矩阵的空空间和空性
Null Space 和 Nullity 是线性代数中的概念,用于标识属性之间的线性关系。
空空间:
任何矩阵 A 的零空间由所有向量 B 组成,使得 AB = 0 且 B 不为零。它也可以被认为是从AB = 0获得的解决方案,其中 A 是大小为mxn已知矩阵,B 是要找到的大小为nxk矩阵。矩阵的零空间的大小为我们提供了属性之间线性关系的数量。
概括说明:
设一个矩阵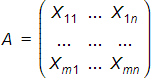
并且在 A 的零空间中有一个向量,即, 
那么 B 满足给定的方程, 
想法——
1. AB = 0 implies every row of A when multiplied by B goes to zero.
2. Variable values in each sample(represented by a row) behave the same.
3. This helps in identifying the linear relationships in the attributes.
4. Every null space vector corresponds to one linear relationship.
无效:
Nullity 可以定义为给定矩阵的零空间中存在的向量数量。换句话说,矩阵A的零空间的维数称为A的零度。属性之间线性关系的个数由零空间的大小给出。零空间向量B可用于识别这些线性关系。
秩零定理:
秩零定理帮助我们将数据矩阵的无效性与数据中的秩和属性数量联系起来。秩零定理由下式给出:
Nullity of A + Rank of A = Total number of attributes of A (i.e. total number of columns in A)
秩:
矩阵的秩是指矩阵中线性无关的行或列的数量。 
秩无效定理证明示例:
考虑具有属性 {X1, X2, X3} 1 2 0 A = 2 4 0 3 6 1 的矩阵 A 那么,A 中的列数 = 3 ![由 QuickLaTeX.com 渲染 \left(\begin{array}{ccc} 1 & 2 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0\\ 3 & 6 & 1 \end{array}\right) [R2 -> R2 - 2R1]](https://mangodoc.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/geek8geeks/Null_Space_and_Nullity_of_a_Matrix_4.jpg) R1 和 R3 线性无关。矩阵A的秩是其梯形形式的非零行数为 2。我们有,AB = 0
R1 和 R3 线性无关。矩阵A的秩是其梯形形式的非零行数为 2。我们有,AB = 0 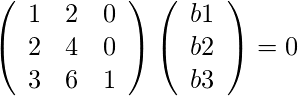 那么我们得到,b1 + 2*b2 = 0 b3 = 0 我们可以得到的空向量是
那么我们得到,b1 + 2*b2 = 0 b3 = 0 我们可以得到的空向量是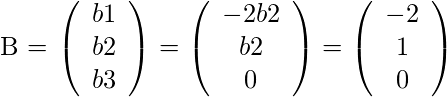 通解中的参数个数是零空间的维数(本例中为1)。因此, A的秩和空值之和为 2 + 1,等于 A 的列数。
通解中的参数个数是零空间的维数(本例中为1)。因此, A的秩和空值之和为 2 + 1,等于 A 的列数。
这种秩和无效关系适用于任何矩阵。
查找矩阵的零空间的Python示例:
# Sympy is a library in python for
# symbolic Mathematics
from sympy import Matrix
# List A
A = [[1, 2, 0], [2, 4, 0], [3, 6, 1]]
# Matrix A
A = Matrix(A)
# Null Space of A
NullSpace = A.nullspace() # Here NullSpace is a list
NullSpace = Matrix(NullSpace) # Here NullSpace is a Matrix
print("Null Space : ", NullSpace)
# checking whether NullSpace satisfies the
# given condition or not as A * NullSpace = 0
# if NullSpace is null space of A
print(A * NullSpace)
输出:
Null Space : Matrix([[-2], [1], [0]])
Matrix([[0], [0], [0]])
查找矩阵的空性的Python示例:
from sympy import Matrix
A = [[1, 2, 0], [2, 4, 0], [3, 6, 1]]
A = Matrix(A)
# Number of Columns
NoC = A.shape[1]
# Rank of A
rank = A.rank()
# Nullity of the Matrix
nullity = NoC - rank
print("Nullity : ", nullity)
输出:
Nullity : 1