电阻率公式
当在物体(导体)上施加电位差时,电子开始移动,从而在物体中产生电流。在电子的这种运动过程中,它们也会与其他电子发生碰撞,从而对电子的流动产生一些反作用,这种反作用电子流动的现象称为电阻(R)。它的SI单位是欧姆(Ω)
影响阻力的因素
- 导体的电阻R与导体的长度成正比
R ∝ l ⇢ (1)
- 当导体呈均匀形状时,导体的电阻与横截面积成反比。
R ∝ 1/A ⇢ (2)
- 导体的电阻还取决于导体的性质以及导体的温度。因此,通过结合等式 (1) 和 (2),
R ∝ l/A
R = ρl/A
ρ(rho) is constant which is called resistivity.
电阻率公式
材料的电阻率定义为在特定温度下每单位长度和每单位横截面积的材料导体的电阻
要么
材料的特性表明材料抵抗或传导电流的强度。它用ρ表示,称为rho。电阻率公式如下:
- ρ = (RA)/l ⇢ (where ‘R’ is resistance, ‘A’ is the Area of cross section ,’l’ is the length)
- ρ = 1/σ ⇢ (σ is the conductivity)
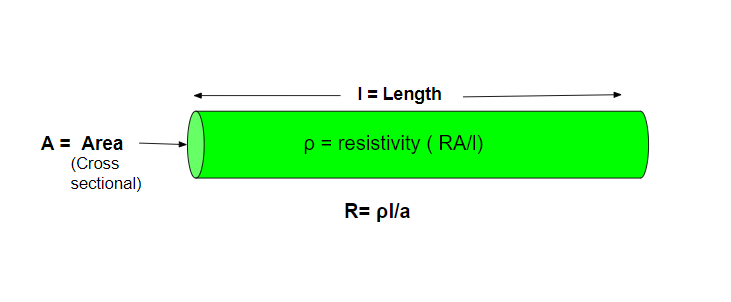
电阻率的推导
Given: R = ρl/a
Where, R – Resistance,
ρ – Resistivity
l – length of material
A – Area of cross-section
Rearranging the above equation,
RA = ρl
ρl = RA
ρ = (RA)/l
SI 电阻率单位
SI unit of R = ohm
SI unit of A = m2
SI unit of l = m
SI unit of ρ = (ohm × m2)/m
ρ = ohm m
SI unit of resistivity is ‘ohm meter(Ωm)’
影响电阻率的因素
- 导体的电阻率与其电阻成正比 [ρ ∝ R]。
- 导体的电阻率与其均匀的横截面积成正比。 [ρ ∝ A]
- 导体的电阻率与其长度成反比。 [ρ ∝ 1/l]
- 电阻率还取决于材料的性质和温度。
示例问题
问题1:计算长度为30cm、面积为0.9m 2的导线的电阻率。那根线的电阻是5Ω?
解决方案:
R = 5Ω
l = 30 cm = o.3 m
A = 0.9m2
ρ = RA / l
ρ = (5 × 0.9)/0.3 Ωm
ρ = 15 Ωm
Therefore resistivity will be 15 Ωm
问题 2:假设材料的导电率为 4 ohm -1 m -1 。计算电阻率?
解决方案:
Conductivity (σ ) = 4 ohm-1m-1
ρ = 1/ σ
ρ = 1/4 ohm m
ρ = 0.25 ohm m
So, resistivity will be 0.25 ohm m
问题 3:为什么合金用于制造标准电阻器?
解决方案:
Alloys have has a high value of resistivity as well its has low temperature coefficient of resistance.
问题4:说出电阻率最高的元素和电阻率最低的金属?
解决方案:
Nichrome has the highest resistivity (1.50 × 10-6 Ωm)
问题 5:铜、康铜和银的电阻率分别为 1.74 × 10 -8 Ωm、39.1 × 10 -8 Ωm 和 1.6 × 10 -8 Ωm,确定哪个导电性最好?
解决方案:
Conductivity = 1/ resistivity
Silver has the best conductivity as it has the lowest resistivity
问题6:计算长度为3m、直径为0.6、电阻为60Ω的金属线的电阻?
解决方案 :
R = 60
Diameter = 0.6 m
Radius (r) = 0.3m
Area of cross section = πr2
A = 3.14 × (0.3 × 0.3)m2
A = 0.2826
Length (l) = 3m
ρ = RA / l
ρ = (60 × 0.2826)/3
ρ = 5.652 Ωm
问题 7:绘制铜、镍铬合金、半导体二极管的电阻率与温度关系图。
回答:
