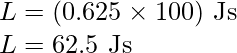旋转运动动力学
刚体既可以平移也可以旋转。因此,在这种情况下,必须同时检查线速度和角速度。为了使这些困难更容易理解,需要分别定义身体的平移和旋转运动。本文将讨论物体绕固定轴旋转运动的动力学。给定的表格列出了与线性运动相关的量及其在旋转运动中的类似物。 Linear Motion Rotational Motion about a Fixed Axis Displacement x Angular displacement θ Velocity v = dx/dt Angular velocity ω = dθ/dt Acceleration a = dv/dt Angular acceleration α = dω/dt Mass M Moment of inertia I Force F = Ma Torque τ = I α Work dW = F ds Work W = τ dθ Kinetic energy K = Mv2/2 Kinetic energy K = Iω2/2 Power P = F v Power P = τω Linear momentum p = Mv Angular momentum L = Iω
在旋转运动中,转动惯量和转矩在直线运动中分别起质量和力的作用。
旋转运动
物体绕空间中固定点沿圆形路径的运动称为旋转运动。
不变形或改变形状的物体的运动,其中所有粒子以共同的角速度围绕轴做圆周运动。例如地球绕自身轴的运动,车轮、齿轮、电机等的运动。
绕固定轴的旋转运动
因为轴是固定的,所以只考虑与固定轴相同方向的扭矩分量。只有这些组件有能力围绕其轴旋转身体。垂直于旋转轴的扭矩分量将倾向于使旋转轴远离其当前位置。假定将出现适当的约束力来抵消或抵消(外部)扭矩的垂直分量的影响,从而使轴保持在其固定位置。因此,不需要考虑扭矩的垂直分量。这意味着对于刚体上的扭矩计算:
- 只需要考虑垂直于轴的平面中存在的力。平行于轴的力会产生垂直于轴的扭矩,不需要考虑。
- 仅必须考虑垂直于轴的位置矢量的分量。沿轴的位置矢量分量将产生垂直于轴的扭矩,无需考虑。
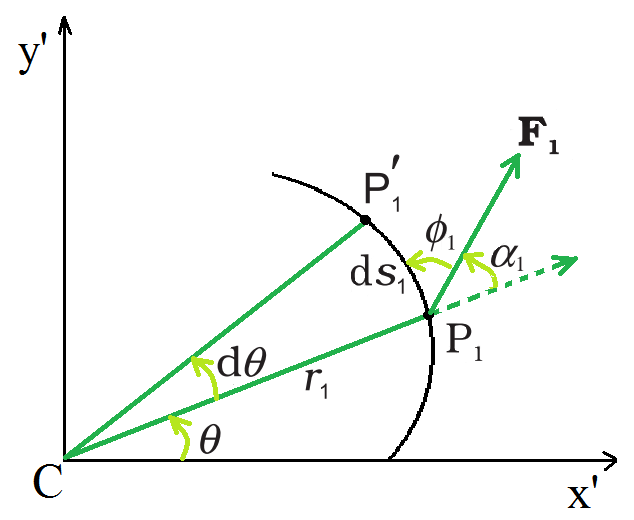
受力 F1 作用于绕固定轴旋转的物体的质点所做的功;粒子描述了一条以 C 为轴心的圆形路径; arc P1P′1(ds1) 给出了粒子的位移
旋转运动和功能原理
该图描绘了围绕固定轴旋转的刚体的横截面,该轴是 z 轴(垂直于页面平面)。如前所述,仅必须考虑垂直于轴的平面中的力。假设 F 1是作用在 P 1位置的物体粒子上的典型力的示例,其作用线垂直于轴。为方便起见,取 x′-y′ 平面(与页面平面一致)。 P 1表示半径为r 1 、以轴为中心C的圆形路径; CP 1 = r 1 。该点在时间 Δt 内到达位置 P 1 '。结果,粒子位移 ds1 具有 ds 1 = r 1 dθ 的大小和在 P 1处与圆形路径相切的方向,如图所示。粒子的角位移由dθ =∠P 1 CP 1 '给出。
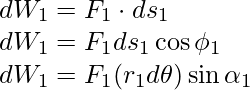
其中∅ 1是 F 1和 P 1处的切线之间的角度,α 1是 F 1和半径矢量 OP 1之间的角度,∅ 1 + α 1 = 90°。
OP 1 × F 1是由于 F 1关于原点的扭矩。 OP 1现在等于 OC + OP 1 ,不考虑 OC 产生的扭矩,因为它是沿轴的。 F 1产生τ 1 = CP × F 1的有效扭矩,该扭矩沿旋转轴定向,大小为τ 1 = r 1 F 1 sinα。
![]()
如果作用在身体上的力很多,则可以通过将每个人所做的功相加来计算在身体上所做的总功。使用数字 τ 1 , τ 2 ,… 来表示由各种力引起的扭矩的大小。
尽管导致扭矩作用在各种粒子上的力,但角位移 d 对于所有粒子都是相同的。因为所有的扭矩都平行于固定轴,所以总扭矩大小只是扭矩大小的代数和。
![]() …………………………………………(一)
…………………………………………(一)
扭矩、转动惯量和角加速度之间的关系
该表达式给出了围绕固定轴作用在旋转体上的总(外部)扭矩所做的功。与对应表达式的相似性![]() 用于线性(平移)运动。
用于线性(平移)运动。
将上述表达式两边除以dt,
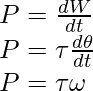 ………………………………..(2)
………………………………..(2)
上面的表达式是瞬时功率。将这个围绕固定轴的旋转运动的幂公式与线性运动的幂公式 P = Fv 进行比较。
完全刚体没有内部运动。结果,外部扭矩所做的功并没有消散,而是继续提高身体的动能。等式 (2) 给出了对身体做功的速率。这等于动能增加的速率。
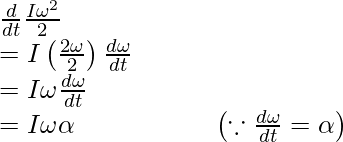
相等的做功率和动能增加率,
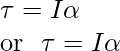 ……………………………………..(3)
……………………………………..(3)
上述表达式类似于牛顿第二定律的线性运动,符号表示为 F = ma。当力引起加速度时,扭矩会引起身体的角加速度。施加的扭矩决定了角加速度,它与身体的转动惯量成反比。对于沿固定轴的旋转,上述表达式是牛顿第二定律。
转动惯量
转动惯量是物体对旋转变化的抵抗力的量度。转动惯量用 I 表示,以千克每平方米 (kgm 2 ) 为单位。它表示为
我 = 先生2
其中 m 是粒子的质量,r 是距旋转轴的距离。 Symmetric body with symmetric axis Moment of inertia Ring Cylinder or disc Uniform sphere Rod with the axis through the end Rod with the axis at the center ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
示例问题
问题 1:给出 (i) 球体、(ii) 圆柱体、(iii) 环和 (iv) 立方体的质心位置,每个质量密度均相同。物体的质心一定在体内吗?
解决方案:
Because the mass density is uniform in all four circumstances, the center of mass is positioned at their geometrical centers.
No, the center of mass of a body does not have to be located on the body. In a circular ring the center of mass is at the ring’s center, where there is no mass.
问题 2:质量可忽略不计的绳索缠绕在质量为 20 公斤、半径为 20 厘米的飞轮的轮缘上。如图所示,对绳索施加 25 N 的稳定拉力。飞轮安装在带有无摩擦轴承的水平轴上。

(a) 计算车轮的角加速度。
(b) 当绳子松开 2m 时,找出拉力所做的功。
解决方案:
(a) Relationship between torque, moment of inertia, and angular acceleration is
![]()
Rearrange the expression,
![]() ………………………………………….(1)
………………………………………….(1)
The expression for the torque is
τ = F R
Substitute the values in the above expression,
τ = (25×0.20) Nm
τ = 5.0 Nm
The moment of inertia of flywheel about its axis is given by,
![]()
Substitute the values in the above expression,
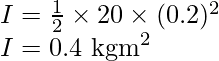
Substitute the values in the expression (1),
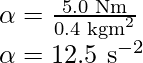
(b) Work done by the pull unwinding 2m of the cord
W = 25 N × 2m = 50 J
问题 3:一个孩子静止地坐在一辆长手推车的一端,在光滑的水平地板上以速度 V 匀速移动。如果孩子以任何方式起身在手推车上跑来跑去,那么(手推车+孩子)系统的CM的速度是多少?一个孩子静止地坐在一辆长手推车的一端,在光滑的水平地板上以速度 V 匀速移动。如果孩子以任何方式起身在手推车上跑来跑去,那么(手推车+孩子)系统的CM的速度是多少?
解决方案:
When the child stands up and runs around on the trolley, the speed of the trolley’s and child’s center of mass remains constant, regardless of the child’s motion. It’s because the child and the trolley form a single system, and the forces at work are entirely internal. There is no change in the system’s momentum and velocity since there is no external force.
问题4:一辆汽车重1800公斤。它的前后轴之间的距离为1.8 m。其重心位于前轴后方 1.05 m。确定水平地面对每个前轮和每个后轮施加的力。
解决方案:
Let F1 and F2 represent the forces that the level ground exerts on the front and back wheels, respectively. The rotational equilibrium about the front wheels is
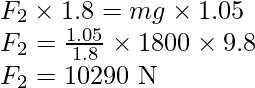
Force on each back wheel is
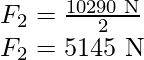
The rotational equilibrium about the back wheels.
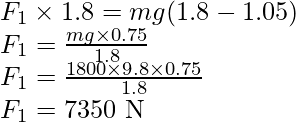
Force on each front wheel is
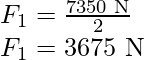
问题 5:一个质量为 20 kg 的实心圆柱体以 100 rad s -1的角速度绕其轴旋转。圆柱体半径为 0.25 m。与圆柱体旋转相关的动能是多少?圆柱绕其轴线的角动量大小是多少?
解决方案:
Given,
The mass of the solid cylinder is 20 kg.
The Angular speed is 100 rad s-1.
The moment of inertia of the solid cylinder about its axis is given by,
![]()
Substitute the values in the above expression,
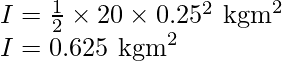
The expression for the rotational kinetic energy is
![]()
Substitute the values in the above expression,
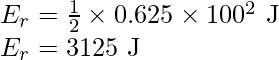
The expression for the angular momentum is
![]()
Substitute the values in the above expression,