问题1 10.36,A,B和C是圆的三个点,圆的中心为O,CBOC = 30°,OBAOB = 60°。如果D是圆弧ABC以外的圆上的一点,请找到∠ADC。
解决方案:
Given: ∠BOC=30° and ∠AOB=60°
To find: ∠ADC
Solution: ∠AOC=2∠ADC ———[The angle subtended by an arc at the centre is double the angle the angle subtended by it any point on the remaining part of the circle.]
∠AOB+∠BOC=2∠ADC
60°+30°=2∠ADC
90+30=2∠ADC
90/2=∠ADC
45=∠ADC

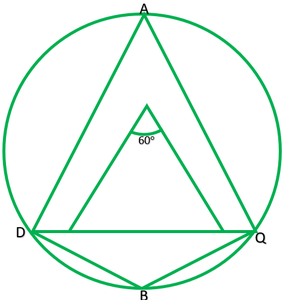
问题2.圆的和弦等于圆的半径。在小弧上的一个点以及在大弧上的一个点上找到弦对着的角度。
解决方案:
Given: PQ=OP
To find: Angle on major arc is ∠A=?
Angle on the minor arc is ∠B=?
Since, =PO=OQ
∴∠POQ=60°
∠POQ=2∠PAQ [The angle subtended by an arc at the centre is double the angle subtended by it any point on the remining point of the circle]
Reflex ∠POQ=360°-60°
Reflex ∠POQ=300°
Reflex ∠POQ=2∠POQ
300°=2∠PBQ
300°/2=∠PBQ
150°=∠PBQ
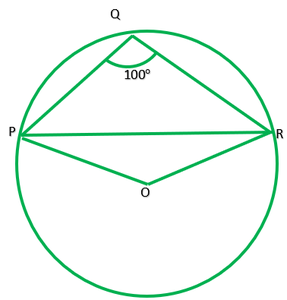
问题3。 10.37,∠PQR= 100°,其中P,Q和R是圆心为O的圆上的点。找到∠OPR。
解决方案:
Given: ∠PQR=100°
To find: ∠OPR=?
Reflex ∠POR=2∠PQR ——–[ The angle subtended by an arc at the centre is double the angle subtended by it any point on the remining point of the circle]
Reflex ∠PQR=2*100
=200°
∠POR=360°-200°
Now in ∆POR,OP=QR [ Radii of same circle]
∠P=∠R and let each =x.
∴∠P+∠O+∠R=180° [angle sum property of ∆]
x+160°+x=180°-160°
2x+160°=180°
x=20°/2=10°
∴∠OPR=10°
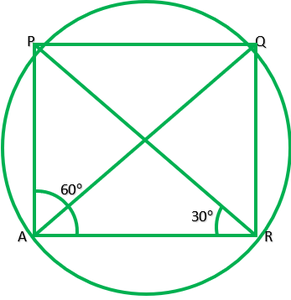
问题4。 10.38,∠ADC= 69°,∠ACB= 31°,找到∠BDC。
解决方案:
Given: ∠ABC=69°,∠ACB=31°
To find: ∠BDC=?
Solution: In ∆ABC
∠A+∠B+∠C=180° ———[Angle sum property of ∆]
∠A+69°+31°=180°
∠A=180°-100°
∠A=80°
∠A and ∠D lie on the same segment therefore,
∠D=∠A
∠D=80°
∠BDC=80°
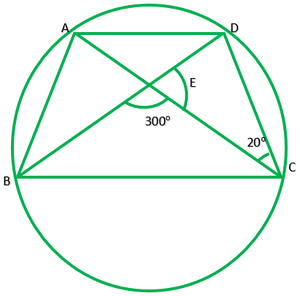
问题5.在图中,A,B,C和D是圆上的四个点。AC和BD在点E相交,使得∠BEC= 130°和andECD = 20°。查找∠BAC。
解决方案:
Given: ∠BEC=130°,∠ECD=20°
To find: ∠BAC?
Solution: In ∆EDC
∠E=180°-130° ———[linear pair]
∠E=50°
∠E+∠C+∠D=180° ——[angle sum property of triangle]
50°+20°+∠D=180°
70°+∠D=180°
∠D=180/70=110°
Since, ∠A and ∠D line in the same segment
∴∠A=∠D
∠A=110°
∠BAC=110°
问题6. ABCD是一个循环的四边形,其对角线在点E处相交。如果∠DBC= 70°,ACBAC为30°,则找到∠BCD。此外,如果AB = BC,则找到∠ECD。
解决方案:
Given: ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral diagonal intersect at E ∠DBC=70°, ∠BAC is 30°. If AB=BC.
To find: ∠BCD and ∠ECD
∠BDC=∠BAC=30° ——-[angle in the same segment]
In ∆BCD,
∠B+∠C+∠D=180° ——–[angle sum property of ttriangle]
∠C+100°=180°
∠C=180°-100°=80°
∴∠BCD=80°
If AB=BC,
Then, ∠BAC=∠BCA
30°=∠BCA
Now, ∠BCA+∠ECD=∠BCD
30°+∠ECD=80°
∠ECD=80°-30°
∴∠ECD=50°

问题7.如果一个循环四边形的对角线是通过该四边形的顶点的圆的直径,则证明它是矩形。
解决方案:
Given: ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. Diagonals of ABCD are also diameters of circle.
To prove: ABCD is a rectangle
AC=BD ———-[diameters of same circle]
OA=OA ———[radii of the same circle]
OA=OC=1/2AC ———2
OB=OD=1/2BD ———-2
From I and 2 diagonals are equal and bisect each other
∴ABCD is a rectangle

问题8.如果梯形的非平行边相等,请证明它是循环的。
解决方案:
Draw DL perpendicular AB and EF perpendicular AB
In ∆DEA and ∆CEB
∠E=∠F ——–[each 90°]
AD=BC ——–[given]
DE=CF ——–[distance between || lines is same every line]
∴∆DEA≅∆CFB ——–[R.H.S]
∠A=∠B ———[by c.p.c.t.] 1
∠1=∠2 (from 1)
Adding 90° on each sides
∠1+90°=∠2+90°
∠1+∠EDC=∠2+FCD
∠ADC=∠BCD
∠D=∠C 2
Now,
∠A+∠A+∠C+∠C=360°
2∠A+2∠C=360°
2(∠A+∠C)=360°
∠A+∠C=360°/2=190°
Because sum of opposite angles is 180°.
ABCD is parallelogram.
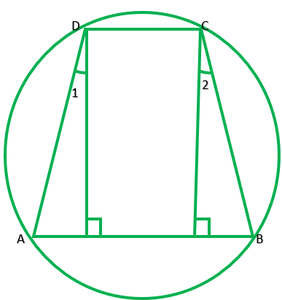
问题9.两个圆在两个点B和C处相交。通过B,绘制了两个线段ABD和PBQ以分别在A,D和P,Q处相交(见图10.40)。证明∠ACP=∠QCD。
解决方案:
To prove: ∠ACP=∠QCD or ∠1=∠2
∠1=∠2 —— [angles in the same segment are equal] 1
∠ 3=∠ 4 ——- [angles in the same segment are equal] 2
∠2=∠4 ——- [vertically opposite angles] 3
From 1 2 and 3
∠1=∠3
∴∠ACP=∠QCB
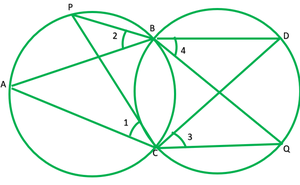
问题10.如果以三角形的两个边作为直径绘制圆,请证明这些圆的交点位于第三边。
解决方案:
Given: ABC is ∆ and AB and AC are diameters of two circles
To prove: Point of intersection is D, lies on the BC.
Construction: Join AD
∠ADB=90° ——-[angles in semicircle] 1
∠ADC=90 ° ——[angles in semicircle] 2
Adding 1 and 2
∠ADB+∠ADC=90°+90°
∠BDC=180°
BDC is a straight line therefore D lies on BC.

问题11. ABC和ADC是两个直角三角形,共同的斜边AC。证明∠CAD=∠CBD。
解决方案:
Given: ABC and ADC are two right angle triangles with common hypotenuse AC.
To prove: ∠ADB=∠CBD
Solution: ∠ABC=∠ADC=90°
Circle drawn by taking AC as diameter passes through B and D.
For chord CD
∠CAD=∠CBD ——-[angle in the same segment]
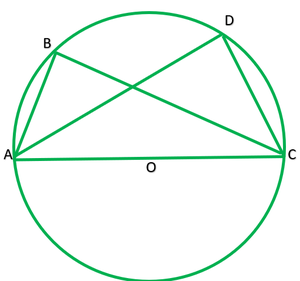
问题12.证明循环平行四边形是矩形。
解决方案:
Given: ABC is a cyclic ||gm
To prove: ABCD is a rectangle.
Because ABCD is a cyclic ||gm
∴∠A+∠C=180°
∠A=∠C [opposite angle of ||gm]
∴∠A=∠C=(180°)/2=90°
∠A=90°
∠C=90°
Similarly,
∠B+∠D=180°
∴∠B=∠D =(180°)/2=90° ———-[opposite of a ||gm]
Each angle of ABCD is 90°
∠B=90°
∠D=90°
Thus, ABCD is a rectangle.
