R 编程中的泊松回归
泊松回归模型用于对计数数据和作为计数的响应变量(Y 值)建模。它显示了哪些 X 值对 Y 值起作用,更明确地说,它对数据进行计数:具有非负整数值的离散数据可以计数。
换句话说,它显示了哪些解释变量对响应变量有显着影响。泊松回归涉及回归模型,其中响应变量是计数形式而不是分数形式。
Mathematical Equation:
Parameters:
- y: This parameter sets as a response variable.
- a and b: The parameter a and b are the numeric coefficients.
- x: This parameter is the predictor variable.
创建泊松回归模型
用于创建泊松回归模型的函数是glm()函数。
Syntax: glm(formula, data, family)
Parameters:
- formula: This parameter is the symbol presenting the relationship between the variables.
- data: The parameter is the data set giving the values of these variables.
- family: This parameter R object to specify the details of the model. It’s value is ‘Poisson’ for Logistic Regression.
例子:
- 方法:要了解我们如何创建:
- 我们使用数据集“warpbreaks”。
- 将“中断”视为响应变量。
- 羊毛“类型”和“张力”作为预测变量。
- 获取制作模型所需的参数。
- 让我们使用 summary()函数来查找模型的摘要以进行数据分析。
- 借助此函数,轻松制作模型。
- 现在我们为“公式”、“数据”和“家庭”之间的关系绘制图表。
代码:
log(y) = a + b1x1 + b2x2 + bnxn.....输出: 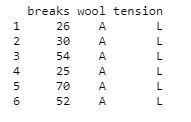
创建回归模型
方法:创建泊松回归模型:
例子:
input <- warpbreaks
print(head(input))
输出: 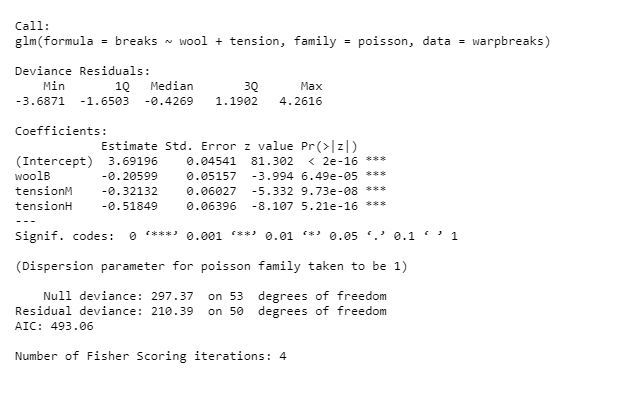
使用glm()函数创建泊松回归模型
方法:在glm()函数的帮助下创建回归模型:
例子:
output <-glm(formula = breaks ~ wool + tension,
data = warpbreaks, family = poisson)
print(summary(output))
输出: 