4 m/s
Now the relative velocity Vba of Bus-B with respect to Bus-A is towards the west of north direction as shown in the figure
Magnitude of Vba = √32+42 => Vba = 5 m/s
Similarly, relative velocity Vab of Bus-A with respect to Bus-B is towards the south of east direction as shown in the figure, so:
Magnitude of Vab = √42+32
Hence,
Vab = 5 m/s