氨基酸——定义、结构、性质、分类
生物分子,有时称为生物分子,是指在生物中发现的分子,这些分子是一个或多个生物过程(例如细胞分裂、形态发生或发育)所必需的。大分子(或聚阴离子)如蛋白质、碳水化合物、脂质和核酸,以及小分子如初级代谢物、次级代谢物和天然产物,都是生物分子的例子。生物材料是这类材料的更广泛的术语。生物分子是生物体的重要组成部分。虽然内源性生物分子是在生物体内制造的,但生物体通常需要外部生物分子,例如特定的营养物质才能存在。
氨基酸
Proteins are complex macromolecules made up of amino acids that are found in all living cells. Amino acids, in other words, are the building blocks of proteins. There are around 500 naturally occurring amino acids that we are aware of.
氨基酸的结构
氨基酸是蛋白质的基本成分。含有氨基和羧基的有机物质称为氨基酸。
除了羧基(-COOH)基团的碳原子之外的任何碳原子都可以连接到氨基(-NH 2 )上。

氨基酸的性质
- 它们是结晶的无色化合物。
- 它们的熔点真的很高。
- 侧链的性质影响在水中的溶解度。
- 它们是两性的,这意味着它们与酸和碱反应。
- 除甘氨酸外,均含有不对称碳,使平面偏振光发生旋转。光学活动是此功能的名称。
氨基酸的分类
根据身体要求分类:
- 非必需氨基酸:这些氨基酸由身体产生,不需要消耗。在二十种氨基酸中,十种是非必需的。甘氨酸、丙氨酸、丝氨酸、半胱氨酸、谷氨酰胺、酪氨酸、脯氨酸、天冬氨酸、天冬酰胺和谷氨酸是氨基酸。
- 必需氨基酸:这些氨基酸不是人体合成的,必须从食物中获取。在二十种氨基酸中,十种是非必需的。缬氨酸、亮氨酸、异亮氨酸、精氨酸、赖氨酸、苏氨酸、苯丙氨酸、色氨酸和组氨酸是构成人体的氨基酸。这些必需氨基酸是我们身体生长所必需的,我们的饮食中缺乏它们会导致像 kwashiorkor 这样的疾病。
天然存在的氨基酸分类:天然存在的氨基酸可分为三组:脂肪族、芳香族和杂环氨基酸。
脂肪族氨基酸:
它们是具有长链的氨基酸。氨基酸进一步分为以下几类:
- 中性氨基酸:它们的分子具有相同数量的羧基和氨基。例如:甘氨酸、丙氨酸、缬氨酸等。
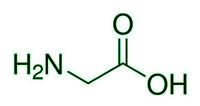
甘氨酸
- 酸性氨基酸:在它们的分子中,它们的羧基比例高于氨基。例如:天冬氨酸、谷氨酸,它含有两个-COOH 基团和一个-NH 2基团。
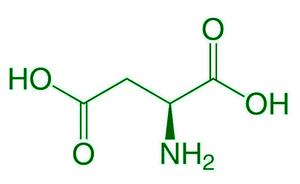
天冬氨酸
- 碱性氨基酸:其分子中氨基的比例高于羧基。示例:赖氨酸、精氨酸和组氨酸,其中包含两个 -NH 2基团和 -COOH 基团。

赖氨酸
- 含硫氨基酸:其结构中含有巯基(-SH)基团。示例:半胱氨酸和蛋氨酸
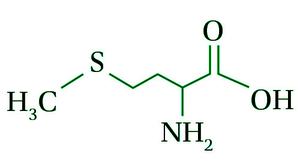
蛋氨酸
芳香族氨基酸:
它们的结构中含有一个苯环。示例:苯丙氨酸和酪氨酸
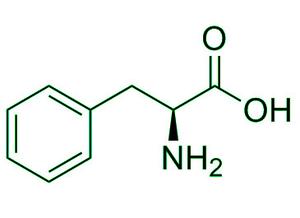
苯丙氨酸
杂环氨基酸:
它们的侧链上有一个杂环,至少有一种除碳以外的元素。示例:色氨酸、脯氨酸和羟脯氨酸
脯氨酸
一些常见的氨基酸是: S. No. α- Amino acid Three-letter abbreviation One letter abbreviation 1. Glycine Gly G 2. Alanine Ala A 3. Valine Val V 4. Leucine Leu L 5. Isoleucine Ile I 6. Phenylalanine Phe F 7. Methionine Met M 8. Tryptophan Trp W 9. Proline Pro P 10. Serine Ser S 11. Cysteine Cys C 12. Asparagine Asn N 13. Glutamine Gln Q 14. Threonine Thr T 15. Tyrosine Tyr Y 16. Aspartic acid Asp D 17. Glutamic acid Glu E 18. Lysine Lys K 19. Arginine Arg R 20. Histidine His H
氨基酸是如何形成蛋白质的?
当一个氨基酸分子的氨基结合形成蛋白质时,它们与另一个氨基酸分子的羧基建立化学连接。肽键是这个过程的结果。这种连接氨基酸的过程一直持续到蛋白质合成所需的所有氨基酸都连接在一起为止。在这两个氨基酸之间,一个水分子在这个过程中丢失了。当两个氨基酸以这种方式连接时,就会形成一个更大的单元,称为肽。多肽由许多连接在一起的肽组成。然后多肽结合在一起形成完整的蛋白质。

肽键
Role of Amino Acid in Our Body
- Amino acids are transformed into physiologically active molecules in a variety of ways. Tyrosine, for example, is transformed into the hormones thyroxine and adrenaline, as well as the skin pigment melanin.
- From the vitamin nicotinamide and the plant hormone indole acetic acid, glycine is involved in the synthesis of heme (haemoglobin protein) and tryptophan.
- Citrulline and ornithine are amino acids that are actively involved in the urea cycle in the liver, which helps to keep ammonia levels below hazardous levels.
示例问题
问题1:哪些食物含有氨基酸?
回答:
Animal and plant sources of amino acids are available. Amino acids can be found in grains, nuts, seeds, beans, legumes, fruits, vegetables, eggs, milk, cheese, fish, and seafood, among other foods.
问题2:每天服用氨基酸安全吗?
回答:
In general, using a small amount of amino acids every day is safe. A high dose of amino acids, on the other hand, is detrimental. They can cause stomach pain, diarrhoea, a dangerous drop in blood pressure, gastrointestinal distress, and other problems.
问题 3:列出 21 种氨基酸?
回答:
Glycine, Alanine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Phenylalanine, Methionine, Tryptophan, Proline, Serine, Cysteine, Asparagine, Glutamine, Tyrosine, Aspartic acid, Glutamic acid, Lysine, Arginine, Histidine, and Selenocysteine are the 21 amino acids.
问题4:氨基酸有副作用吗?
回答:
Excess amino acid consumption raises the risk of hypertension, heart illness, weariness, and contraction loss.
问题 5:氨基酸对您的身体有什么作用?
回答:
Proteins are nutrients that help you create muscle. Proteins are made up of amino acids, which are the basic building components. As a result, they aid in the growth and healing of the body’s damaged cells and tissues. Some amino acids, such as tyrosine, are transformed into physiologically active substances such as the hormones thyroxine and adrenaline, as well as the skin pigment melanin.
问题6:氨基酸会影响肾脏吗?
回答:
Citrulline and ornithine are two amino acids that are involved in the urea cycle in the liver. This contributes to keeping ammonia levels below dangerous levels.