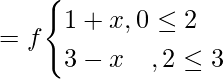问题1.如果有雾和雾,请查找
(i)f(x)= e x , 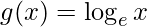
解决方案:
Let f: R → (0, ∞); and g: (0, ∞) → R
Clearly, the range of g is a subset of the domain of f.
So, fog: (0, ∞) → R and we know, (fog)(x) = f(g(x))
![]()
![]()
(fog)(x) = x
Clearly, the range of f is a subset of the domain of g.
⇒ fog: R→ R
(gof)(x) = g (f (x))
= g(ex)
![]()
(gof)(x) = x
(ii)f(x)= x 2 ,g(x)= cos x
解决方案:
f: R→ [0, ∞) ; g: R→[−1, 1]
Clearly, the range of g is not a subset of the domain of f.
⇒ Domain (fog) = {x: x ∈ domain of g and g (x) ∈ domain of f}
⇒ Domain (fog) = x: x ∈ R and cos x ∈ R}
⇒ Domain of (fog) = R
(fog): R→ R
(fog)(x) = f (g(x))
= f(cosx)
(fog)(x) = cos2x
Clearly, the range of f is a subset of the domain of g.
⇒ fog: R→R
(gof)(x) = g(f (x))
= g (x2)
(gof)(x) = cos x2
(iii)f(x)= | x |,g(x)= sin x
解决方案:
f: R → (0, ∞) ; g : R→[−1, 1]
Clearly, the range of g is a subset of the domain of f.
⇒ fog: R→R
(fog)(x) = f (g (x))
= f (sin x)
(fog)(x) = |sin x|
Clearly, the range of f is a subset of the domain of g.
⇒ fog : R→ R
(gof)(x) = g (f (x))
= g (|x|)
(gof)(x) = sin |x|
(iv)f(x)= x + 1,g(x)= e x
解决方案:
f: R→R ; g: R → [ 1, ∞)
Clearly, range of g is a subset of domain of f.
⇒ fog: R→R
(fog)(x) = f (g (x))
= f(ex)
(fog)(x) = ex + 1
Clearly, range of f is a subset of domain of g.
⇒ fog: R→R
(gof)(x) = g(f (x))
= g(x+1)
(gof)(x) = ex+1
(v)f(x)= sin -1 x,g(x)= x 2
解决方案:
f: [−1,1]→ [(-π)/2 ,π/2]; g : R → [0, ∞)
Domain (fog) = {x: x ∈ R and x ∈ [−1, 1]}
So, Domain of (fog) = [−1, 1]
fog: [−1,1] → R
(fog)(x) = f (g (x))
= f(x2)
(fog)(x) = sin−1(x2)
Clearly, the range of f is a subset of the domain of g.
fog: [−1, 1] → R
(gof)(x) = g (f (x))
= g (sin−1 x)
(gof)(x) = (sin−1x)2
(vi)f(x)= x + 1,g(x)= sinx
解决方案:
f: R→R ; g: R→[−1, 1]
Clearly, the range of g is a subset of the domain of f.
Set of the domain of f.
⇒ fog: R→ R
(fog)(x) = f(g(x))
= f(sinx)
(fog)(x) = sin x + 1
Now we have to compute gof,
Clearly, the range of f is a subset of the domain of g.
⇒ fog: R → R
(gof)(x) = g (f (x))
= g(x+1)
(gof)(x) = sin(x+1)
(vii)f(x)= x + 1,g(x)= 2x + 3
解决方案:
f: R→R ; g: R → R
Clearly, the range of g is a subset of the domain of f.
⇒ fog: R→ R
(fog)(x) = f (g (x))
= f(2x+3)
= 2x + 3 + 1
(fog)(x) = 2x + 4
Clearly, the range of f is a subset of the domain of g.
⇒ fog: R → R
(gof)(x) = g (f (x))
= g (x+1)
= 2 (x + 1) + 3
(gof)(x) = 2x + 5
(viii)f(x)= c,g(x)= sin x 2
解决方案:
f: R → {c} ; g: R→ [ 0, 1 ]
Clearly, the range of g is a subset of the domain of f.
fog: R→R
(fog)(x) = f(g(x))
= f(sinx2)
(fog)(x) = c
Clearly, the range of f is a subset of the domain of g.
⇒ fog: R→ R
(gof)(x) = g (f (x))
= g(c)
(gof)(x) = sinc2
(ix)f(x)= x 2 + 2并且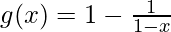
解决方案:
f: R → [2, ∞)
For domain of g: 1− x ≠ 0
⇒ x ≠ 1
⇒ Domain of g = R − {1}
![]()
=![]()
![]()
Range of g = R − {1}
So, g: R − {1} → R − {1}
Clearly, the range of g is a subset of the domain of f.
⇒ fog: R − {1} → R
(fog) (x) = f (g (x))
![]()
![]()
Clearly, the range of f is a subset of the domain of g.
⇒ gof: R→R
(gof)(x) = g (f (x))
= g(x2 + 2)
![]()
问题2。令f(x)= x 2 + x + 1且g(x)= sin x。显示雾≠gof。
解决方案:
Given f(x) = x2 + x + 1 and g(x) = sin x
Now we have to prove fog ≠ gof
(fog)(x) = f(g(x))
= f(sin x)
(fog)(x) = sin2x + sin x + 1 …..(1)
And (gof)(x) = g (f (x))
= g (x2+ x + 1)
(gof)(x) = sin (x2+ x + 1) ….(2)
From (1) and (2), we get
fog ≠ gof.
问题3.如果f(x)= | x |,则证明fof = f。
解决方案:
Given f(x) = |x|,
Now we have to prove that fof = f.
Consider (fof)(x) = f (f(x))
= f(|x|)
= ||x||
= |x|
= f(x)
So, (fof) (x) = f (x), ∀x ∈ R
Hence, fof = f.
问题4.如果f(x)= 2x + 5和g(x)= x 2 +1是两个实函数,则描述以下每个函数:
(i)雾
解决方案:
f(x) and g(x) are polynomials.
⇒ f: R → R and g: R → R.
So, fog: R → R and gof: R → R.
(i) (fog) (x) = f (g (x))
= f (x2 + 1)
= 2 (x2 + 1) + 5
=2x2 + 2 + 5
= 2x2 +7
(ii)高尔夫球
解决方案:
(gof)(x) = g (f (x))
= g (2x +5)
= (2x + 5)2 + 1
= 4x2 + 20x + 26
(iii)fof
解决方案:
(fof)(x) = f (f (x))
= f (2x +5)
= 2 (2x + 5) + 5
= 4x + 10 + 5
= 4x + 15
(iv)f 2 (x)
解决方案:
f2(x) = f(x) x f(x)
= (2x + 5)(2x + 5)
= (2x + 5)2
= 4x2 + 20x +25
问题5.如果f(x)= sin x和g(x)= 2x是两个实函数,则描述gof和fog。这些功能相等吗?
解决方案:
Given f(x) = sin x and g(x) = 2x
We know that
f: R→ [−1, 1] and g: R→ R
Clearly, the range of f is a subset of the domain of g.
gof: R→ R
(gof)(x) = g(f(x))
= g(sin x)
= 2 sin x
Clearly, the range of g is a subset of the domain of f.
fog: R → R
So, (fog)(x) = f(g(x))
= f(2x)
= sin(2x)
Clearly, fog ≠ gof
Hence they are not equal functions.
问题6.令f,g,h是由f(x)= sin x,g(x)= 2x和h(x)= cos x给出的实函数。证明雾= go(fh)。
解决方案:
Given that f(x) = sin x, g (x) = 2x and h (x) = cos x
Now, fog(x) = f(g(x))
= f(2x)
fog(x) = sin2x ….(1)
And (go (f h)) (x) = g ((f(x). h(x))
= g (sin x cos x)
= 2sin x cos x
= sin (2x) ….(2)
From (1) and (2), fog(x) = go(fh) (x).
问题7.令f为任何实函数,令g为g(x)= 2x给出的函数。证明:gof = f + f。
解决方案:
We know, (gof)(x) = g(f(x))
= 2(f(x))
= f(x) + f(x)
= f + f.
Hence proved.
问题8。 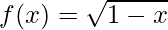 和
和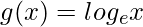 有两个实函数,即雾和果岭。
有两个实函数,即雾和果岭。
解决方案:
Clearly the domain of f and g are R.
Now, fog(x) = f(g(x))
![]()
fog(x)![]()
(gof)(x) = g(f(x))
![]()
(gof)(x)![]()
问题9.如果f(x)= tan x并且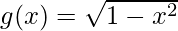 ,找到雾气和自由度。
,找到雾气和自由度。
解决方案:
fog(x) = f(g(x))
![]()
![]()
(gof)(x) = g(f(x))
= g(tan x)
![]()
问题10.如果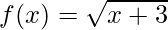 和g(x)= x 2 +1是两个实函数,求雾和gof。
和g(x)= x 2 +1是两个实函数,求雾和gof。
解决方案:
fog(x) = f(g(x))
= f(x2 + 1)
![]()
(gof)(x) = g(f(x))
![]()
![]()
(gof)(x) = x + 4
问题11:设F是由下式给出一个真正的函数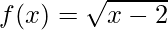 。找:
。找:
(i)fof
解决方案:
fof(x) = f(f(x))
![]()
![]()
(ii)fofof
解决方案:
We know, fof(x) = f(f(x))
![]()
Thus,![]()
Now, fofof(x) = fof(f(x))
![]()
![]()
(iii)f 2
解决方案:
f2(x) = f(x).f(x)
=![]()
f2(x) = x – 2
问题12 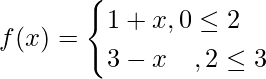 找到fof。
找到fof。
解决方案:
Range of f = [0,3]
fof(x) = f(f(x))