先决条件–有限自动机
1. DFA:
DFA是指确定性有限自动机。有限自动机(FA)被认为是确定性的,如果对应于输入符号,则只有一个结果状态,即只有一个过渡。
确定性有限自动机由五个元组组成,表示为:
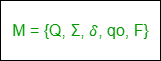
在哪里,
问:有限控制中存在一个非空的有限状态集(qo,q1,q2,…)。
Σ:输入符号的非空有限集。
δ:这是一个转换函数,带有两个参数,一个状态和一个输入符号,它返回一个状态。
qo:它是开始状态,是Q中的状态之一。
F:它是属于Q的集合中非空的最终状态/接受状态集合。
2. NFA:
NFA是指不确定性有限自动机。如果在同一输入符号上从一个状态起不止一种可能的转移,则称有限自动机(FA)是不确定的。
非确定性有限自动机也是由五个元组组成的集合,表示为:
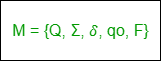
在哪里,
问:一组非空的有限状态。
Σ:一组非空的有限输入符号。
δ:这是一个转换函数,它从Q取一个状态,从Q取一个输入符号,并返回Q的子集。
qo:NFA的初始状态和Q的成员。
F:一组非空的最终状态和Q的成员。
DFA和NFA之间的区别:
| SR.NO. | DFA | NFA |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | DFA stands for Deterministic Finite Automata. | NFA stands for Nondeterministic Finite Automata. |
| 2 | For each symbolic representation of the alphabet, there is only one state transition in DFA. | No need to specify how does the NFA react according to some symbol. |
| 3 | DFA cannot use Empty String transition. | NFA can use Empty String transition. |
| 4 | DFA can be understood as one machine. | NFA can be understood as multiple little machines computing at the same time. |
| 5 | In DFA, the next possible state is distinctly set. | In NFA, each pair of state and input symbol can have many possible next states. |
| 6 | DFA is more difficult to construct. | NFA is easier to construct. |
| 7 | DFA rejects the string in case it terminates in a state that is different from the accepting state. | NFA rejects the string in the event of all branches dying or refusing the string. |
| 8 | Time needed for executing an input string is less. | Time needed for executing an input string is more. |
| 9 | All DFA are NFA. | Not all NFA are DFA. |
| 10 | DFA requires more space. | NFA requires less space then DFA. |
| 11. | Dead state may be required. | Dead state is not required. |
| 12. | δ: QxΣ -> Q i.e. next possible state belongs to Q. | δ: QxΣ -> 2^Q i.e. next possible state belongs to power set of Q. |