在本文中,我们将讨论二项式随机变量。
先决条件:随机变量
一种特定类型的离散随机变量,用于计算特定事件在固定次数的尝试或试验中发生的频率。
为了使变量成为二项式随机变量,必须满足以下所有条件:
- 试验次数固定(样本量固定)。
- 在每个试验中,感兴趣的事件要么发生,要么不发生。
- 在每个试验中,发生(或不发生)的概率是相同的。
- 审判是相互独立的。
数学符号
n = number of trials
p = probability of success in each trial
k = number of success in n trials
现在我们尝试找出n次试验中k次成功的概率。
在这里,每个试验的成功概率与其他试验无关,为p。
因此,我们首先选择将成功的k个试验,而在其余nk个试验中将失败的试验。这样做的方法数量是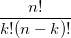
由于所有n个事件都是独立的,因此n次试验中k次成功的概率等于每个试验的概率相乘。
在这里,它的k个成功和nk个失败,因此实现k个成功和nk个失败的每种方式的概率为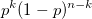
因此,最终概率为
(number of ways to achieve k success
and n-k failures)
*
(probability for each way to achieve k
success and n-k failure)
然后,二项式随机变量概率由下式给出: 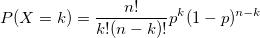
令X为二项式随机变量,试验次数为n,每次试验成功的概率为p。
预期的成功次数是
E[X] = np
成功次数的方差由下式给出:
Var[X] = np(1-p)
例1 :考虑一个随机实验,其中将一枚有偏见的硬币(正面概率= 1/3)投掷10次。求出出现的正面个数为5的概率。
解决方案 :
设X为n = 10且p = 1/3的二项式随机变量P(X = 5)=? 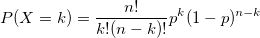
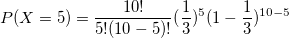
这是相同的实现
C++
// C++ program to compute Binomial Probability
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// function to calculate nCr i.e., number of
// ways to choose r out of n objects
int nCr(int n, int r)
{
// Since nCr is same as nC(n-r)
// To decrease number of iterations
if (r > n / 2)
r = n - r;
int answer = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= r; i++) {
answer *= (n - r + i);
answer /= i;
}
return answer;
}
// function to calculate binomial r.v. probability
float binomialProbability(int n, int k, float p)
{
return nCr(n, k) * pow(p, k) *
pow(1 - p, n - k);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 10;
int k = 5;
float p = 1.0 / 3;
float probability = binomialProbability(n, k, p);
cout << "Probability of " << k;
cout << " heads when a coin is tossed " << n;
cout << " times where probability of each head is " << p << endl;
cout << " is = " << probability << endl;
} Java
// Java program to compute Binomial Probability
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// function to calculate nCr i.e., number of
// ways to choose r out of n objects
static int nCr(int n, int r)
{
// Since nCr is same as nC(n-r)
// To decrease number of iterations
if (r > n / 2)
r = n - r;
int answer = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= r; i++) {
answer *= (n - r + i);
answer /= i;
}
return answer;
}
// function to calculate binomial r.v. probability
static float binomialProbability(int n, int k, float p)
{
return nCr(n, k) * (float)Math.pow(p, k) *
(float)Math.pow(1 - p, n - k);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 10;
int k = 5;
float p = (float)1.0 / 3;
float probability = binomialProbability(n, k, p);
System.out.print("Probability of " +k);
System.out.print(" heads when a coin is tossed " +n);
System.out.println(" times where probability of each head is " +p);
System.out.println( " is = " + probability );
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Mr. Somesh Awasthi */Python3
# Python3 program to compute Binomial
# Probability
# function to calculate nCr i.e.,
# number of ways to choose r out
# of n objects
def nCr(n, r):
# Since nCr is same as nC(n-r)
# To decrease number of iterations
if (r > n / 2):
r = n - r;
answer = 1;
for i in range(1, r + 1):
answer *= (n - r + i);
answer /= i;
return answer;
# function to calculate binomial r.v.
# probability
def binomialProbability(n, k, p):
return (nCr(n, k) * pow(p, k) *
pow(1 - p, n - k));
# Driver code
n = 10;
k = 5;
p = 1.0 / 3;
probability = binomialProbability(n, k, p);
print("Probability of", k,
"heads when a coin is tossed", end = " ");
print(n, "times where probability of each head is",
round(p, 6));
print("is = ", round(probability, 6));
# This code is contributed by mitsC#
// C# program to compute Binomial
// Probability.
using System;
class GFG {
// function to calculate nCr
// i.e., number of ways to
// choose r out of n objects
static int nCr(int n, int r)
{
// Since nCr is same as
// nC(n-r) To decrease
// number of iterations
if (r > n / 2)
r = n - r;
int answer = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= r; i++)
{
answer *= (n - r + i);
answer /= i;
}
return answer;
}
// function to calculate binomial
// r.v. probability
static float binomialProbability(
int n, int k, float p)
{
return nCr(n, k) *
(float)Math.Pow(p, k)
* (float)Math.Pow(1 - p,
n - k);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int n = 10;
int k = 5;
float p = (float)1.0 / 3;
float probability =
binomialProbability(n, k, p);
Console.Write("Probability of "
+ k);
Console.Write(" heads when a coin "
+ "is tossed " + n);
Console.Write(" times where "
+ "probability of each head is "
+ p);
Console.Write( " is = "
+ probability );
}
}
// This code is contributed by nitin mittal.PHP
$n / 2)
$r = $n - $r;
$answer = 1;
for ($i = 1; $i <= $r; $i++) {
$answer *= ($n - $r + $i);
$answer /= $i;
}
return $answer;
}
// function to calculate binomial r.v.
// probability
function binomialProbability($n, $k, $p)
{
return nCr($n, $k) * pow($p, $k) *
pow(1 - $p, $n - $k);
}
// Driver code
$n = 10;
$k = 5;
$p = 1.0 / 3;
$probability =
binomialProbability($n, $k, $p);
echo "Probability of " . $k;
echo " heads when a coin is tossed "
. $n;
echo " times where probability of "
. "each head is " . $p ;
echo " is = " . $probability ;
// This code is contributed by nitin mittal.
?>输出:
Probability of 5 heads when a coin is tossed 10 times where probability of each head is 0.333333
is = 0.136565
参考:
stat200