如何在Python中执行 Fisher 精确检验
Fisher精确检验是一种统计检验,用于确定两个类别变量是否具有非随机联系,或者我们可以说它用于检查两个类别变量是否具有显着关系。在本文中,让我们学习如何执行 Fisher 精确检验。在Python中,可以使用 SciPy 库中的 Fisher_exact()函数执行精确测试。
Syntax: scipy.stats.fisher_exact(table, alternative=’two-sided’)
Parameters:
table : array like 2X2 contigency table. negative integers aren’t allowed.
alternative: it’s an optional value which represents the alternative hypothesis. values can be {‘two-sided’, ‘less’, ‘greater’}, by default it is two sided
- less : one sided
- greater: one sided
Returns : oddratio and p_value.
假设的类型
- 零假设:行和列之间没有关联,或者分类是独立的。
- 备择假设:行和列之间存在关联,或者分类是相关的。
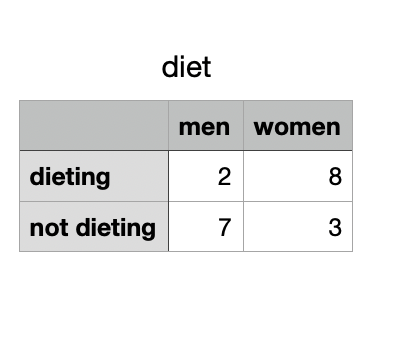
我们用于示例的 2X2 列联表是:
2 名男性和 8 名女性遵循节食计划。 7男3女没有。
Python3
# importing packages
import scipy.stats as stats
# creating data
data = [[2, 8], [7, 3]]
# performing fishers exact test on the data
odd_ratio, p_value = stats.fisher_exact(data)
print('odd ratio is : ' + str(odd_ratio))
print('p_value is : ' + str(p_value))输出:
odd ratio is : 0.10714285714285714
p_value is : 0.06977851869492728如果我们将显着性水平设为 0.05,则我们无法拒绝原假设,因为 p_value 高于 0.05。替代假设被拒绝。