链码是一种无损压缩技术,用于表示图像中的对象。一个对象的任何连续边界的坐标都可以表示为字符串数字,其中每个数字都代表一个特定的方向,在该方向上存在连接的直线上的下一个点。以一个点作为参考/起点,在绘制从链生成的点时,可以重新绘制原始图形。
本文介绍如何生成2-D直线的8邻域链代码。在矩形网格中,一个点最多可以具有8个周围的点,如下所示。线上的下一个点必须是这8个周围点之一。每个方向都分配有一个代码。使用此代码,我们可以找出接下来应绘制的周围点。
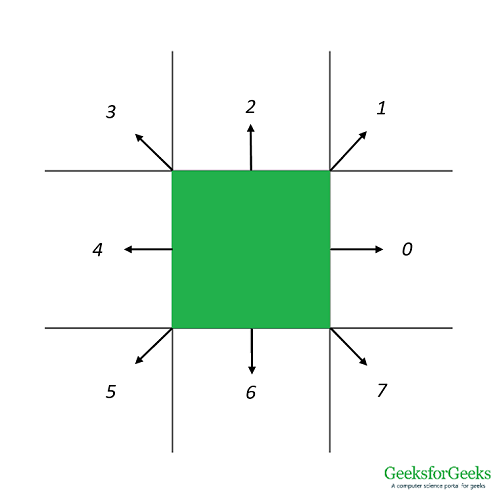
链码可以通过使用每个方向的条件语句来生成,但是对于具有大量方向(3-D网格最多可以具有26个方向)的系统进行描述变得非常繁琐。相反,我们使用哈希函数。 X( ![]() )和Y(
)和Y( ![]() )计算两个连续点的坐标并进行哈希处理,以生成两个点之间的链码的密钥。
)计算两个连续点的坐标并进行哈希处理,以生成两个点之间的链码的密钥。
链码清单: ![]()
哈希函数: ![]()
哈希表:-
| 1 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 8 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 7 | 2 |
| -1 | 1 | 6 | 3 |
| -1 | 0 | 3 | 4 |
| -1 | -1 | 0 | 5 |
| 0 | -1 | 1 | 6 |
| 1 | -1 | 2 | 7 |
该函数不会生成值4,因此会将伪值存储在此处。
例子:
输入:(2,-3),(-4,2)输出:从(2,-3)到(-4,2)的直线的链码是333433 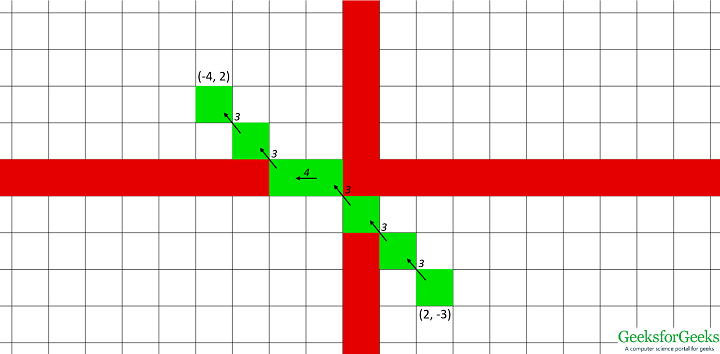 输入:(-7,-4),(9,3)输出:从(-7,-4)到(9,3)的直线的链码是0101010100101010
输入:(-7,-4),(9,3)输出:从(-7,-4)到(9,3)的直线的链码是0101010100101010 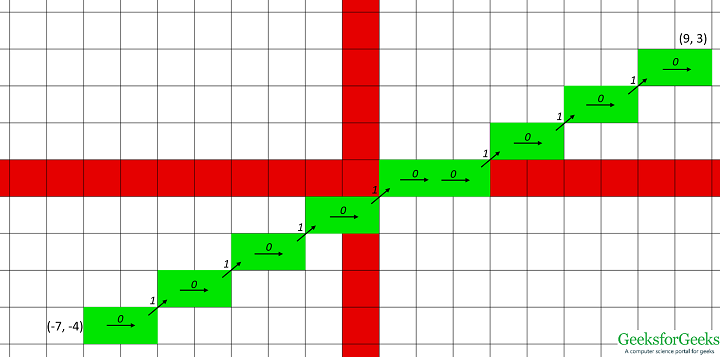
Python3
# Python3 code for generating 8-neighbourhood chain
# code for a 2-D line
codeList = [5, 6, 7, 4, -1, 0, 3, 2, 1]
# This function generates the chaincode
# for transition between two neighbour points
def getChainCode(x1, y1, x2, y2):
dx = x2 - x1
dy = y2 - y1
hashKey = 3 * dy + dx + 4
return codeList[hashKey]
'''This function generates the list of
chaincodes for given list of points'''
def generateChainCode(ListOfPoints):
chainCode = []
for i in range(len(ListOfPoints) - 1):
a = ListOfPoints[i]
b = ListOfPoints[i + 1]
chainCode.append(getChainCode(a[0], a[1], b[0], b[1]))
return chainCode
'''This function generates the list of points for
a staright line using Bresenham's Algorithm'''
def Bresenham2D(x1, y1, x2, y2):
ListOfPoints = []
ListOfPoints.append([x1, y1])
xdif = x2 - x1
ydif = y2 - y1
dx = abs(xdif)
dy = abs(ydif)
if(xdif > 0):
xs = 1
else:
xs = -1
if (ydif > 0):
ys = 1
else:
ys = -1
if (dx > dy):
# Driving axis is the X-axis
p = 2 * dy - dx
while (x1 != x2):
x1 += xs
if (p >= 0):
y1 += ys
p -= 2 * dx
p += 2 * dy
ListOfPoints.append([x1, y1])
else:
# Driving axis is the Y-axis
p = 2 * dx-dy
while(y1 != y2):
y1 += ys
if (p >= 0):
x1 += xs
p -= 2 * dy
p += 2 * dx
ListOfPoints.append([x1, y1])
return ListOfPoints
def DriverFunction():
(x1, y1) = (-9, -3)
(x2, y2) = (10, 1)
ListOfPoints = Bresenham2D(x1, y1, x2, y2)
chainCode = generateChainCode(ListOfPoints)
chainCodeString = "".join(str(e) for e in chainCode)
print ('Chain code for the straight line from', (x1, y1),
'to', (x2, y2), 'is', chainCodeString)
DriverFunction()输出:
Chain code for the straight line from (-9, -3) to (10, 1) is 0010000100010000100