Python中的 Matplotlib.colors.PowerNorm 类
Matplotlib是Python中用于数组二维图的惊人可视化库。 Matplotlib 是一个基于 NumPy 数组构建的多平台数据可视化库,旨在与更广泛的 SciPy 堆栈配合使用。
matplotlib.colors.PowerNor
matplotlib.colors.PowerNorm类属于matplotlib.colors模块。 matplotlib.colors 模块用于将颜色或数字参数转换为 RGBA 或 RGB。此模块用于将数字映射到颜色或在一维颜色数组(也称为颜色图)中进行颜色规范转换。
matplotlib.colors.PowerNorm 类用于将值线性映射到 - 的范围,然后在该范围内应用幂律归一化。它的基类是 matplotlib.colors.Normalize。
类的方法:
- inverse(self, value):此方法返回颜色图的反转值。
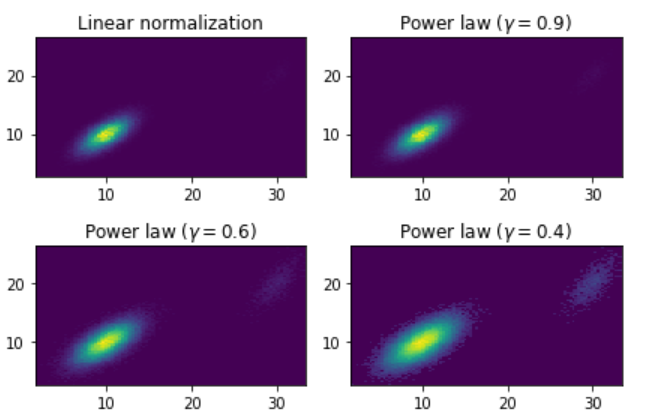
示例 1:
Python3
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.colors as mcolors
import numpy as np
from numpy.random import multivariate_normal
# data for reproducibility
data = np.vstack([
multivariate_normal([10, 10],
[[3, 2],
[2, 3]],
size = 100000),
multivariate_normal([30, 20],
[[2, 3],
[1, 3]],
size = 1000)
])
gammas_array = [0.9, 0.6, 0.4]
figure, axs = plt.subplots(nrows = 2,
ncols = 2)
axs[0, 0].set_title('Linear normalization')
axs[0, 0].hist2d(data[:, 0],
data[:, 1],
bins = 100)
for ax, gamma in zip(axs.flat[1:],
gammas_array):
ax.set_title(r'Power law $(\gamma =% 1.1f)$' % gamma)
ax.hist2d(data[:, 0],
data[:, 1],
bins = 100,
norm = mcolors.PowerNorm(gamma))
figure.tight_layout()
plt.show()Python3
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.colors as colors
max_N = 100
A, B = np.mgrid[-3:3:complex(0, max_N),
-2:2:complex(0, max_N)]
# PowerNorm: using power-law
# trend in X
A, B = np.mgrid[0:3:complex(0, max_N),
0:2:complex(0, max_N)]
X1 = (1 + np.sin(B * 10.)) * A**(2.)
figure, axes = plt.subplots(2, 1)
pcm = axes[0].pcolormesh(A, B, X1,
norm = colors.PowerNorm(gamma = 1./2.),
cmap ='PuBu_r')
figure.colorbar(pcm, ax = axes[0],
extend ='max')
pcm = axes[1].pcolormesh(A, B, X1,
cmap ='PuBu_r')
figure.colorbar(pcm, ax = axes[1],
extend ='max')
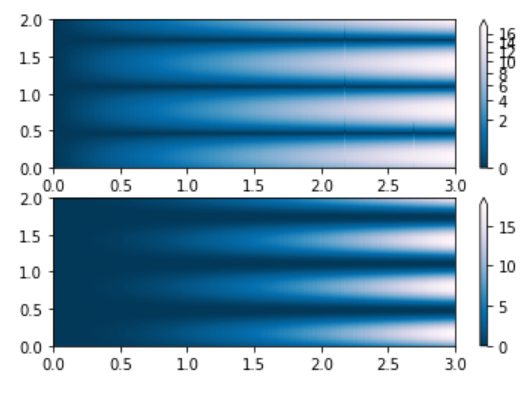
plt.show()输出:
示例 2:
Python3
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.colors as colors
max_N = 100
A, B = np.mgrid[-3:3:complex(0, max_N),
-2:2:complex(0, max_N)]
# PowerNorm: using power-law
# trend in X
A, B = np.mgrid[0:3:complex(0, max_N),
0:2:complex(0, max_N)]
X1 = (1 + np.sin(B * 10.)) * A**(2.)
figure, axes = plt.subplots(2, 1)
pcm = axes[0].pcolormesh(A, B, X1,
norm = colors.PowerNorm(gamma = 1./2.),
cmap ='PuBu_r')
figure.colorbar(pcm, ax = axes[0],
extend ='max')
pcm = axes[1].pcolormesh(A, B, X1,
cmap ='PuBu_r')
figure.colorbar(pcm, ax = axes[1],
extend ='max')
plt.show()
输出: