- ASP.Net Razor代码块(1)
- ASP.Net Razor代码块
- ASP.NET Core-Razor布局视图
- ASP.NET Core-Razor布局视图(1)
- ASP.NET Core-Razor View导入
- ASP.NET Core-Razor View导入(1)
- ASP.NET Core-Razor View开始(1)
- ASP.NET Core-Razor View开始
- ASP.NET Core-Razor标记助手(1)
- ASP.NET Core-Razor标记助手
- ASP.Net Razor教程(1)
- ASP.Net Razor教程
- ASP.NET MVC-Razor
- ASP.NET MVC-Razor(1)
- ASP.Net Razor代码表达式(1)
- ASP.Net Razor代码表达式
- ASP.Net Razor HTML帮助器(1)
- ASP.Net Razor HTML帮助器
- ASP.NET Core-新项目
- ASP.NET Core-新项目(1)
- asp.net razor 获取列表而不刷新 - C# (1)
- ASP.NET Core教程(1)
- ASP.NET Core教程
- asp.net razor 获取列表而不刷新 - C# 代码示例
- ASP.NET Core-视图
- ASP.NET Core-视图(1)
- ASP.Net Razor控件结构(1)
- ASP.Net Razor控件结构
- ASP.NET Core-配置(1)
📅 最后修改于: 2020-11-21 05:01:52 🧑 作者: Mango
在本章中,我们将继续讨论标签助手。我们还将在应用程序中添加新功能,并使它能够编辑现有员工的详细信息。我们将在每个员工的侧面添加一个链接,该链接将转到HomeController上的Edit动作。
@model HomePageViewModel
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Home";
}
Welcome!
@foreach (var employee in Model.Employees) {
@employee.Name
Details
Edit
}
我们还没有“编辑”操作,但是我们需要一个可以编辑的员工ID。因此,让我们首先通过右键单击Views→Home文件夹并选择Add→New Items来创建一个新视图。
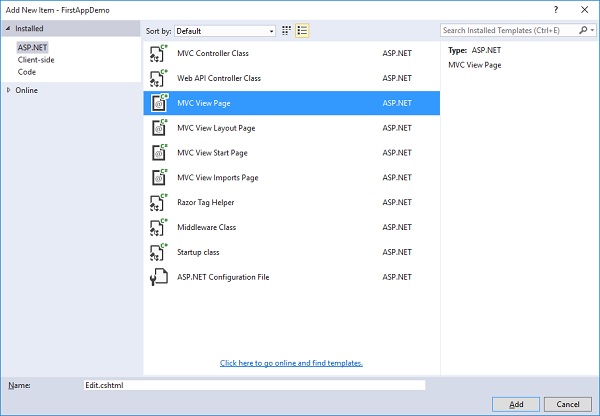
在中间窗格中,选择“ MVC视图页”;调用页面Edit.cshtml。现在,单击添加按钮。
在Edit.cshtml文件中添加以下代码。
@model Employee
@{
ViewBag.Title = $"Edit {Model.Name}";
}
Edit @Model.Name
对于此页面的标题,我们可以说我们要编辑然后提供员工姓名。
-
Edit前面的美元符号将允许运行时使用该属性中的值(例如员工姓名)替换Model.Name。
-
在form标记内部,我们可以使用诸如asp-action和asp-controller之类的标记助手。这样,当用户提交此表单时,它将直接进入特定的控制器操作。
-
在这种情况下,我们要转到同一控制器上的Edit动作,并且我们要明确表示对于此表单上的方法,它应该使用HttpPost。
-
表单的默认方法是GET,我们不想使用GET操作来编辑员工。
-
在标签标签中,我们使用了asp-for标签助手,它表示这是模型的Name属性的标签。此标记帮助程序可以将Html.For属性设置为正确的值,并设置此标签的内部文本,以便它实际显示我们想要的内容,例如员工姓名。
让我们转到HomeController类,添加Edit操作,该操作返回给用户一个用于编辑员工的表单的视图,然后我们将需要第二个Edit操作,该操作将响应HttpPost,如下所示。
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult Edit(int id) {
var context = new FirstAppDemoDbContext();
SQLEmployeeData sqlData = new SQLEmployeeData(context);
var model = sqlData.Get(id);
if (model == null) {
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
return View(model);
}
首先,我们需要一个编辑操作,该操作将响应GET请求。这将需要一个员工ID。这里的代码将类似于“ Details”操作中的代码。我们将首先提取用户要编辑的员工的数据。我们还需要确保该雇员确实存在。如果不存在,我们会将用户重定向回索引视图。但是,当有员工存在时,我们将渲染“编辑”视图。
我们还需要响应表单将发送的HttpPost。
让我们在HomeController.cs文件中添加一个新类,如以下程序所示。
public class EmployeeEditViewModel {
[Required, MaxLength(80)]
public string Name { get; set; }
}
在将响应HttpPost的Edit Action中,将使用EmployeeEditViewModel,而不是雇员本身,因为我们只想捕获Edit.cshtml文件中形式正确的项目。
以下是“编辑”操作的实现。
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult Edit(int id, EmployeeEditViewModel input) {
var context = new FirstAppDemoDbContext();
SQLEmployeeData sqlData = new SQLEmployeeData(context);
var employee = sqlData.Get(id);
if (employee != null && ModelState.IsValid) {
employee.Name = input.Name;
context.SaveChanges();
return RedirectToAction("Details", new { id = employee.Id });
}
return View(employee);
}
根据我们的路由规则,应始终从URL中具有ID的URL交付编辑表单,例如/ home / edit / 1 。
-
表单总是要发回到相同的URL / home / edit / 1。
-
MVC框架将能够从URL中提取该ID并将其作为参数传递。
-
我们始终需要检查ModelState是否有效,并且在我们对数据库执行更新操作之前,还要确保该员工在数据库中并且该数据库不为null。
-
如果所有这些都不成立,我们将返回一个视图并允许用户重试。尽管在具有并发用户的真实应用程序中,如果employee为空,则可能是因为员工详细信息被某人删除了。
-
如果该员工不存在,请告诉用户该员工不存在。
-
否则,请检查ModelState。如果ModelState无效,则返回一个视图。这允许修复编辑并使ModelState有效。
-
将名称从“输入”视图模型复制到从数据库中检索到的雇员,然后保存更改。 SaveChagnes()方法将把所有这些更改刷新到数据库中。
以下是HomeController的完整实现。
using Microsoft.AspNet.Mvc;
using FirstAppDemo.ViewModels;
using FirstAppDemo.Services;
using FirstAppDemo.Entities;
using FirstAppDemo.Models;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace FirstAppDemo.Controllers {
public class HomeController : Controller {
public ViewResult Index() {
var model = new HomePageViewModel();
using (var context = new FirstAppDemoDbContext()) {
SQLEmployeeData sqlData = new SQLEmployeeData(context);
model.Employees = sqlData.GetAll();
}
return View(model);
}
public IActionResult Details(int id) {
var context = new FirstAppDemoDbContext();
SQLEmployeeData sqlData = new SQLEmployeeData(context);
var model = sqlData.Get(id)
if (model == null) {
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
return View(model);
}
[HttpGet]
public IActionResult Edit(int id) {
var context = new FirstAppDemoDbContext();
SQLEmployeeData sqlData = new SQLEmployeeData(context);
var model = sqlData.Get(id);
if (model == null) {
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
return View(model);
}
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult Edit(int id, EmployeeEditViewModel input) {
var context = new FirstAppDemoDbContext();
SQLEmployeeData sqlData = new SQLEmployeeData(context);
var employee = sqlData.Get(id);
if (employee != null && ModelState.IsValid) {
employee.Name = input.Name;
context.SaveChanges();
return RedirectToAction("Details", new { id = employee.Id });
}
return View(employee);
}
}
public class SQLEmployeeData {
private FirstAppDemoDbContext _context { get; set; }
public SQLEmployeeData(FirstAppDemoDbContext context) {
_context = context;
}
public void Add(Employee emp) {
_context.Add(emp);
_context.SaveChanges();
}
public Employee Get(int ID) {
return _context.Employees.FirstOrDefault(e => e.Id == ID);
}
public IEnumerable GetAll() {
return _context.Employees.ToList();
}
}
public class HomePageViewModel {
public IEnumerable Employees { get; set; }
}
public class EmployeeEditViewModel {
[Required, MaxLength(80)]
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
让我们编译程序并运行应用程序。
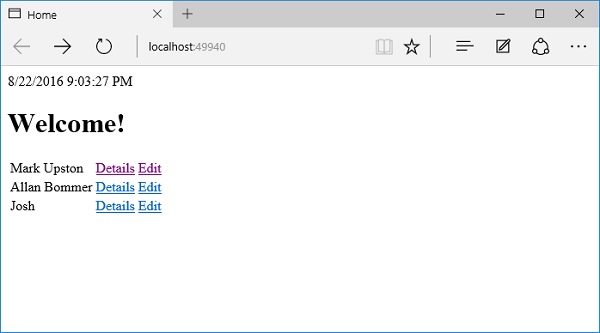
现在,我们有一个“编辑”链接;让我们通过单击“编辑”链接来编辑Josh的详细信息。
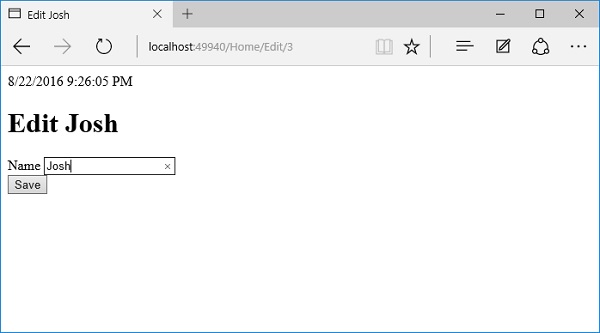
让我们将名称更改为Josh Groban。
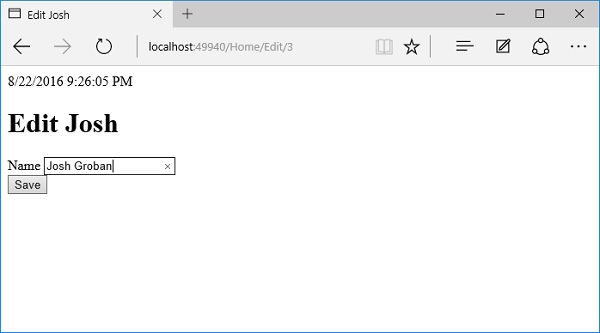
单击保存按钮。
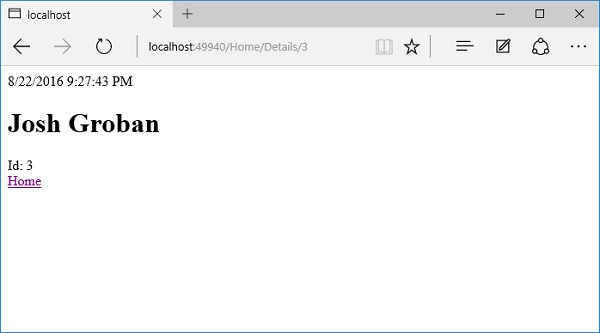
您可以看到该名称已更改为Josh Groban,如上面的屏幕截图所示。现在让我们单击“主页”链接。
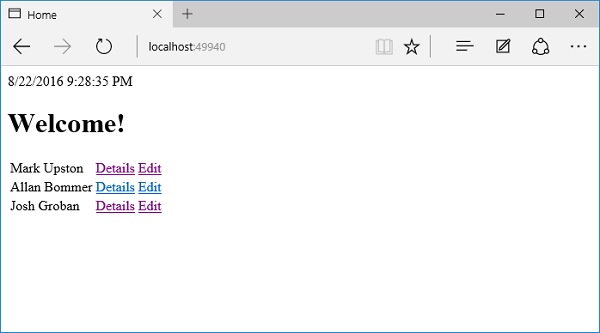
在主页上,您现在将看到更新的名称。